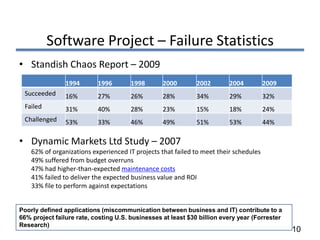
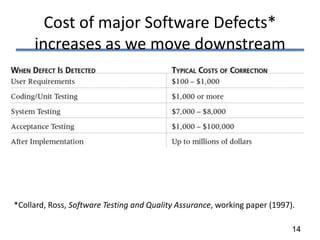
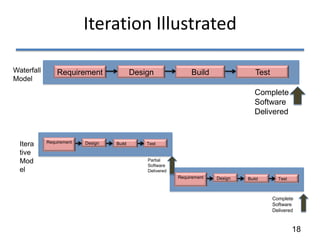
The document discusses various software development life cycle (SDLC) models, including:
- The waterfall model, which uses sequential phases of requirements, design, coding, testing, and deployment. It is structured but rigid.
- Iterative development models, which allow for feedback loops and releasing partial software in iterations to get faster feedback.
- Agile methodologies like Scrum, which embrace changing requirements, focus on working software over documentation, and value customer collaboration over contracts. Key aspects are iterative development, regular refactoring, and communicating for learning.
- Pitfalls of agile include skill gaps, lack of traceability, poor communication, and not staying close enough to customers. Overall, agile aims to







![Software Project :
A recent example [May, 2011]
Montclair State University is suing Oracle over an ERP system
implementation intended to enable a greater degree of student and
faculty self service for many academic and business processes via a
university portal.
Oracle was chosen in 2009 to implement PeopleSoft in support of the
project, named the Bell Tower Initiative for the school's landmark tower.
The university contracted for $4.3 million in software and technical
support along with a $15.75 million fixed fee implementation agreement
Suit claims that they will incur $20 million in expenses beyond the
planned cost of the project.
A recent report from Europe shows that in average 60% contract
experience cost-overrun with 30% failure rate
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swlifecycle-13272951663403-phpapp02-120122234359-phpapp02/85/Software-Lifecycle-8-320.jpg)