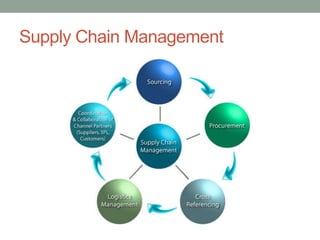
This document discusses key concepts in e-commerce including conducting business transactions online through buying and selling of products, services, and information via computer networks and the internet. It outlines fundamentals of e-commerce like prioritizing key purchase information for users and ensuring good user experience, search functionality, and support options. It also discusses e-business infrastructure, risks in the e-commerce environment like security, and concepts like supply chain management, e-marketing, customer relationship management, and mobile commerce.