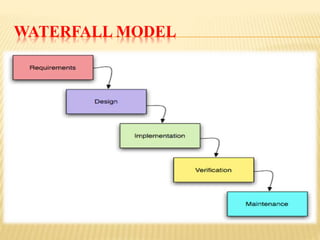
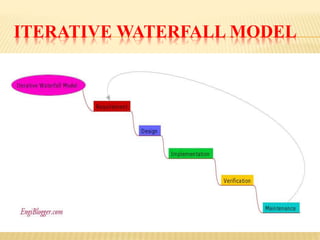
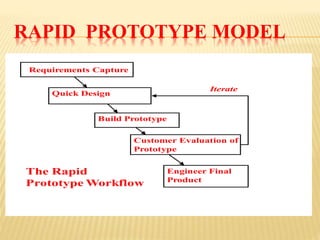
This document discusses various software development life cycle (SDLC) models including waterfall, iterative waterfall, rapid prototype, evolutionary, spiral, fish, V-shape, RAD, and incremental models. For each model, it provides a brief description and highlights the advantages and disadvantages. The models differ in their structure, approach to requirements, testing, flexibility, and ability to handle risk and changing requirements.