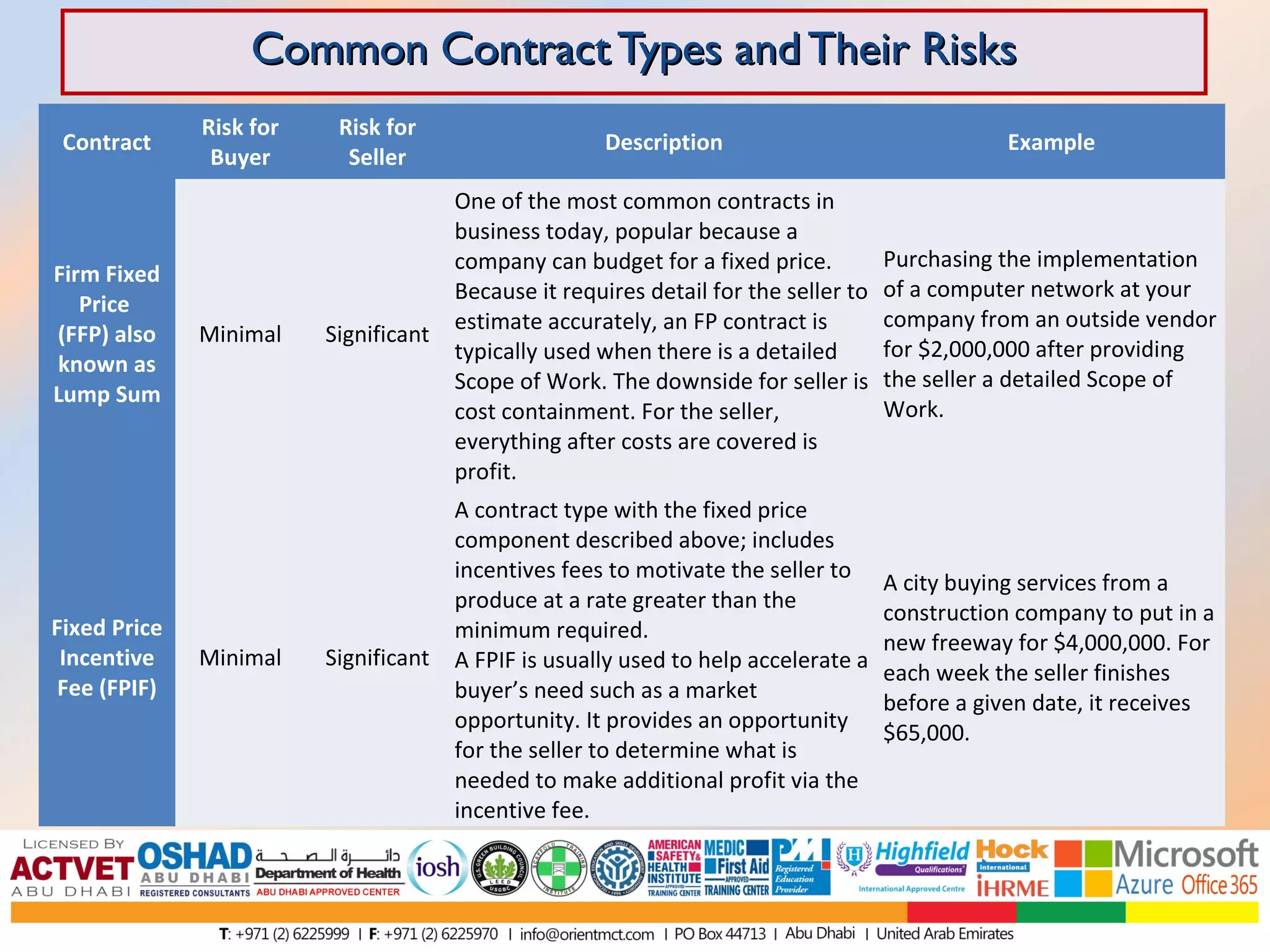
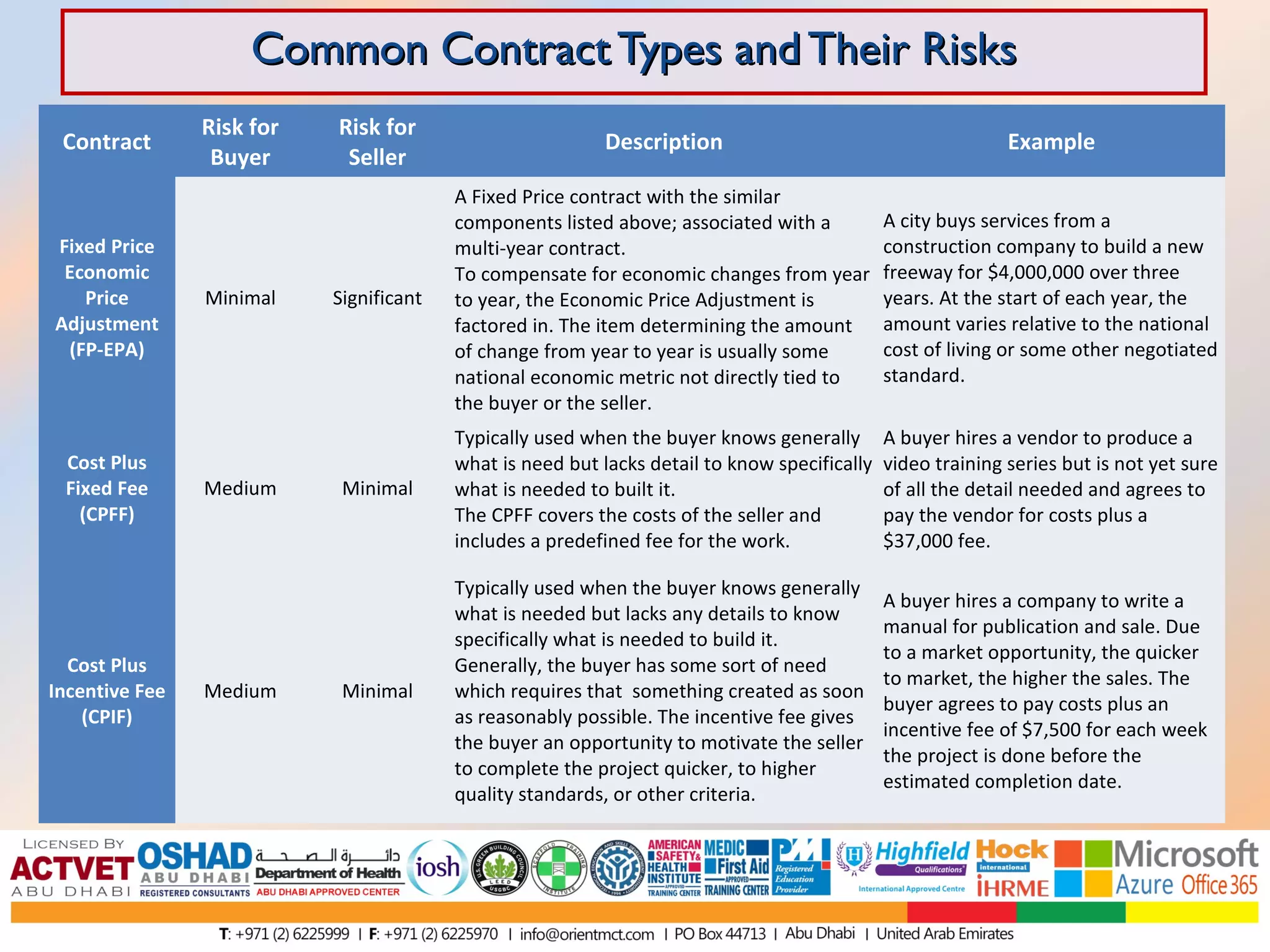
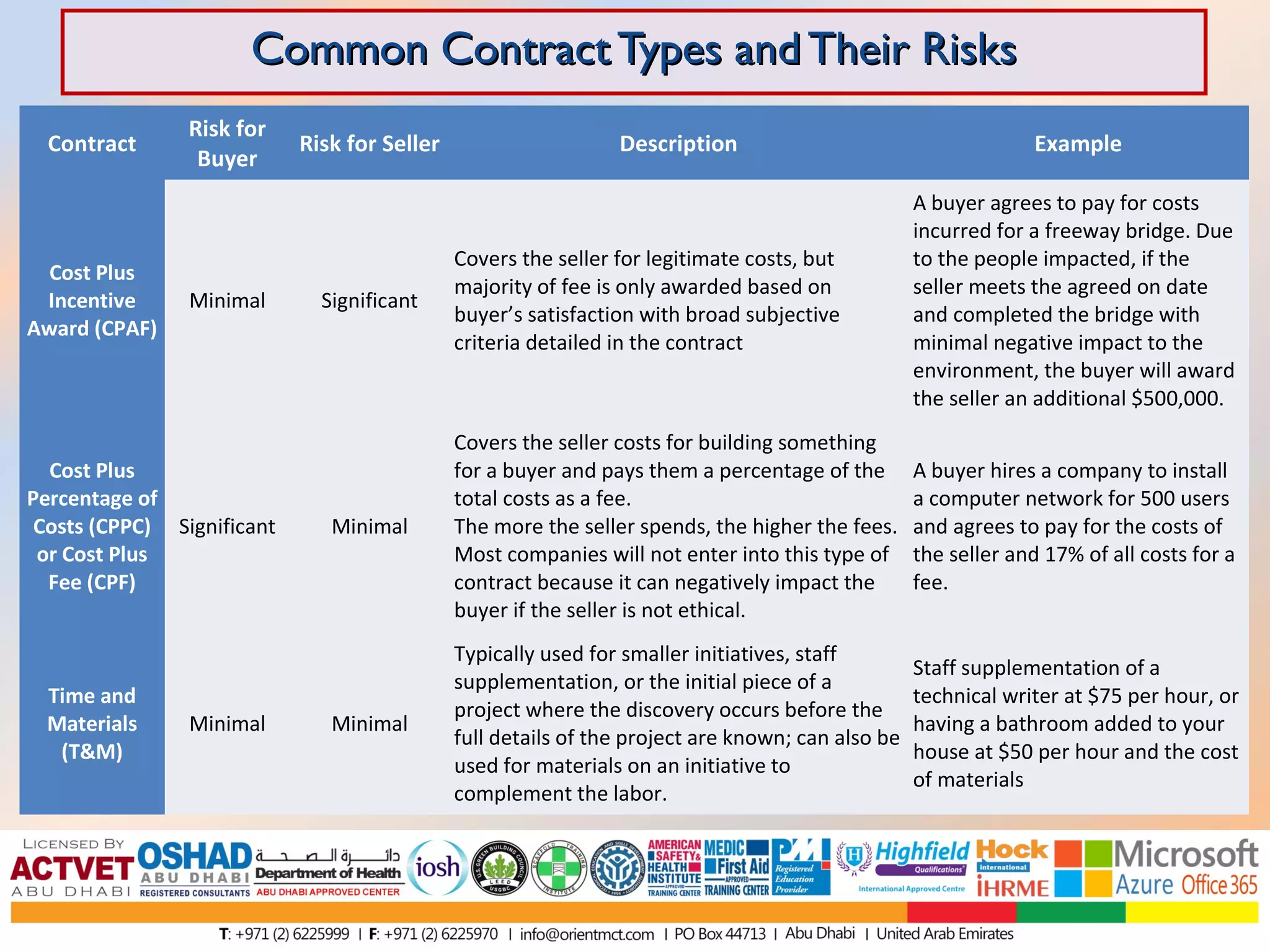
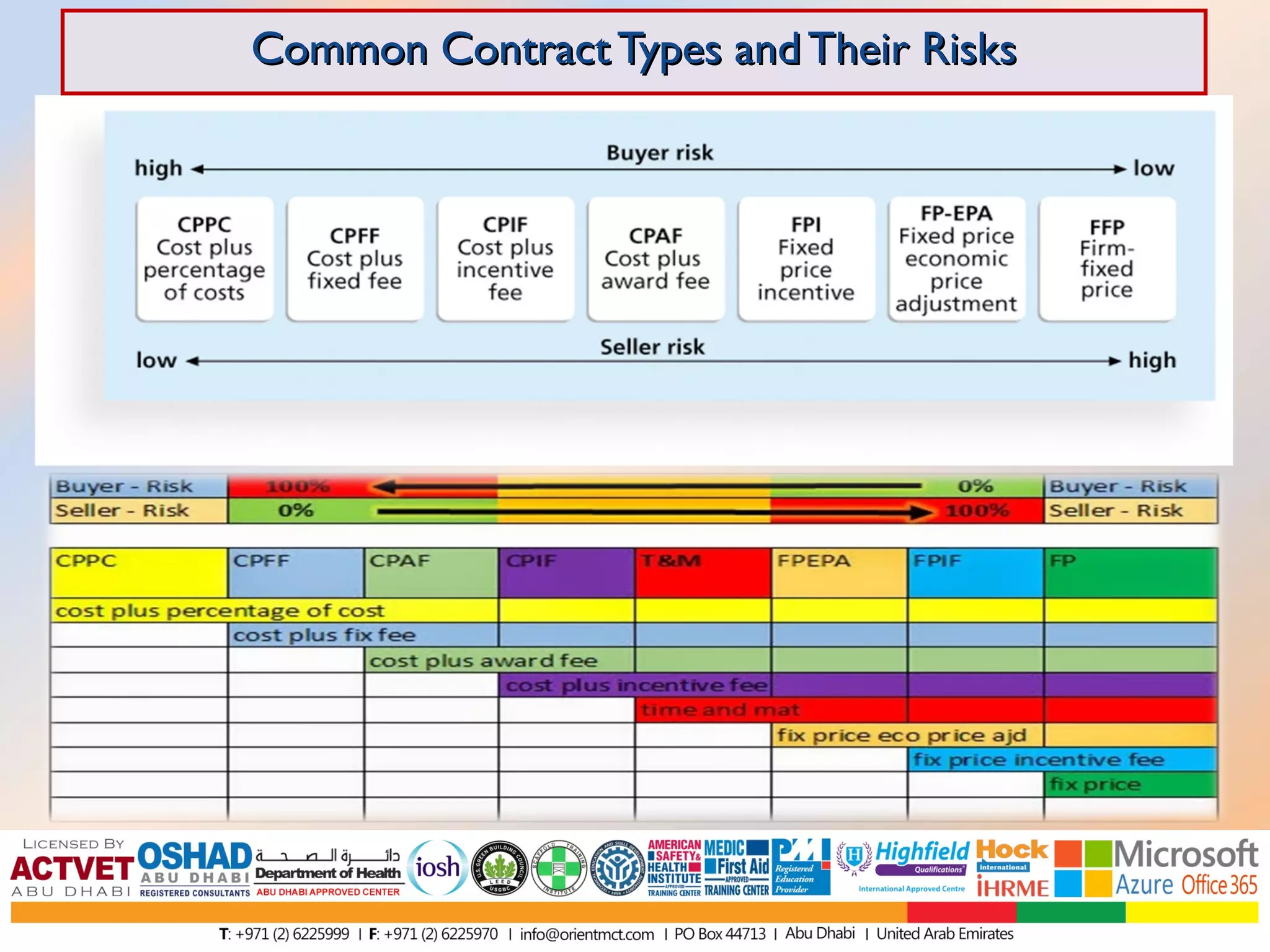
This document discusses and compares various common contract types including fixed-price contracts like firm fixed price (FFP) and fixed price incentive fee (FPIF) contracts which set a fixed total price upfront and carry more risk for sellers. Cost-reimbursable contracts like cost plus fixed fee (CPFF) and cost plus incentive fee (CPIF) cover sellers' costs plus a fee and carry more risk for buyers. Time and materials (T&M) contracts are a hybrid that pay hourly rates and material costs. Each type allocates risk differently between buyers and sellers.