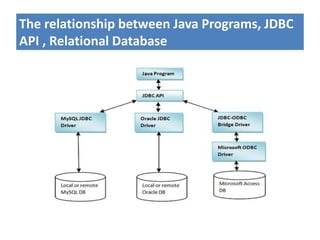
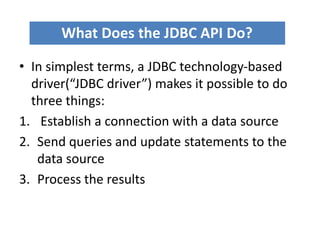
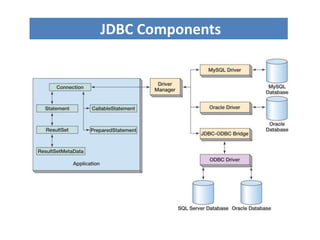
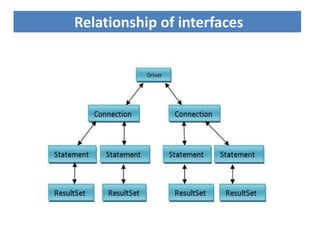
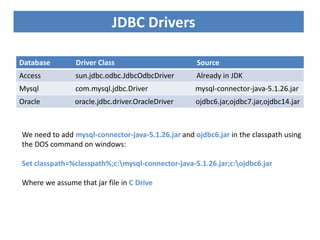
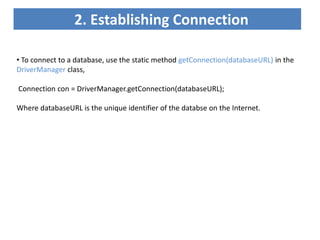
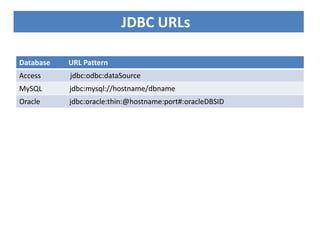
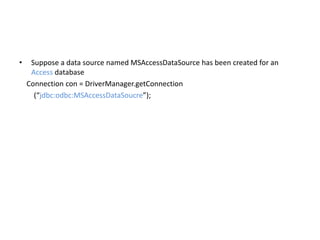
JDBC is the Java API for connecting to and interacting with relational databases. It includes interfaces and classes that allow Java programs to establish a connection with a database, execute SQL statements, process results, and retrieve metadata. The key interfaces are Driver, Connection, Statement, and ResultSet. A JDBC program loads a JDBC driver, obtains a Connection, uses it to create Statements for querying or updating the database, processes the ResultSet, and closes the connection.







![import java.sql.*;
public class SimpleJDBC{
public static void main(String args[])
throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException{
Class.forName(“oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver”); //Load driver
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection
(jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe, ”root” , ”root”); //Connect to a database
Statement st=con.createStatement(); //Create Statement
ResultSet rs=st.executeQuery(“select * from student”); //Execute a statement
//Iterate through the result and print the student names
While(rs.next())
System.out.print(rs.getString(1));
System.out.println(“t”rs.getString(2));
con.close(); //Close the connection
}
}
SimpleJDBC.java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbcbynitesh-160101151222/85/Jdbc-16-320.jpg)