1. Software development life cycle models break down the development process into distinct phases to manage complexity. Common models include waterfall, incremental, evolutionary (like prototyping and spiral), and component-based.
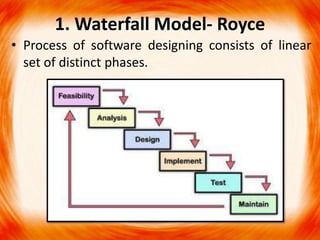
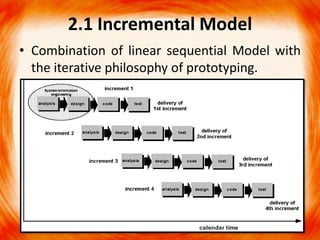
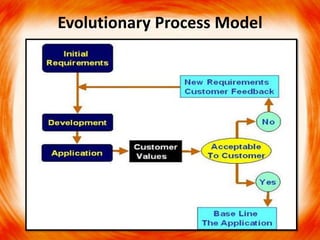
2. The waterfall model follows linear sequential phases from requirements to maintenance. Incremental models iterate through phases. Evolutionary models use prototypes to evolve requirements through customer feedback.
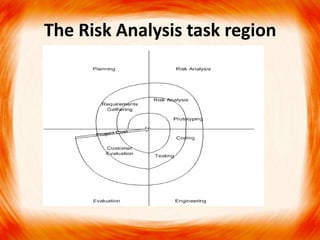
3. The spiral model is an evolutionary model representing phases as loops in a spiral, with risk assessment and reduction at each phase. It aims to minimize risk through iterative development and prototyping.