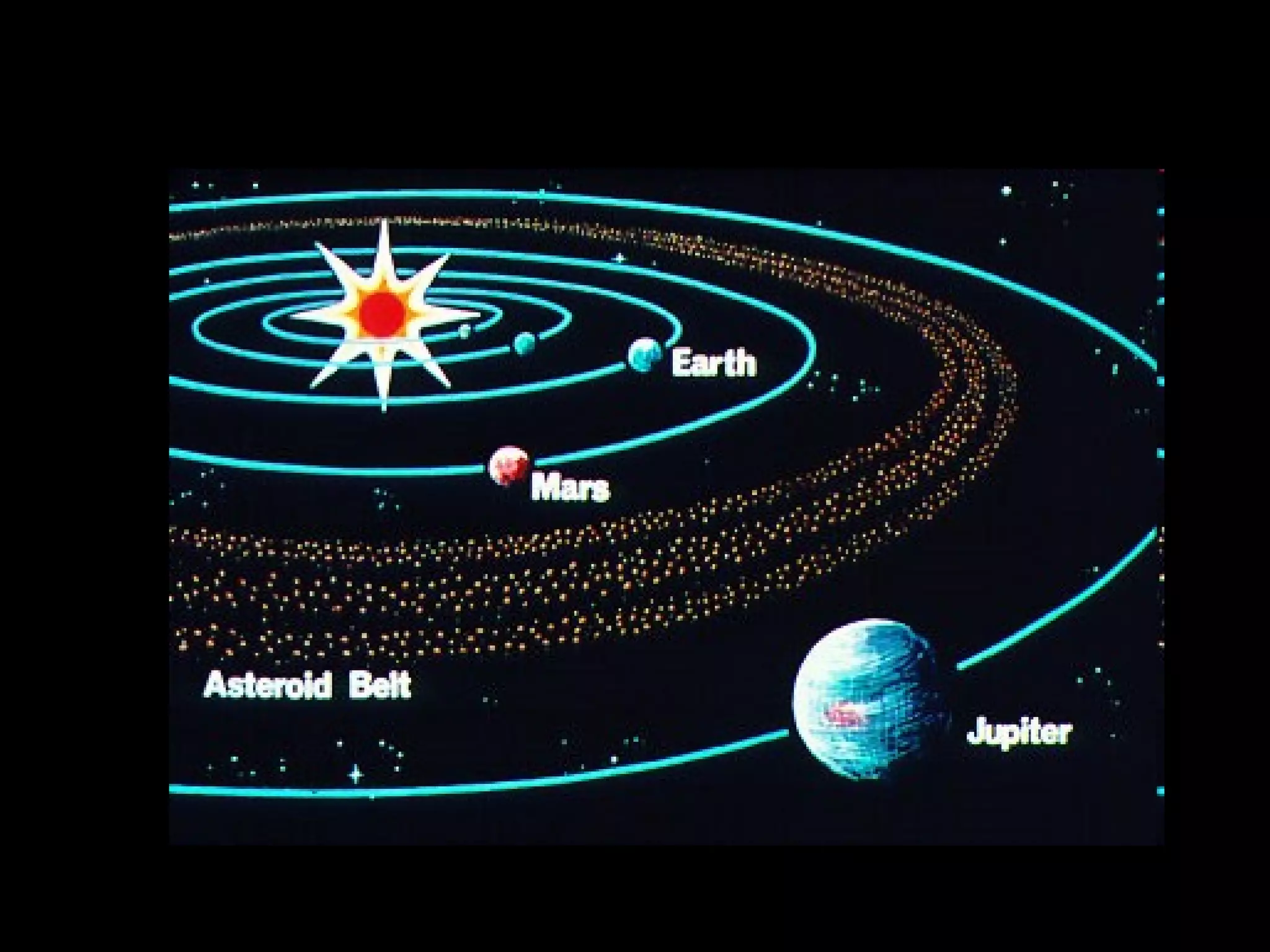
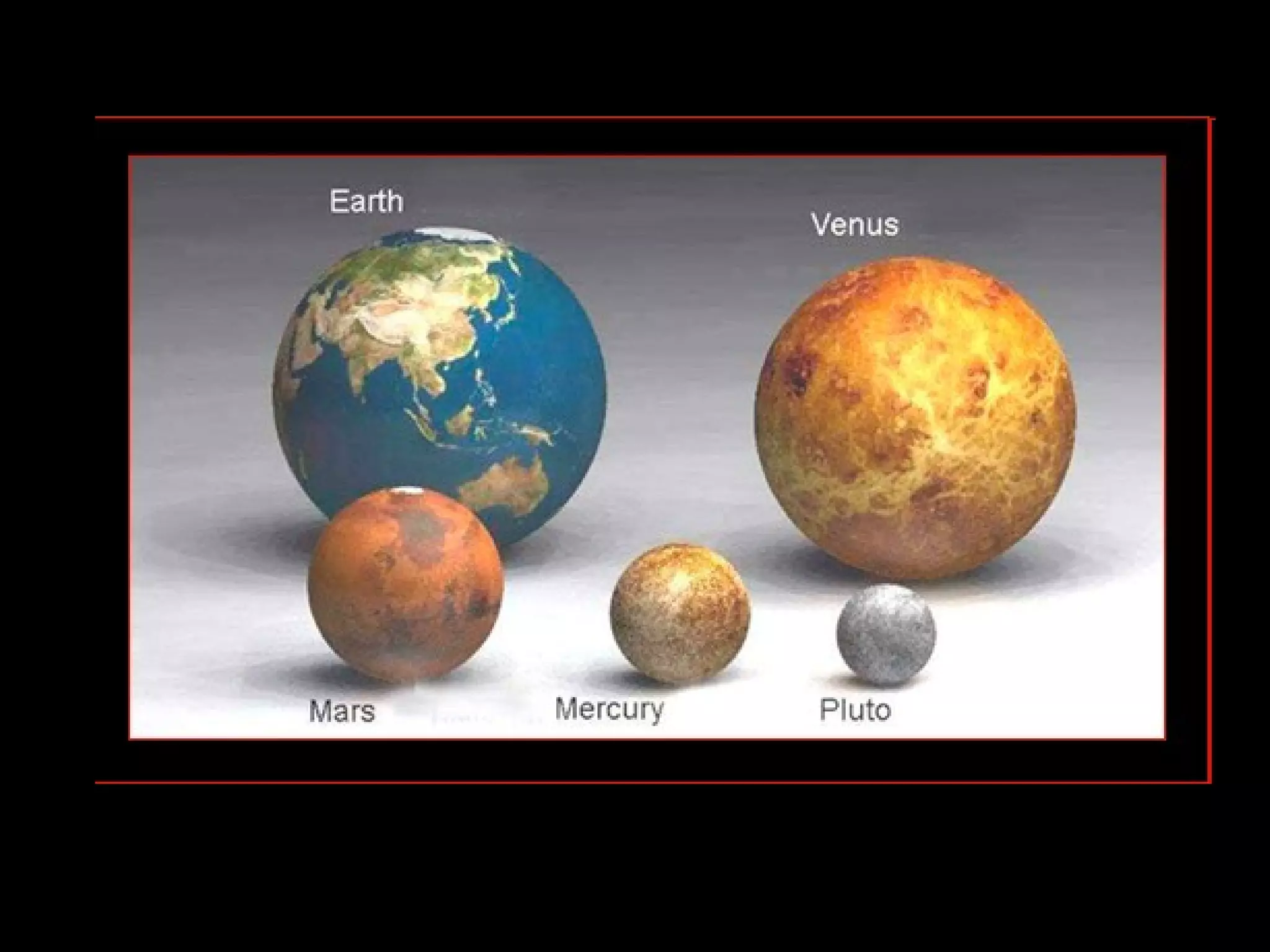
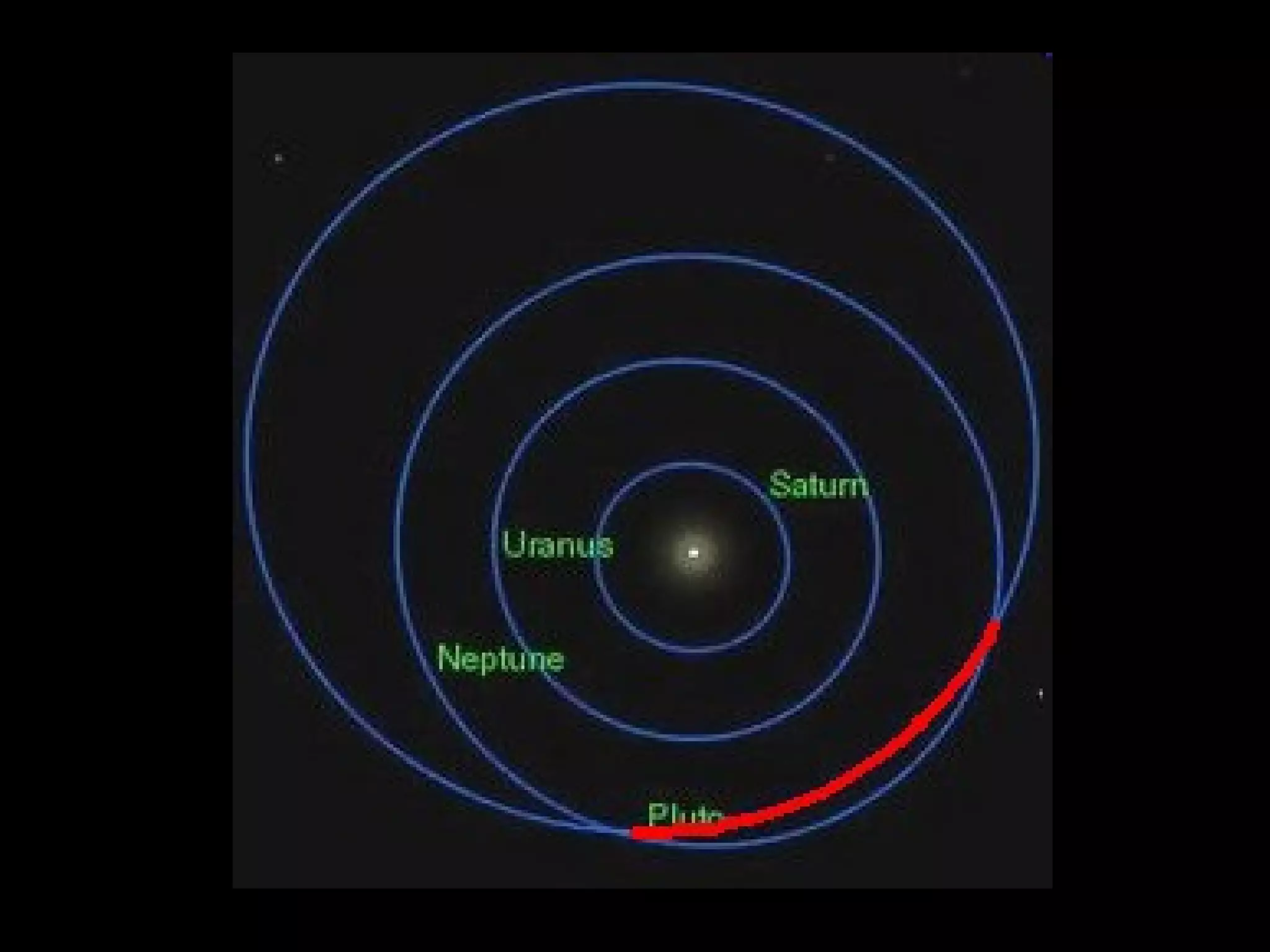
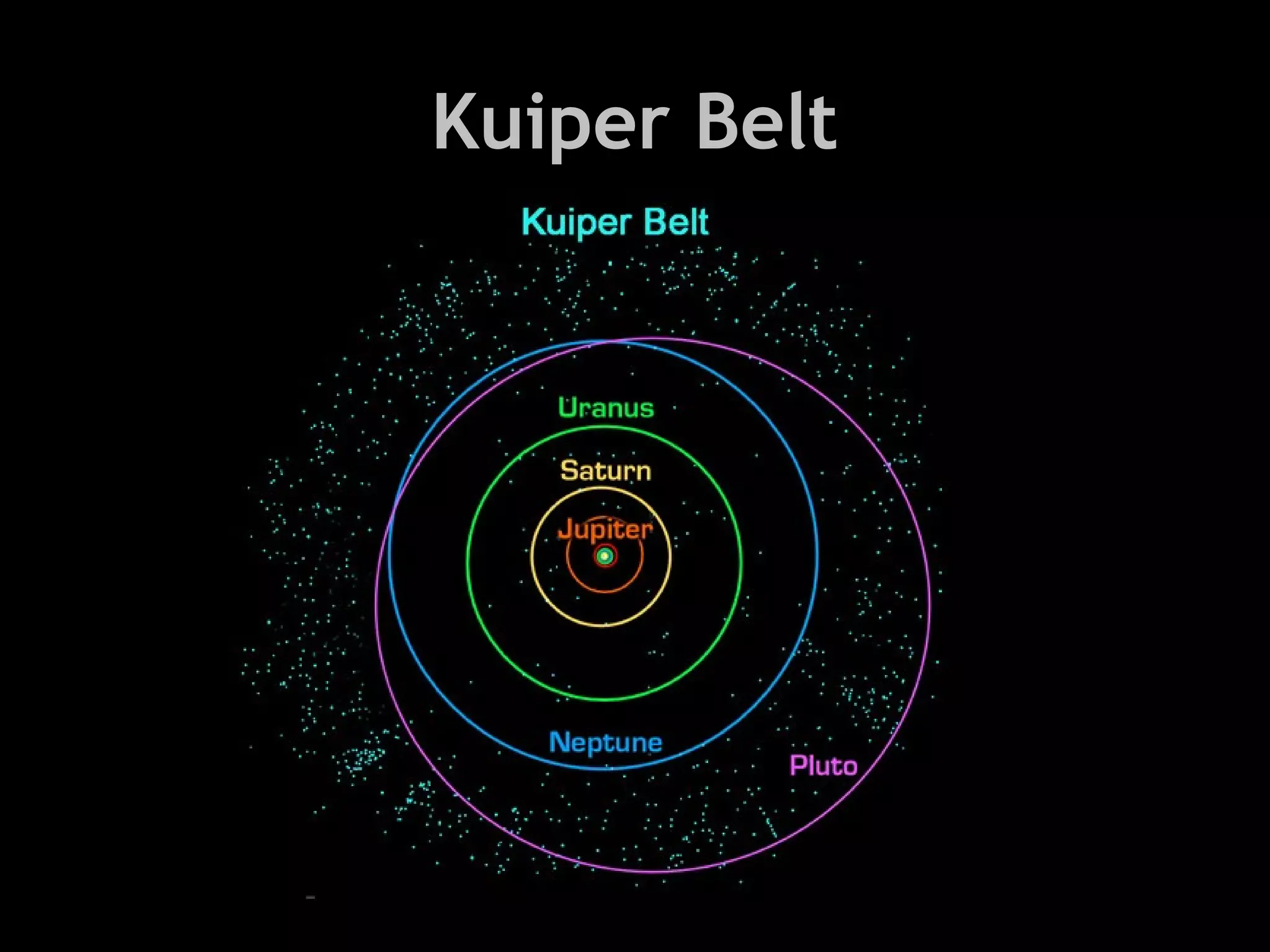
