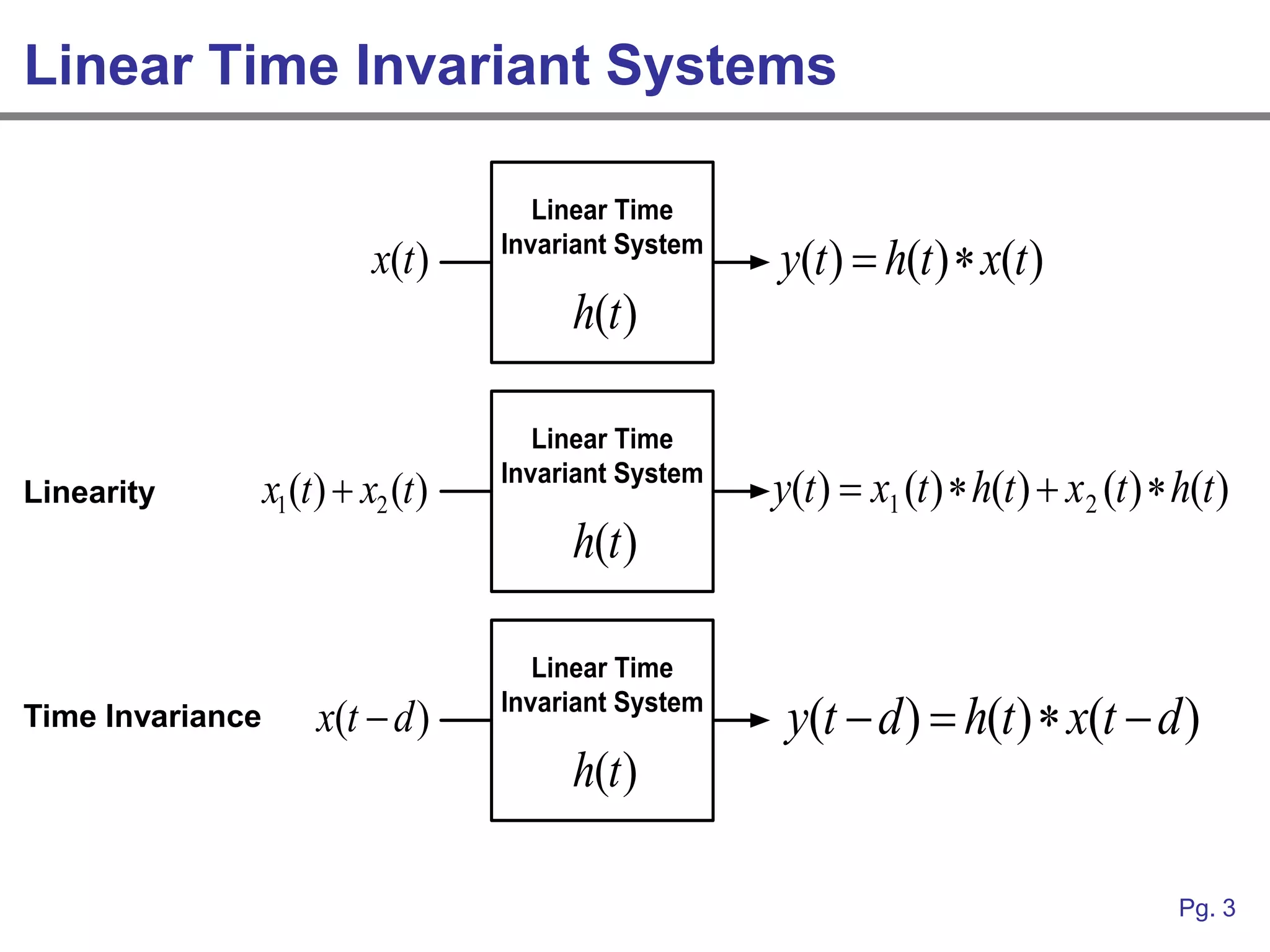
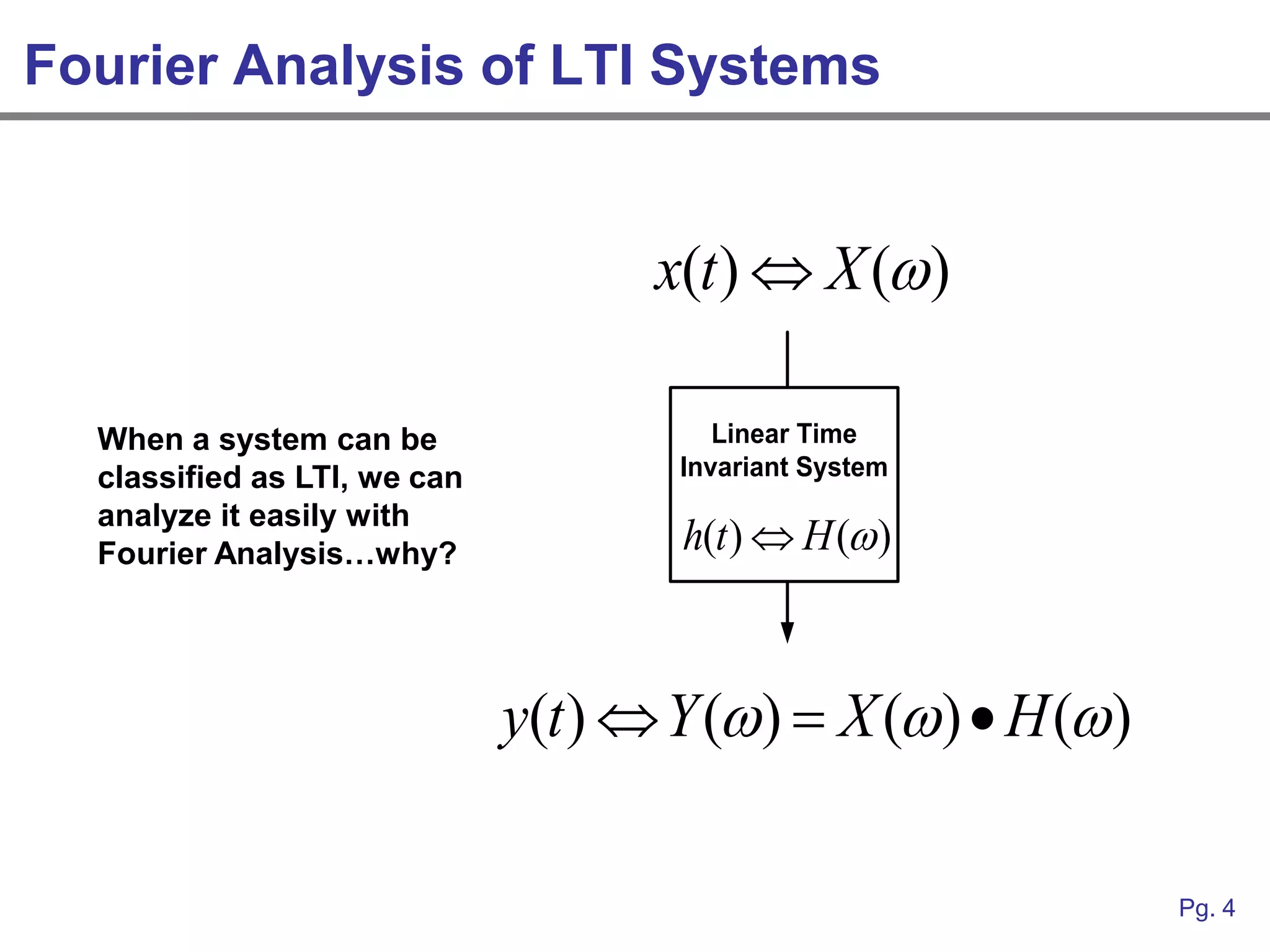
