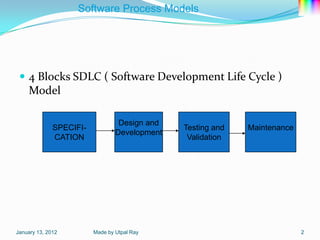
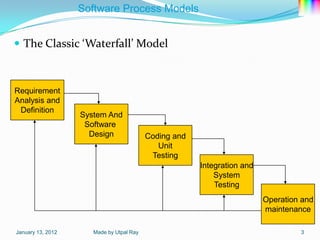
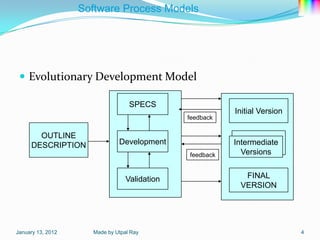
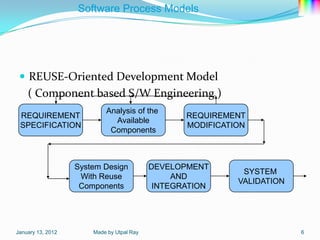
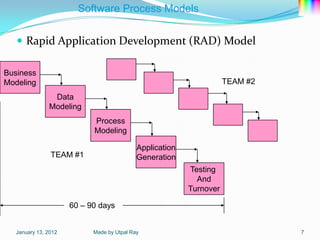
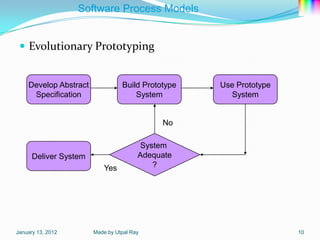
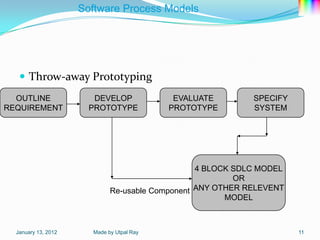
The document describes several software process models: the 4 block SDLC model, waterfall model, evolutionary development model, incremental development model, reuse-oriented development model, rapid application development model, and software prototyping models including evolutionary prototyping and throw-away prototyping. It also outlines Boehm's spiral model and notes this as a homework task.