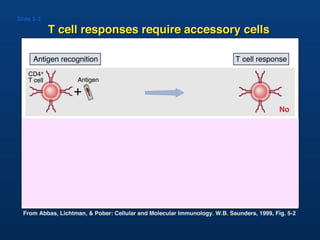
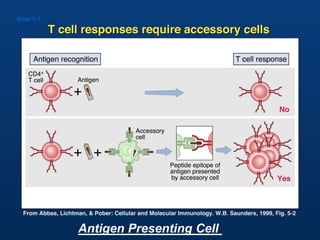
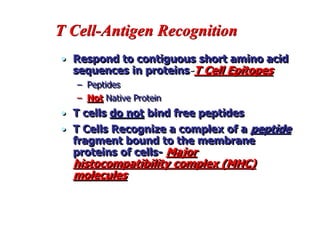
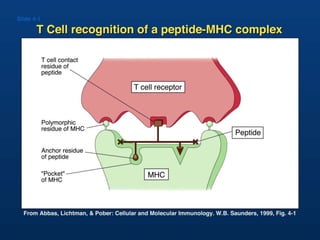
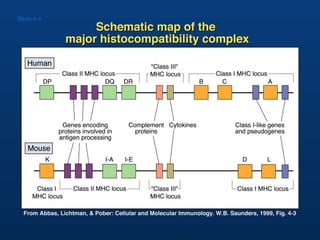
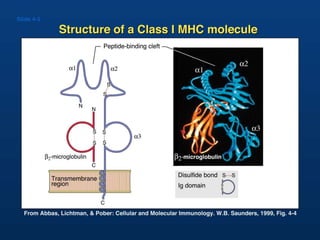
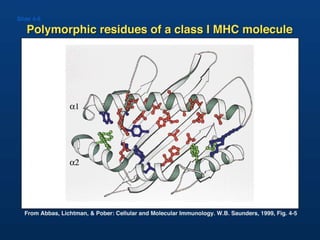
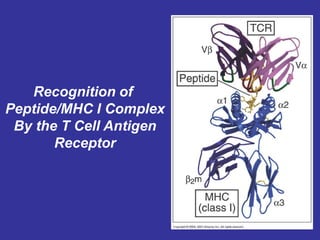
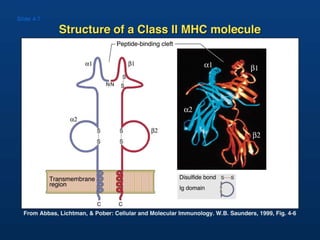
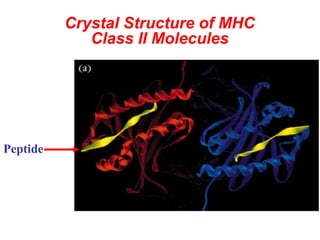
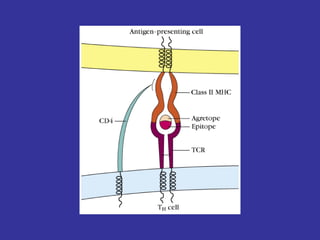
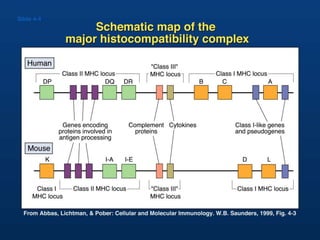
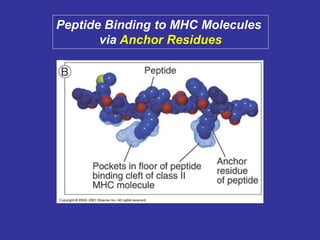
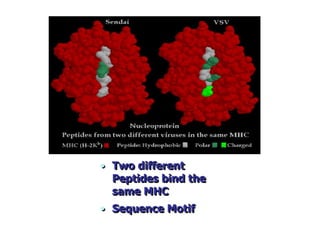
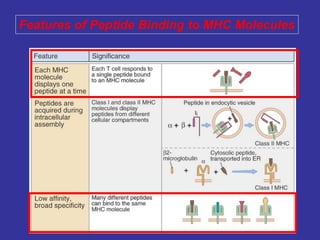
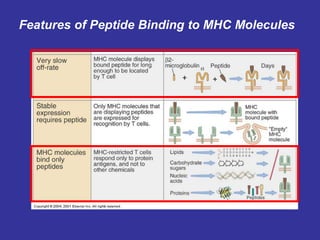
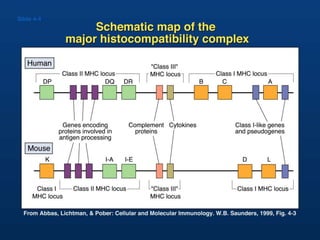
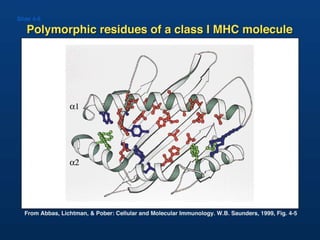
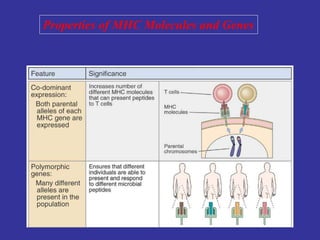
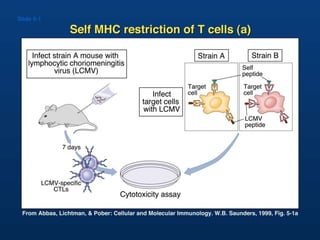
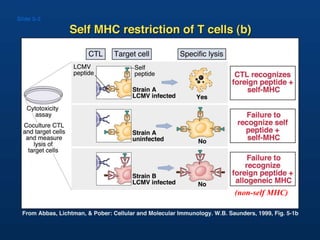
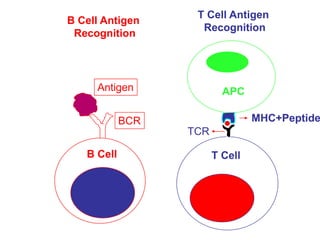
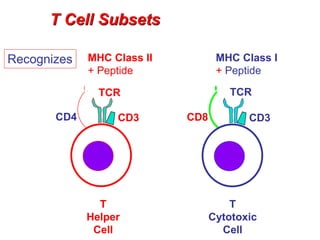
T lymphocytes recognize short peptide fragments of proteins bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. There are two classes of MHC molecules - MHC class I presents peptides to CD8+ T cells on all nucleated cells, while MHC class II presents peptides to CD4+ T cells on professional antigen-presenting cells. Peptides bind to MHC molecules through anchor residues in a specific sequence motif, and a single MHC molecule can bind many different peptides. MHC molecules are highly polymorphic, which limits T cell recognition to peptides bound to self MHC molecules only.