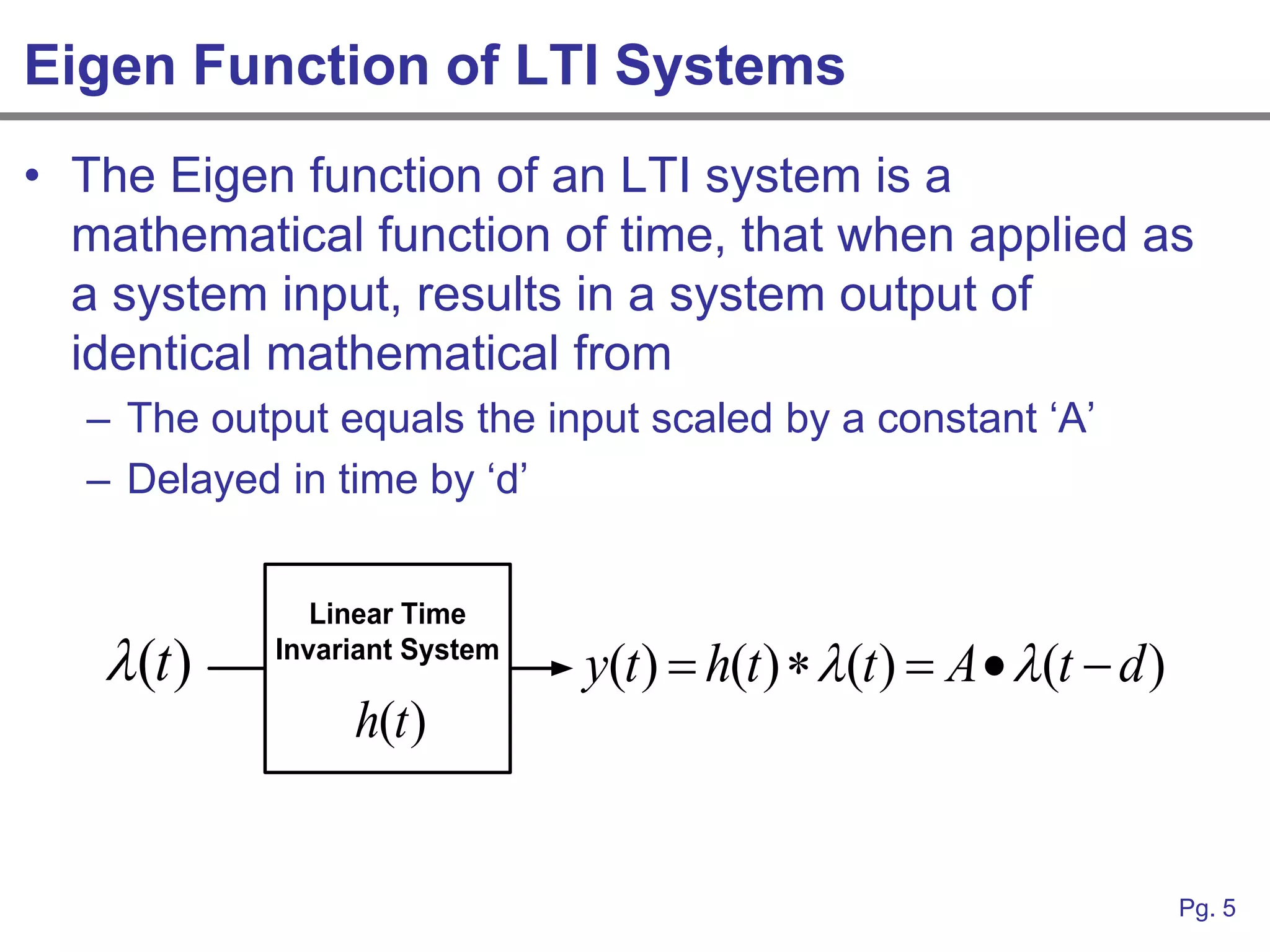
