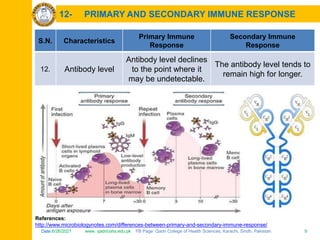
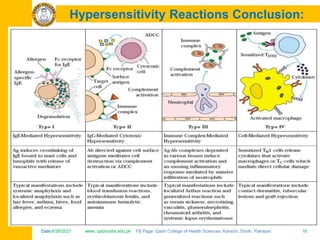
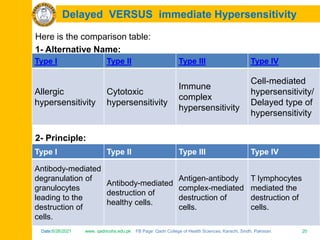
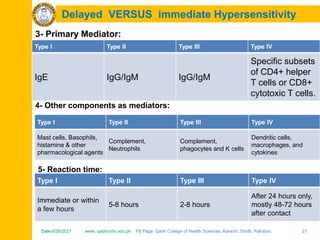
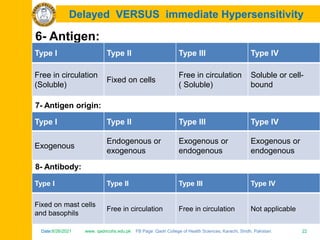
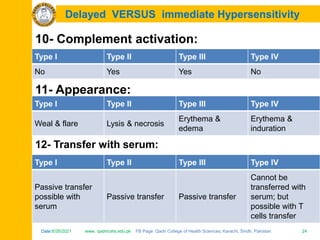
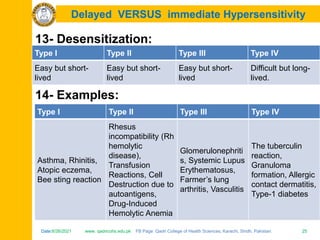
The document discusses the defense mechanisms of the body and summarizes key points about primary and secondary immune responses and types of hypersensitivity reactions. It describes how the primary immune response occurs during first-time exposure to an antigen and produces fewer, lower affinity antibodies over 7-10 days. The secondary immune response occurs on subsequent exposures and produces more, higher affinity antibodies within 3-5 days. It also defines and compares the four types of hypersensitivity reactions: Type I is immediate allergy mediated by IgE; Type II is cytotoxic; Type III is immune complex mediated; Type IV is cell-mediated and delayed.