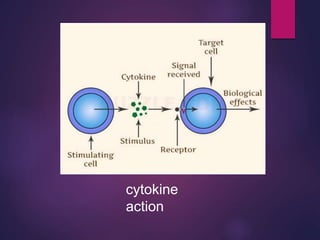
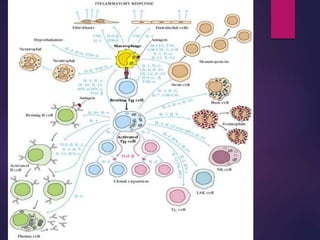
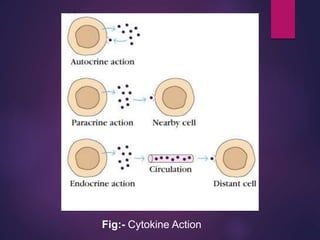
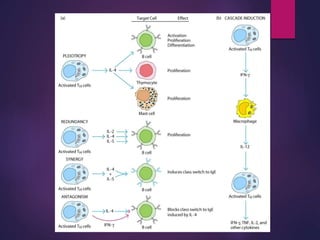
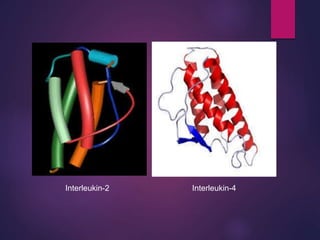
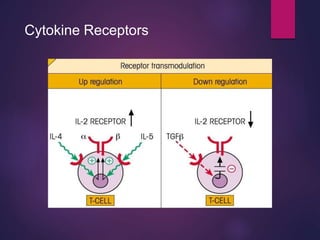
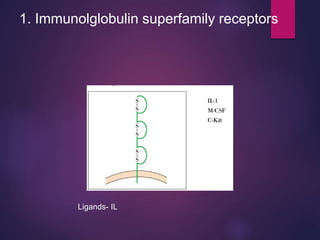
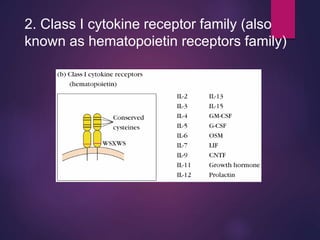
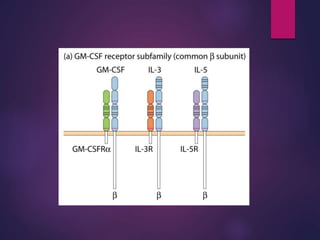
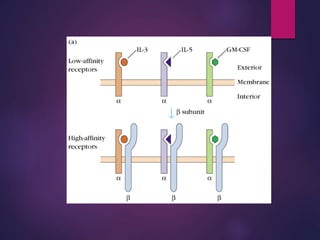
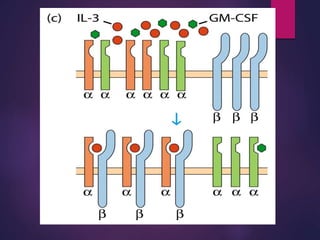
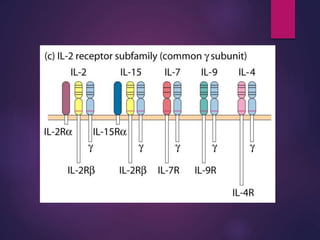
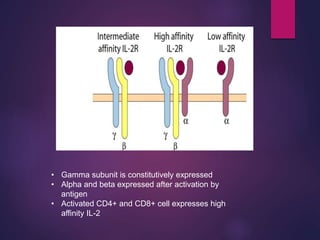
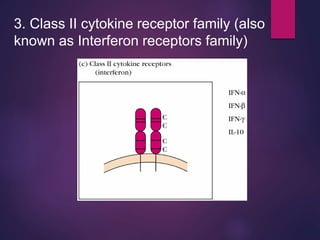
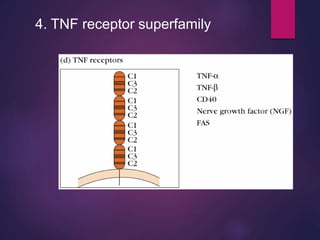
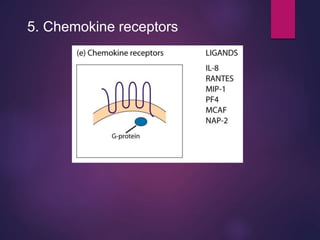
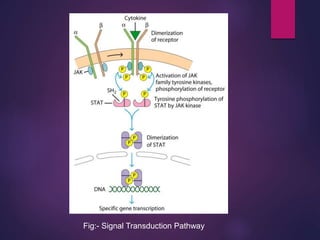
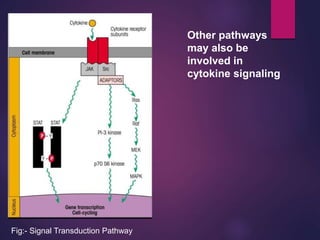
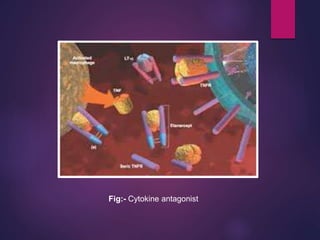
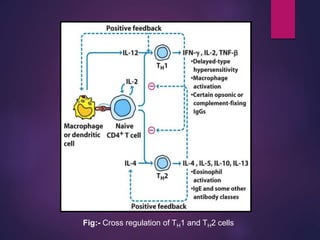
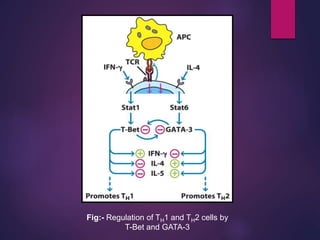
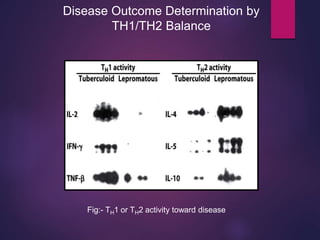
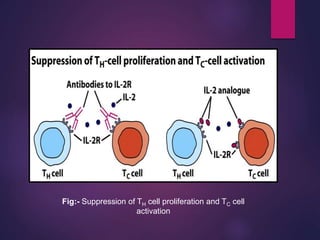
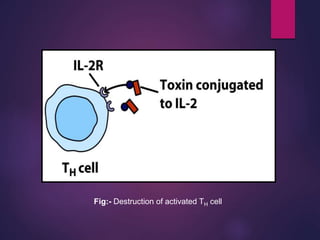
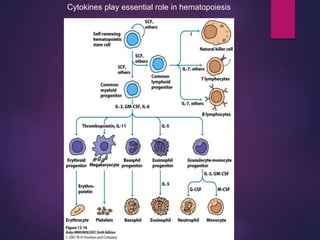
Cytokines are low molecular weight proteins or peptides that are important signaling molecules that regulate immunity and inflammation. They act as intercellular messengers to regulate the intensity and duration of immune responses by binding to receptors on target cells. There are four main structural families of cytokines - hematopoietin receptor family, interferon receptor family, TNF receptor family, and chemokine receptor family. Cytokines can act through autocrine, paracrine, or endocrine signaling and activate signaling pathways like JAK-STAT. An imbalance in the levels of cytokines produced by TH1 and TH2 cells can lead to different disease outcomes. Cytokine-related diseases include septic shock, toxic shock syndrome, and some cancers and infections.