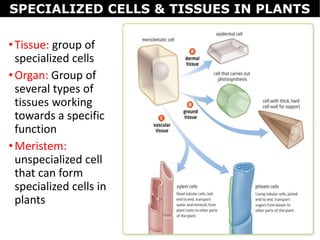
This document discusses plant cells, tissues, and organs. It describes how plant cells can be specialized into tissues for specific functions. The major plant organs are then examined in more detail: leaves contain tissues like palisade and mesophyll for photosynthesis; stems provide structure and transport through vascular bundles; roots absorb water and minerals through root hairs and vascular tissue; and flowers facilitate reproduction through pollination and seed production. The roles of meristem, buds, and plant hormones in growth and repair are also outlined.