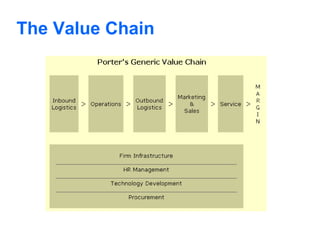
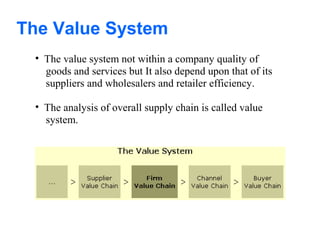
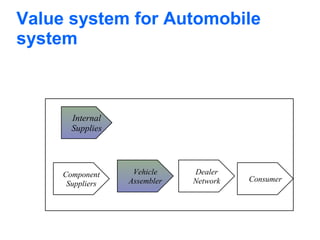
E-business uses web technologies to support business processes internally and externally, allowing closer collaboration with partners and suppliers to better satisfy customers. E-commerce specifically refers to buying and selling of products/services electronically without paper. E-business is broader, providing benefits beyond core e-commerce processes. Porter's value chain model describes a company's internal activities that add value, like inbound logistics and operations, while the value system analyzes the supply chain between organizations to deliver value to the consumer.