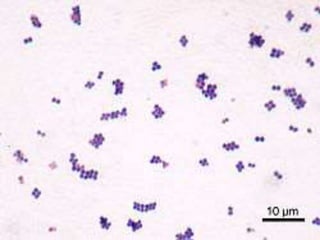
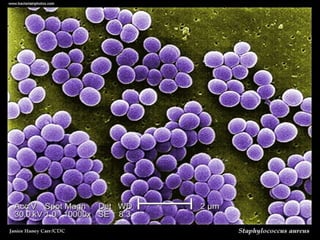
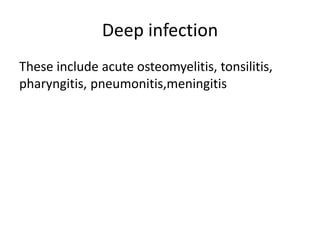
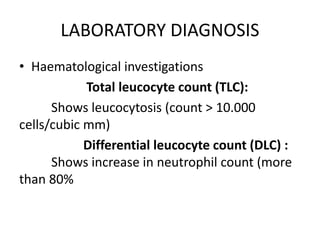
This document discusses Staphylococcus, including its morphology, cultural characteristics, pathogenicity, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment. Staphylococcus is a gram-positive, round bacterium that grows in clusters and produces golden yellow colonies on nutrient agar. It can cause both superficial and deep infections in humans and produces toxins that lead to conditions like toxic shock syndrome and scalded skin syndrome. Laboratory diagnosis involves examining samples under a microscope, culturing them on selective media, and identifying colonies using tests like coagulase. Effective antibiotic treatments include penicillin, methicillin, and vancomycin.