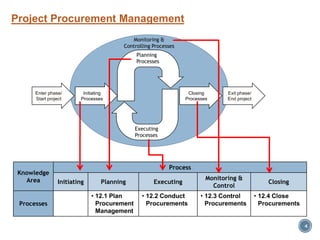
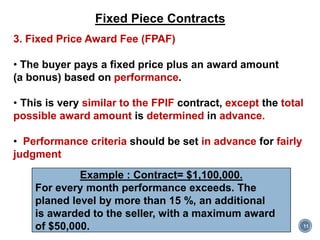
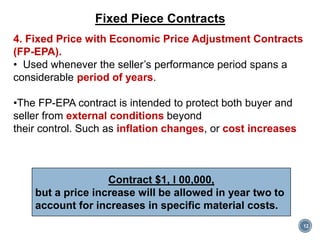
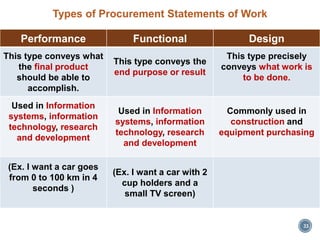
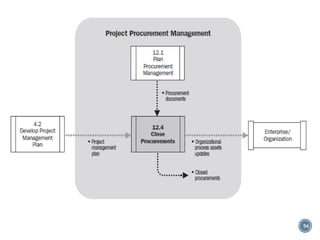
The document discusses project procurement management. It covers the key processes of planning procurement, conducting procurements, controlling procurements, and closing procurements.
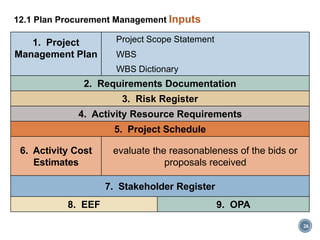
The section on planning procurement (12.1) involves documenting procurement decisions, specifying the procurement approach, and identifying potential sellers. This includes conducting a make-or-buy analysis to determine whether items should be procured externally or produced internally.
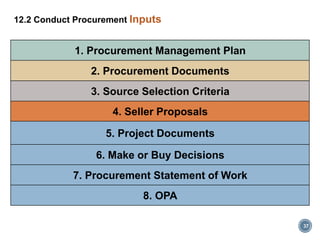
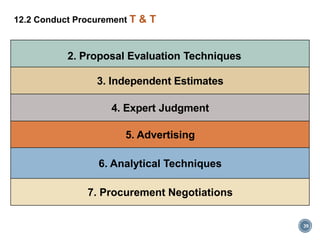
The section on conducting procurements (12.2) covers obtaining seller responses, selecting sellers, and awarding contracts. This involves releasing procurement documents, evaluating proposals, and negotiating with sellers.
The document provides an overview of the major inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs for each procurement management process