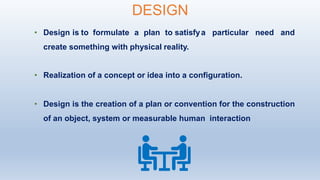
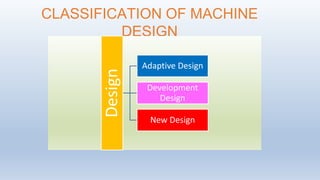
The document discusses machine design and standardization. It defines machine design as designing machine elements and arranging them optimally to perform useful work. It categorizes machine design into adaptive, development, and new design. Standardization is defined as obligatory norms for product characteristics like materials and dimensions to reduce variety. Standards include company, national, and international standards for materials, shapes, fits, tolerances, surface finish, and testing. Benefits of standardization include inventory control, interchangeability, improved quality, and safety.