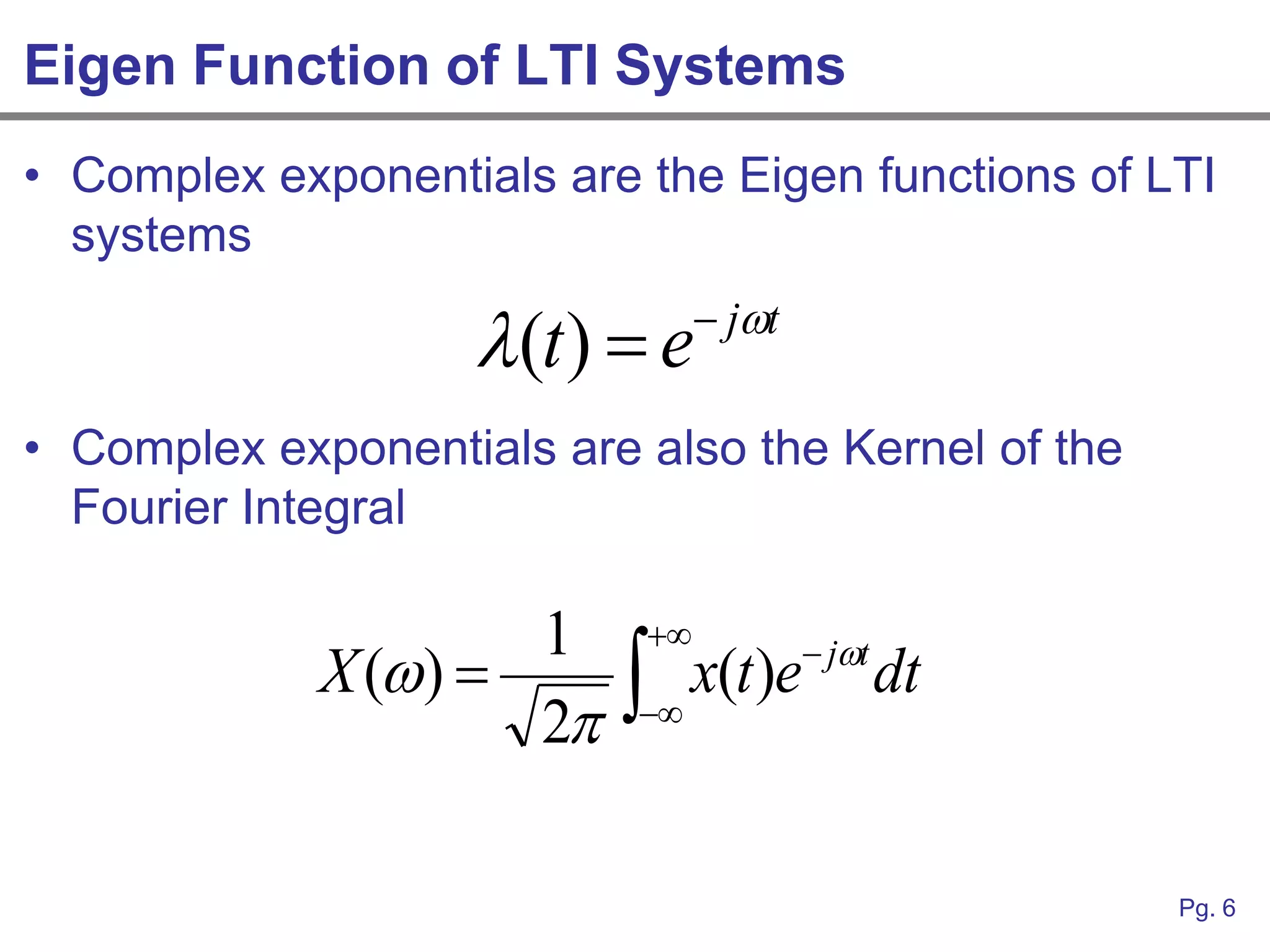
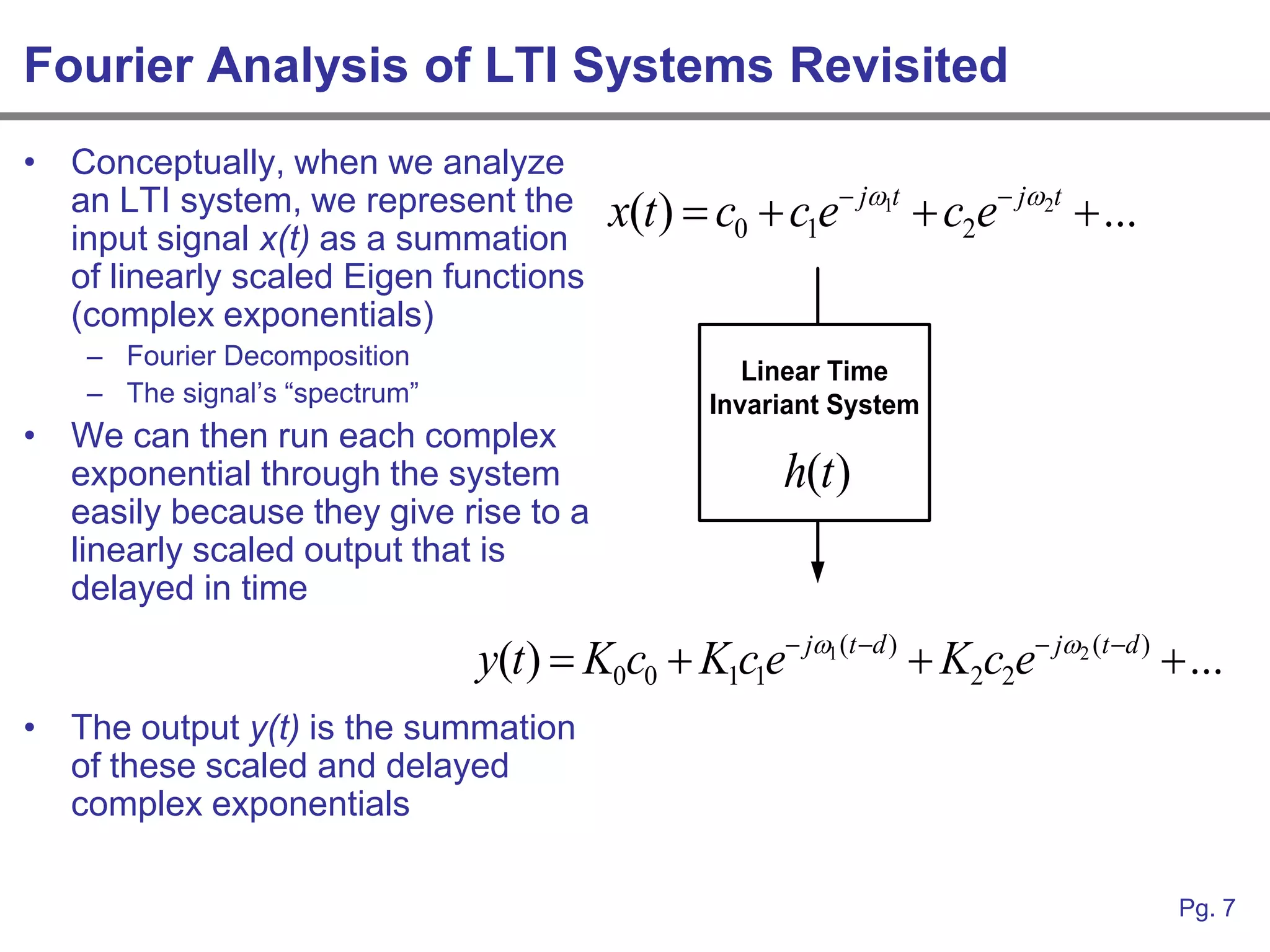