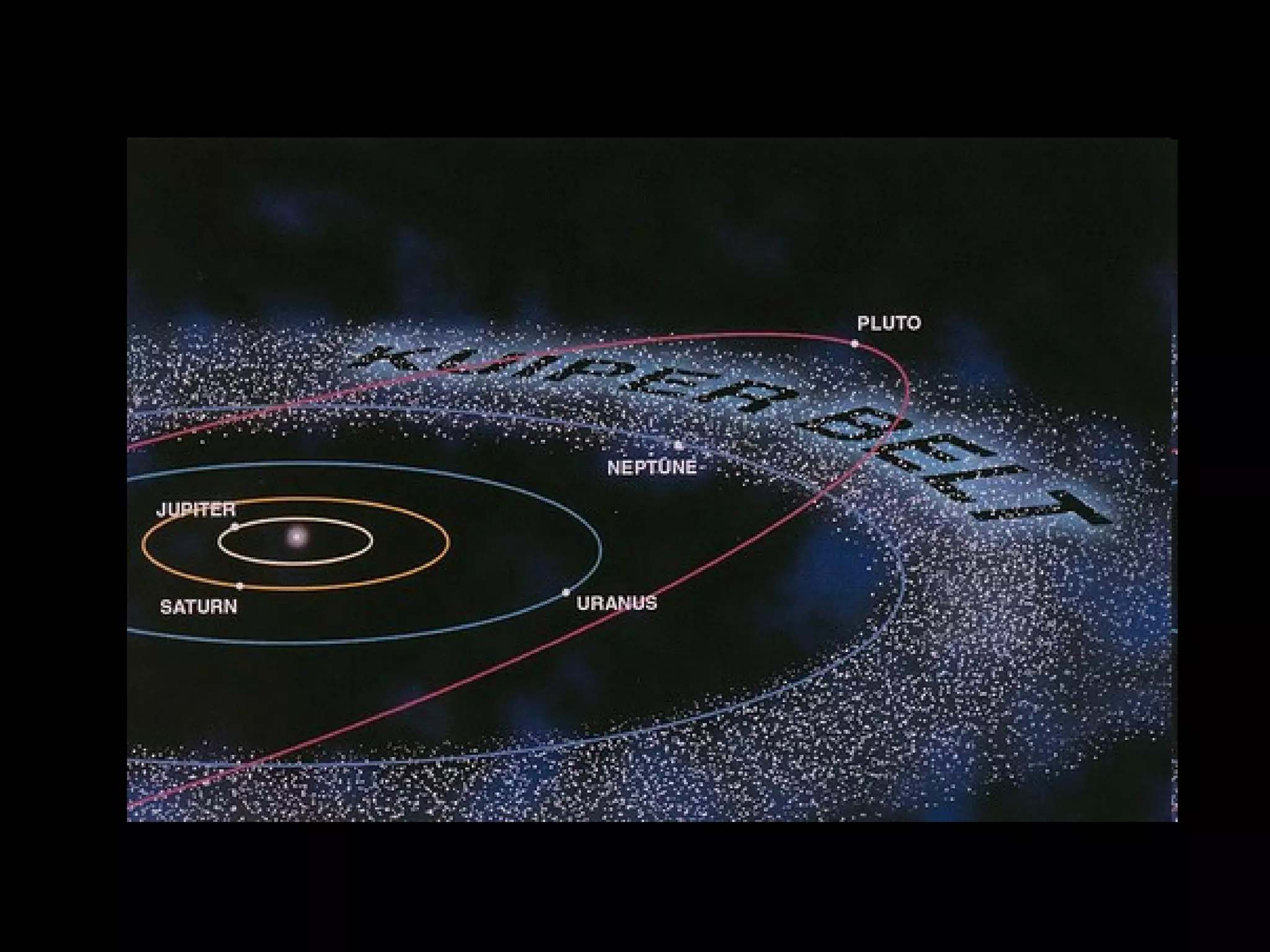
This document provides information about different types of celestial bodies in our solar system. It discusses the key differences between terrestrial and Jovian planets, as well as their composition and examples. Small planets like Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are described. Gas giants like Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are also outlined. Characteristics of dwarf planets such as Ceres, Pluto, Eris, Makemake and Haumea are summarized. Other bodies like comets, asteroids, meteoroids, and black holes are also briefly defined.