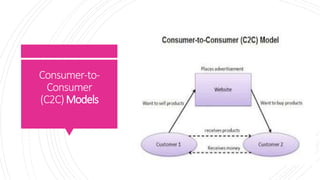
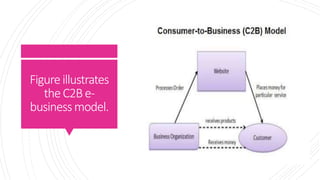
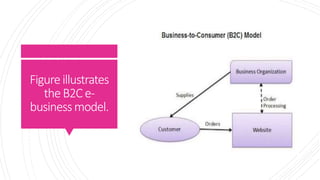
This document defines and discusses e-business. It begins by defining e-business as using communication and information technologies to support business activities. It then discusses the key components of e-business including e-commerce, e-marketing, and e-operations. The document also outlines several common e-business models including business-to-consumer, business-to-business, and consumer-to-consumer and discusses their key features and examples. Finally, it discusses some common applications and benefits of implementing e-business strategies.