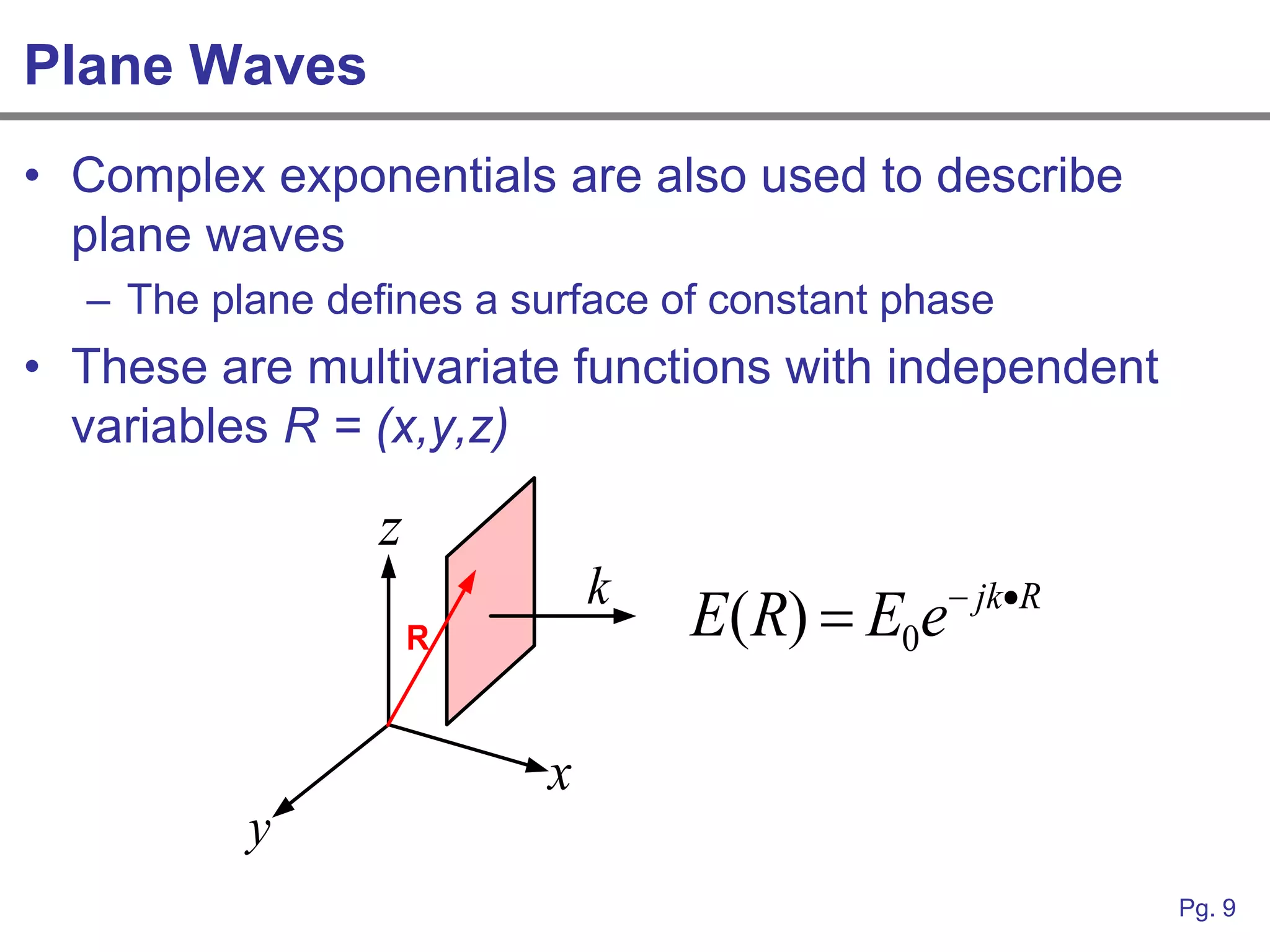
