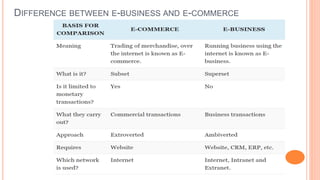
E-business refers to the use of the internet to support business processes, including buying, selling, and managing customer relations, while e-commerce is a subset of e-business focused specifically on online transactions. E-business enhances operational efficiency, allows for automated processes, and fosters improved communication and collaboration internationally. The rise of the internet has transformed traditional business models and practices, impacting all aspects of organizational efficiency and competitiveness.