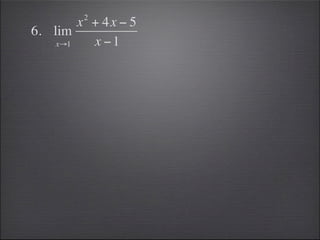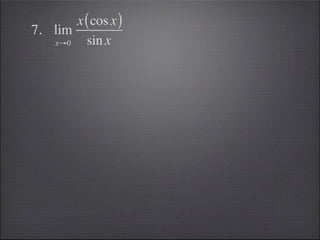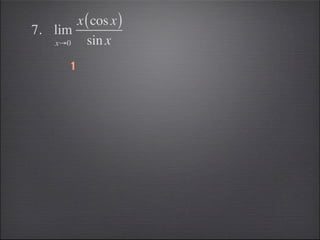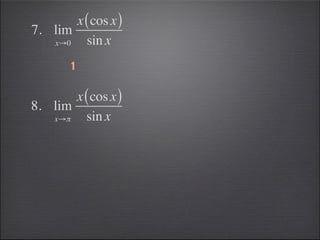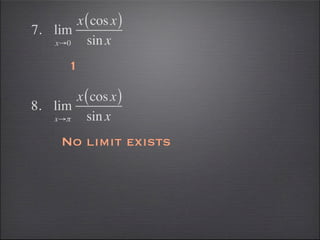This document contains examples and explanations of limits involving various functions. Some key points covered include:
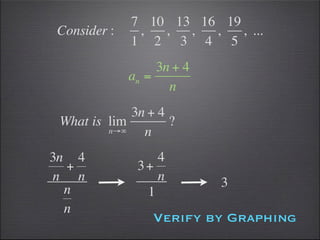
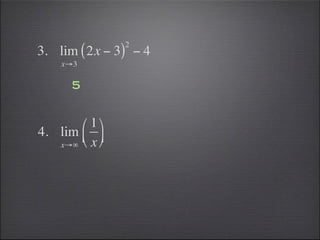
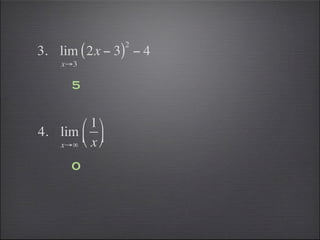
- Substitution can be used to evaluate limits, such as substituting 2 into -2x^3.
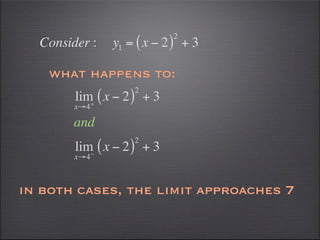
- Left and right hand limits must agree for the overall limit to exist.
- The limit of a piecewise function exists if the left and right limits are the same.
- Graphs can help verify limit calculations and show discontinuities.
- Special limits involving trigonometric and greatest integer functions are evaluated.


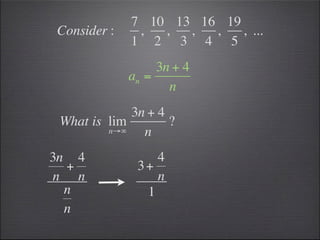
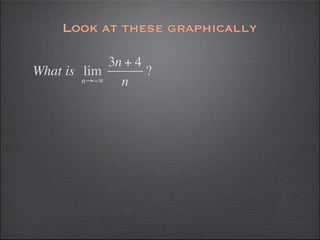
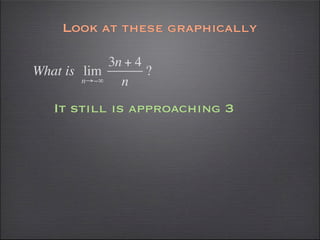
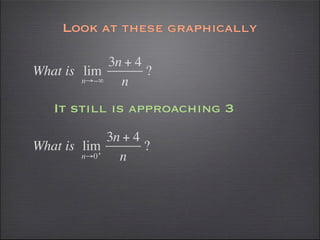


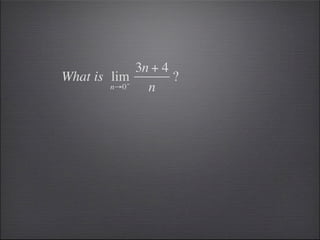
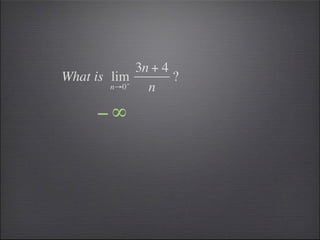
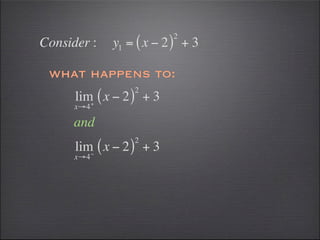
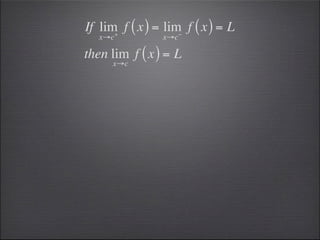



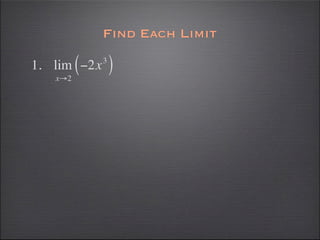






![5. lim [ x ]
x→2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1201ch12day1-120802205101-phpapp01/85/1201-ch-12-day-1-31-320.jpg)
![5. lim [ x ] Greatest Integer
x→2 Function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1201ch12day1-120802205101-phpapp01/85/1201-ch-12-day-1-32-320.jpg)
![5. lim [ x ] Greatest Integer
x→2 Function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1201ch12day1-120802205101-phpapp01/85/1201-ch-12-day-1-33-320.jpg)
![5. lim [ x ] Greatest Integer
x→2 Function
lim
x→2 +
[ x] = 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1201ch12day1-120802205101-phpapp01/85/1201-ch-12-day-1-34-320.jpg)
![5. lim [ x ] Greatest Integer
x→2 Function
lim
x→2 +
[ x] = 2
lim
x→2 −
[ x] = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1201ch12day1-120802205101-phpapp01/85/1201-ch-12-day-1-35-320.jpg)
![5. lim [ x ] Greatest Integer
x→2 Function
lim
x→2 +
[ x] = 2
lim
x→2 −
[ x] = 1
Because the left-hand and right-hand
limits do not agree, this limit does
not exist.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1201ch12day1-120802205101-phpapp01/85/1201-ch-12-day-1-36-320.jpg)