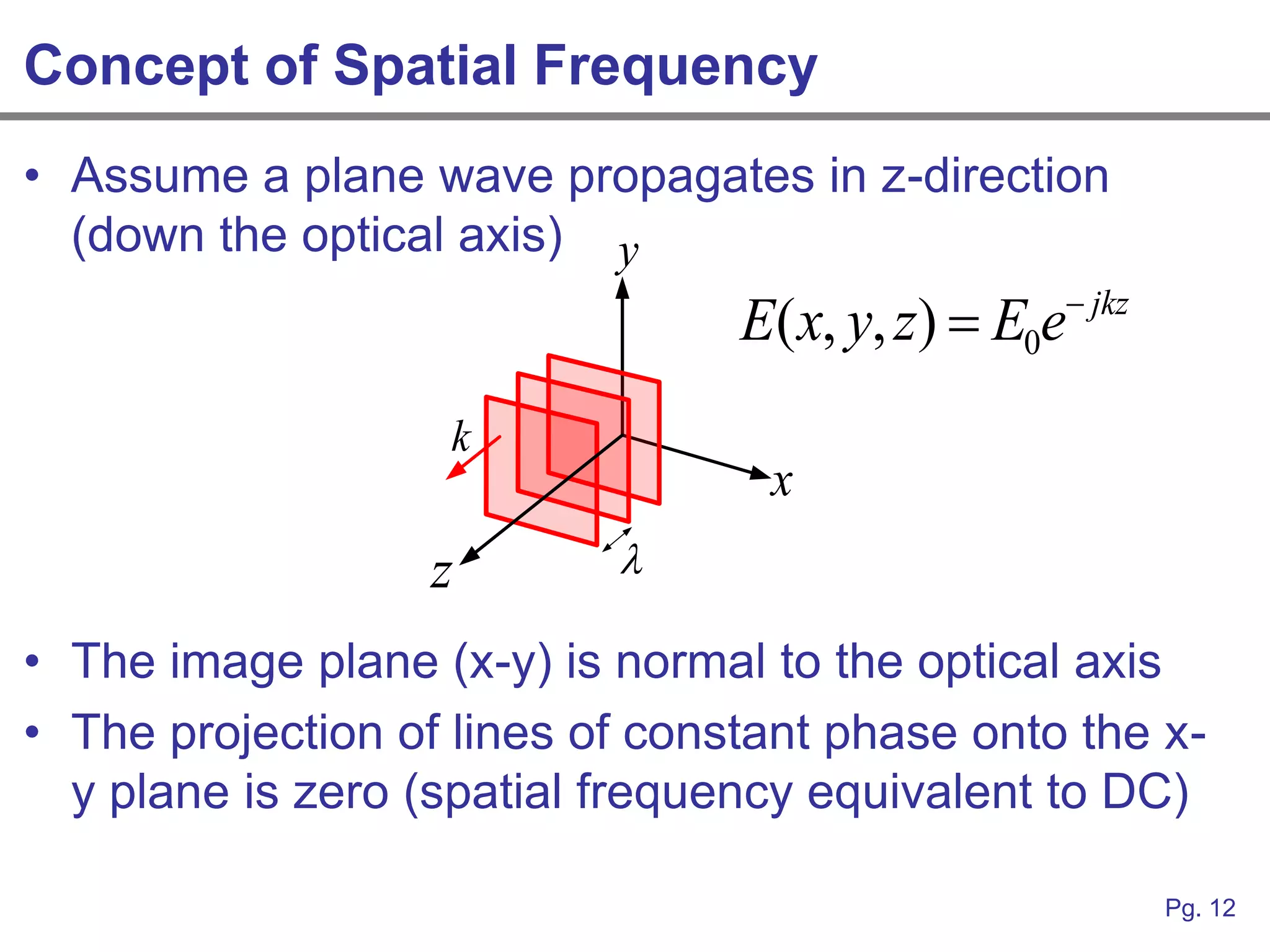
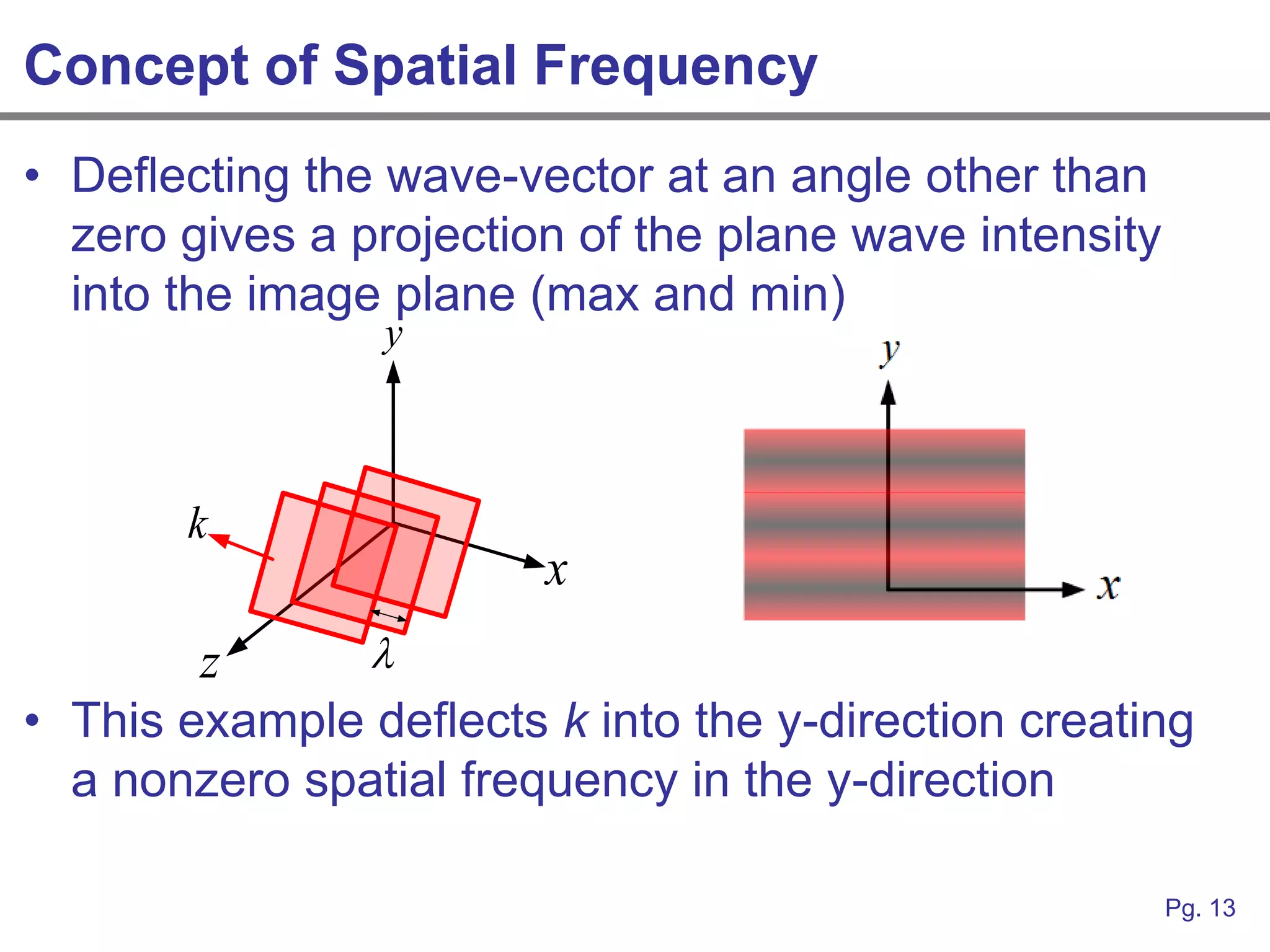
