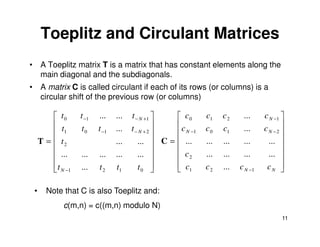
This document provides definitions and notations for 2-D systems and matrices. It defines how continuous and sampled 2-D signals like images are represented. It introduces some common 2-D functions used in signal processing like the Dirac delta, rectangle, and sinc functions. It describes how 2-D linear systems can be represented by matrices and discusses properties of the 2-D Fourier transform including the frequency response and eigenfunctions. It also introduces concepts of Toeplitz and circulant matrices and provides an example of convolving periodic sequences using circulant matrices. Finally, it defines orthogonal and unitary matrices.

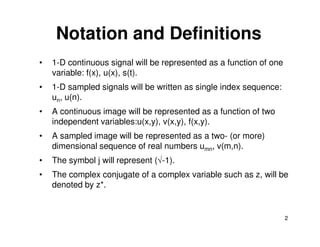

![2-D Linear System
x(m,n) y(m,n) = H [x(m,n)]
y(m,n)
H [.]
• Linear system criterion:
H [a1x1(m,n) + a2x2(m,n)] = a1H [x1(m,n)] + a2H [x2(m,n)]
= a1 y1(m,n) + a2 y2(m,n)
• Impulse response:
System response (output) given a delta kronecker input:
h(m,n; m’,n’) ≡ H [δ(m - m’, n - n’)]
– PSF (point spread function) → impulse response whose inputs
and outputs represent a positive quantity, such as intensity.
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/022dsystemsmatrix-120321102336-phpapp01/85/02-2d-systems-matrix-5-320.jpg)
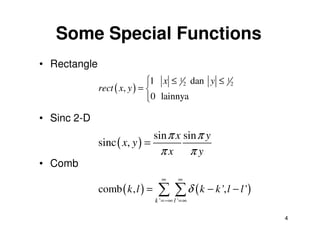
![The Fourier Transform
• 2-D Fourier/ Inverse Fourier Transform Formulations:
∞ ∞
F (ξ1 ,ξ 2 ) = ∫ ∫ f ( x, y ) exp − j 2π ( xξ1 + yξ 2 ) dxdy
−∞ −∞
∞ ∞
f ( x, y ) = ∫ ∫ F (ξ1 ,ξ 2 ) exp j 2π ( xξ1 + yξ 2 ) dξ1dξ 2
−∞ −∞
f(x,y) F(ξ1, ξ2)
δ(x,y) 1
δ(x ± x0, y ± y0) exp(±j2πx0ξ1). exp(±j2πy0ξ2)
exp(±j2πx0η1). exp(±j2πy0 η2) δ(ξ1 -+ η1, ξ2 -+ η2)
exp[-π(x2 + y2 )] exp[-π(ξ12 + ξ22 )]
rect(x, y) sinc(ξ1, ξ2)
tri(x, y) sinc2(ξ1, ξ2)
comb(x, y) comb(ξ1, ξ2)
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/022dsystemsmatrix-120321102336-phpapp01/85/02-2d-systems-matrix-6-320.jpg)
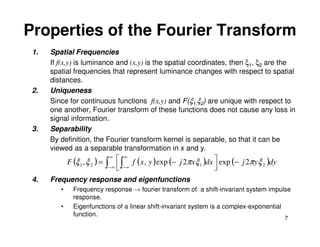
![Matrix Theory
• One- and two-dimensional sequence will be represented by vectors
and matrices.
u (1) a (1,1) a (1, 2 ) ... a (1, N )
u (2 ) a (2 ,1) a (2 , 2 ) ... a (2 , N )
u ≡ {u (n )} = A ≡ {a (m , n )} =
... ... ... ... ...
u (n ) a (M ,1) a (M , 2 ) ... a (M , N )
• Transpose: AT = {a(m,n)}T = {a(n,m)}
• Transposition and Conjugation Rules
1. A*T = [AT]*
2. [AB] = BTAT
3. [A-1]T = [AT]-1
4. [AB]* = A*B*
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/022dsystemsmatrix-120321102336-phpapp01/85/02-2d-systems-matrix-10-320.jpg)