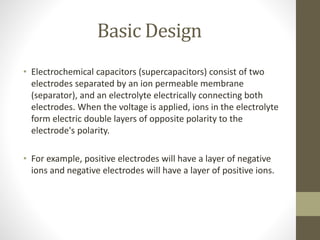
Supercapacitors are electrochemical capacitors that can store unusually high amounts of energy compared to regular capacitors. They consist of two electrodes separated by an ion-permeable membrane and electrolyte. When voltage is applied, ions in the electrolyte form electric double layers on the electrodes, storing energy. Though supercapacitors have advantages like high power rates and longevity, their main disadvantage is lower energy storage per unit weight compared to batteries. They can be used for applications requiring high power or energy recuperation.



![History
The first supercapacitor based on a double layer
mechanism was developed in 1957 by General Electric
using a porous carbon electrode [Becker, H.I., “Low
voltage electrolytic capacitor”, U.S. Patent 2800616, 23
July 1957].
It was believed that the energy was stored in the carbon
pores and it exhibited "exceptionally high capacitance",
although the mechanism was unknown at that time. It
was the Standard Oil Company, Cleveland (SOHIO) in
1966 that patented a device that stored energy in the
double layer interface [Rightmire, R.A., “Electrical energy
storage apparatus”, U.S. Patent 3288641, 29 Nov 1966.].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copyofsupcap-150329063534-conversion-gate01/85/Supercapacitor-By-praveen-4-320.jpg)