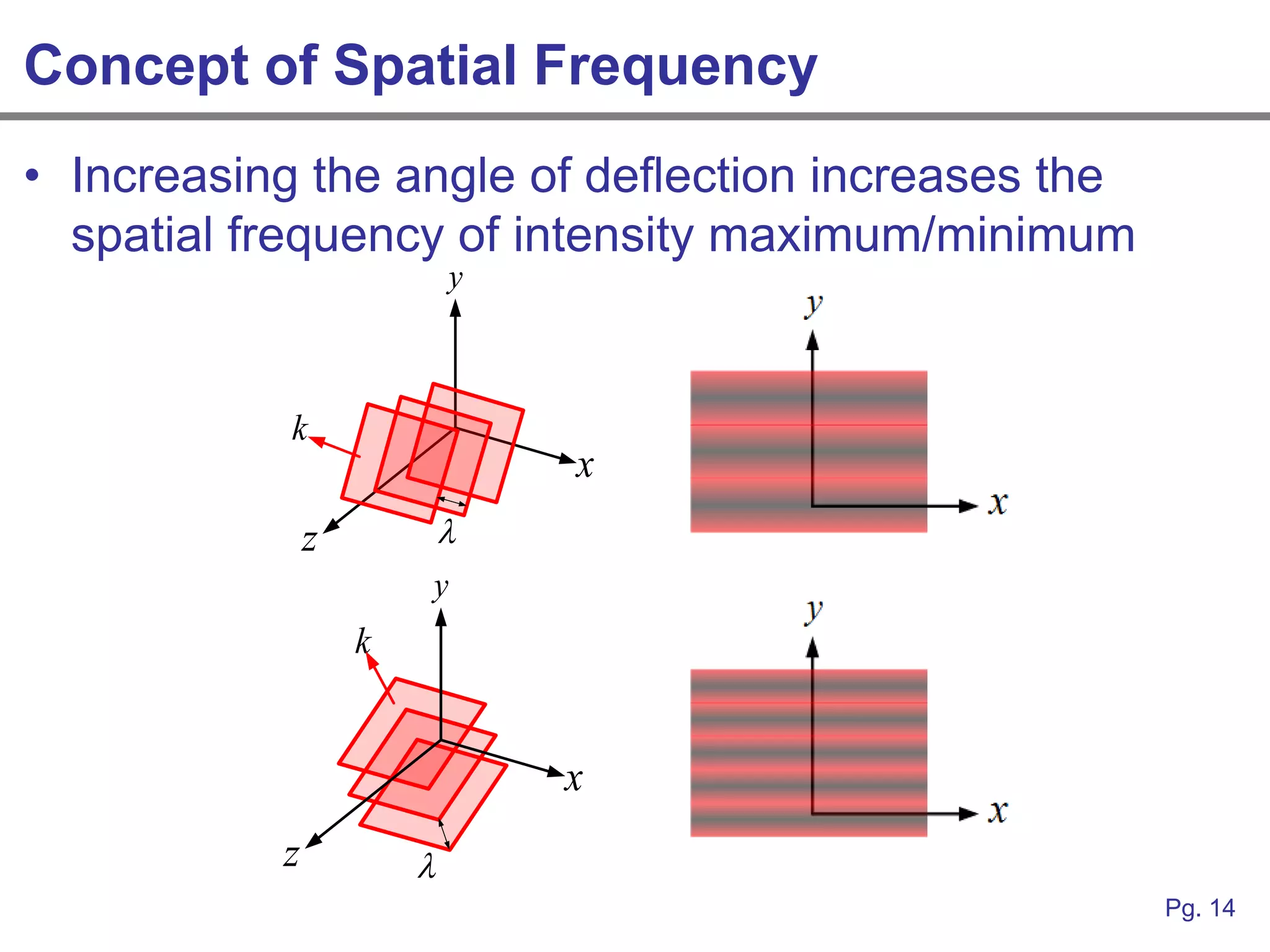
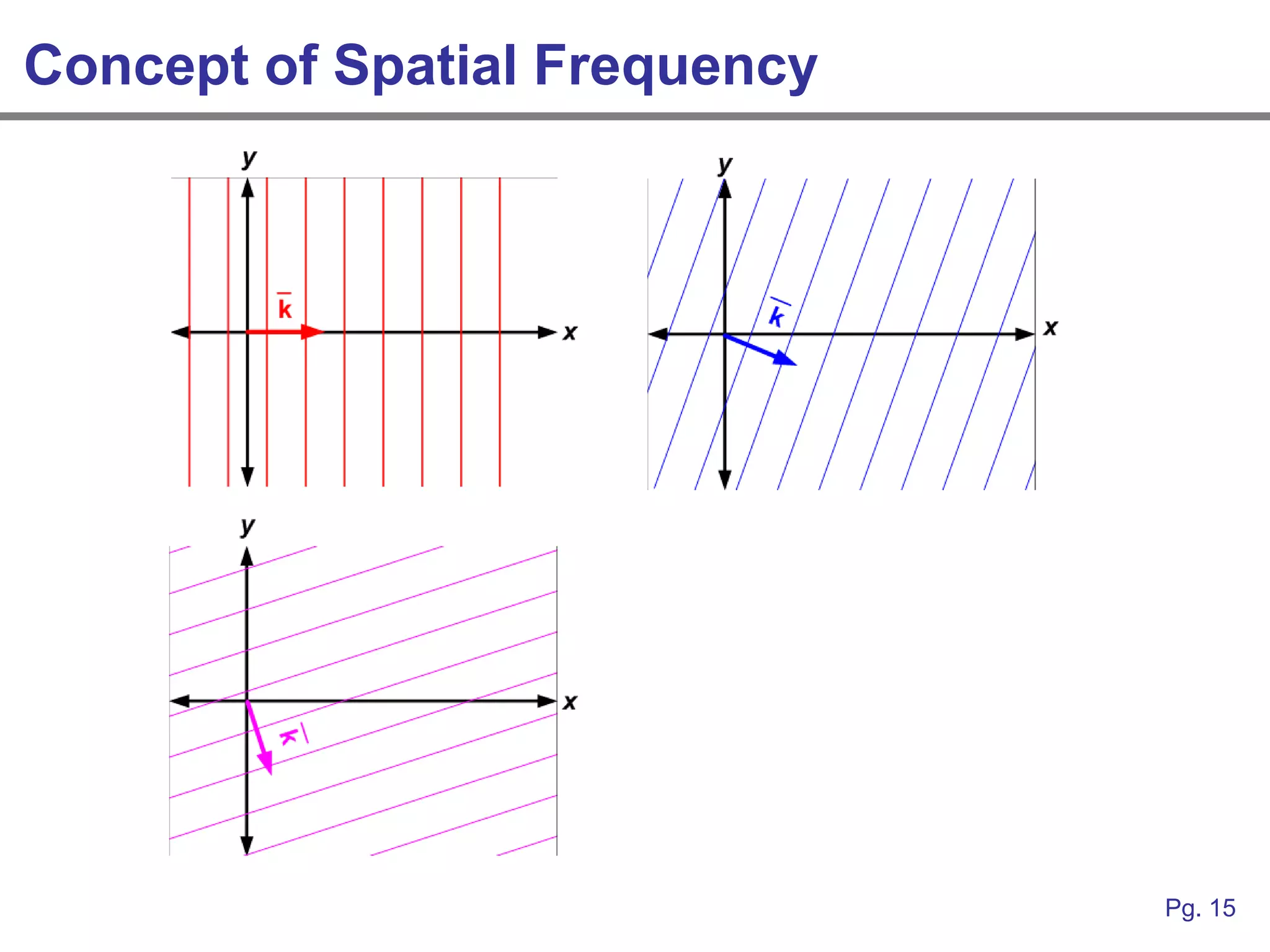
