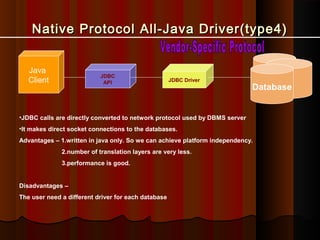
This document discusses Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and its components. It begins with an introduction to JDBC, explaining that JDBC is a Java API that allows Java programs to execute SQL statements and interact with multiple database sources. It then discusses the four types of JDBC drivers - JDBC-ODBC bridge drivers, native-API partly Java drivers, network protocol all-Java drivers, and native protocol all-Java drivers - and their characteristics. The document proceeds to explain the standard seven steps to querying databases using JDBC: loading the driver, defining the connection URL, establishing the connection, creating a statement object, executing a query or update, processing results, and closing the connection.