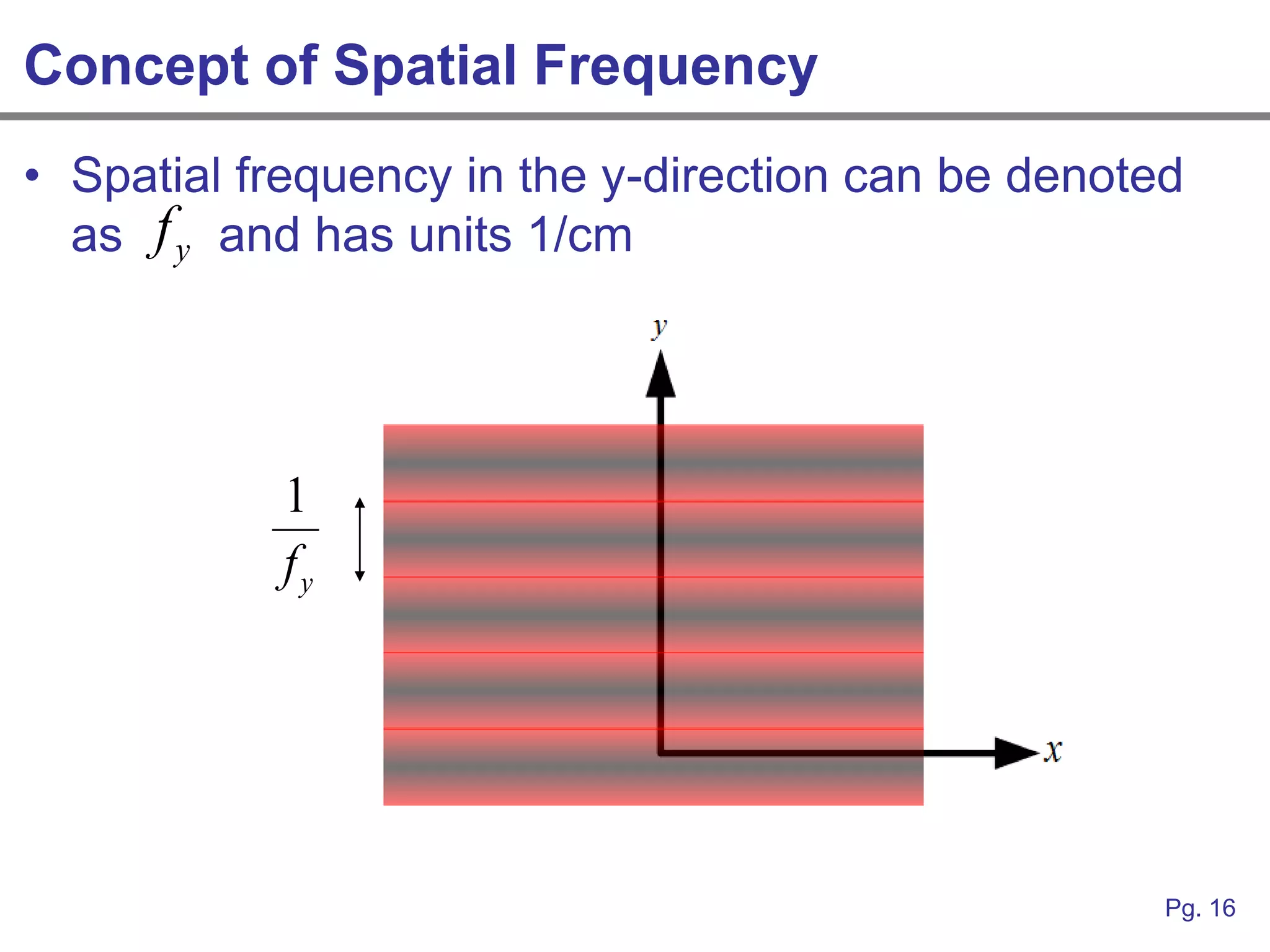
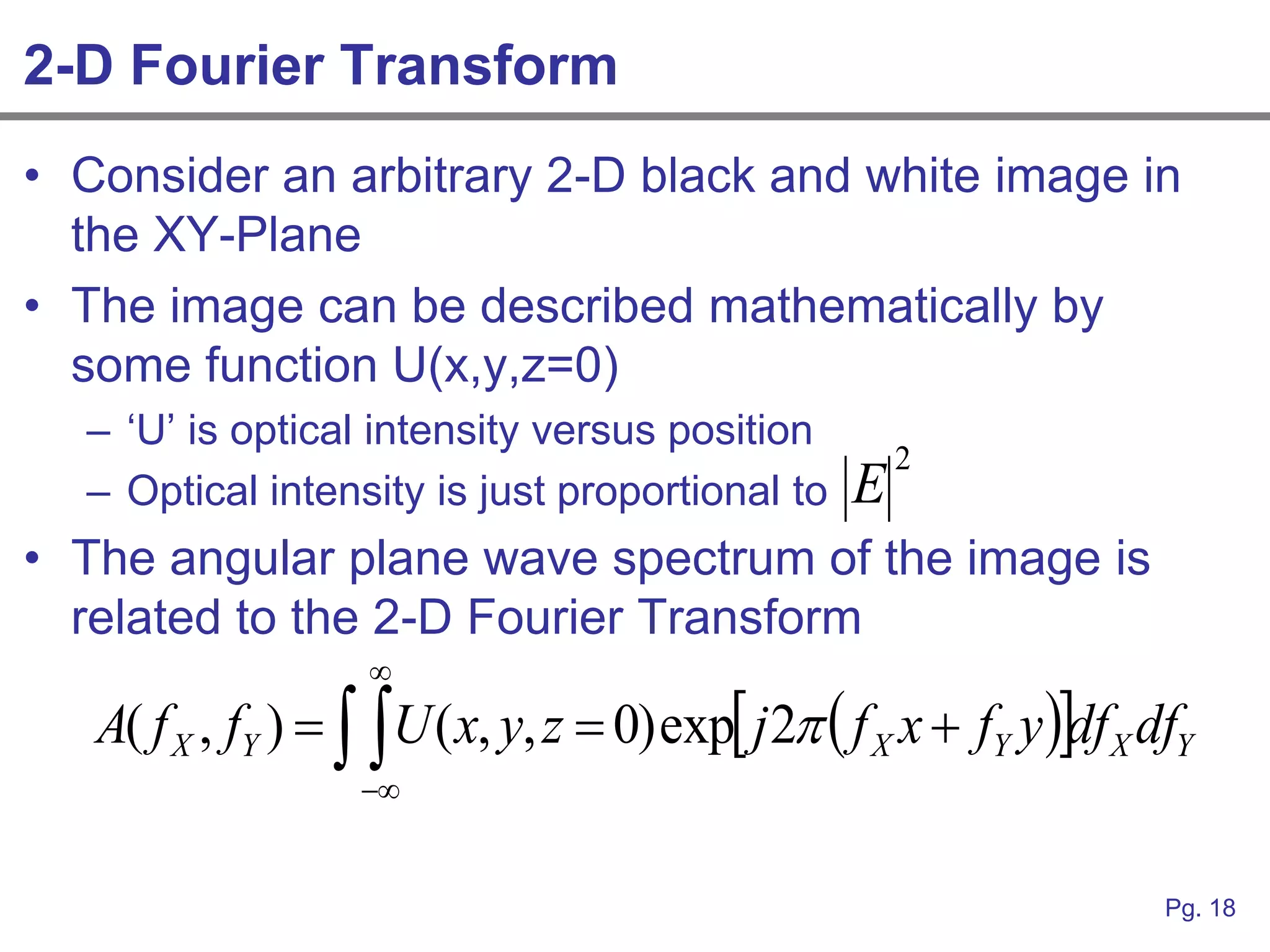
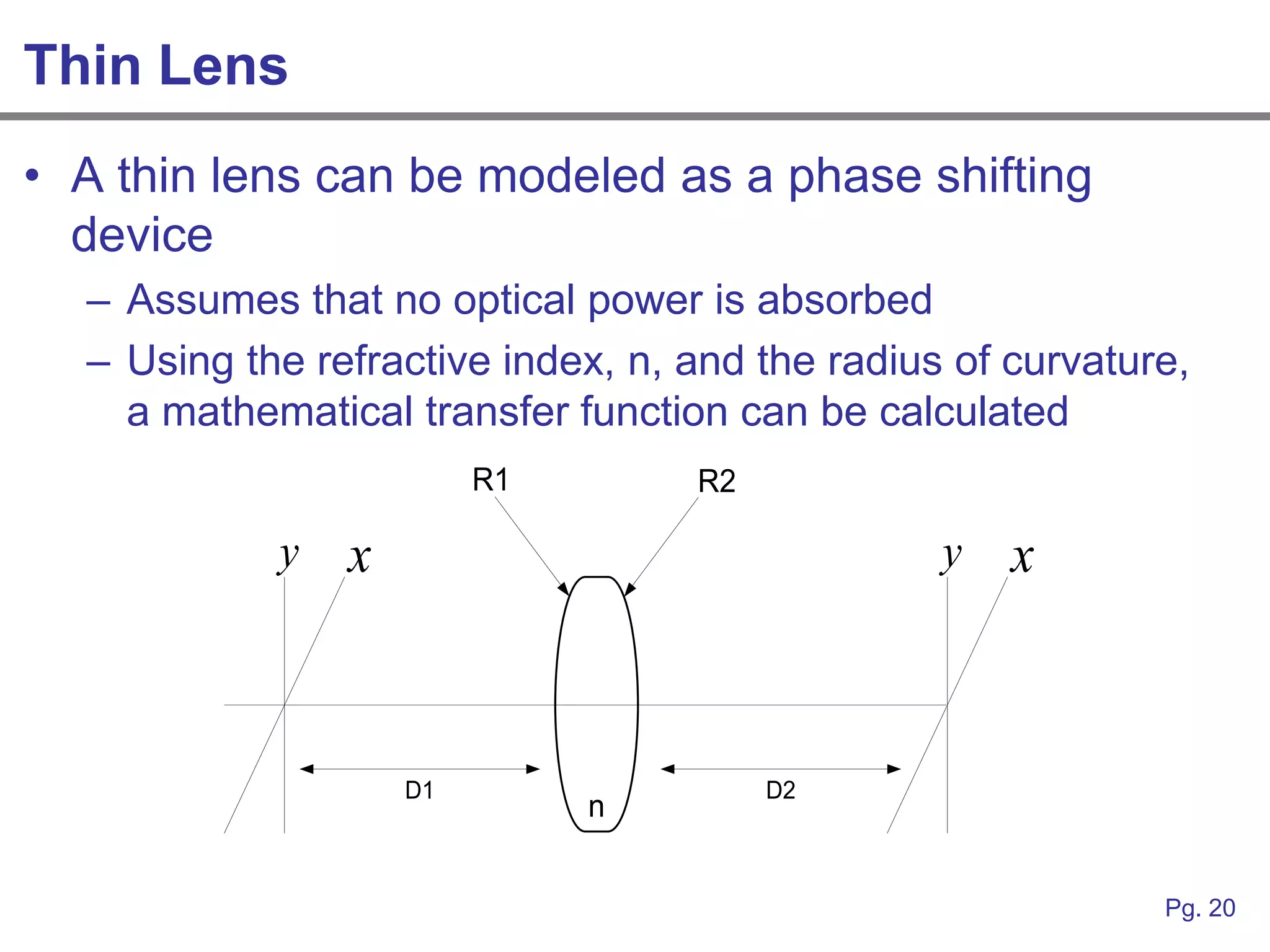
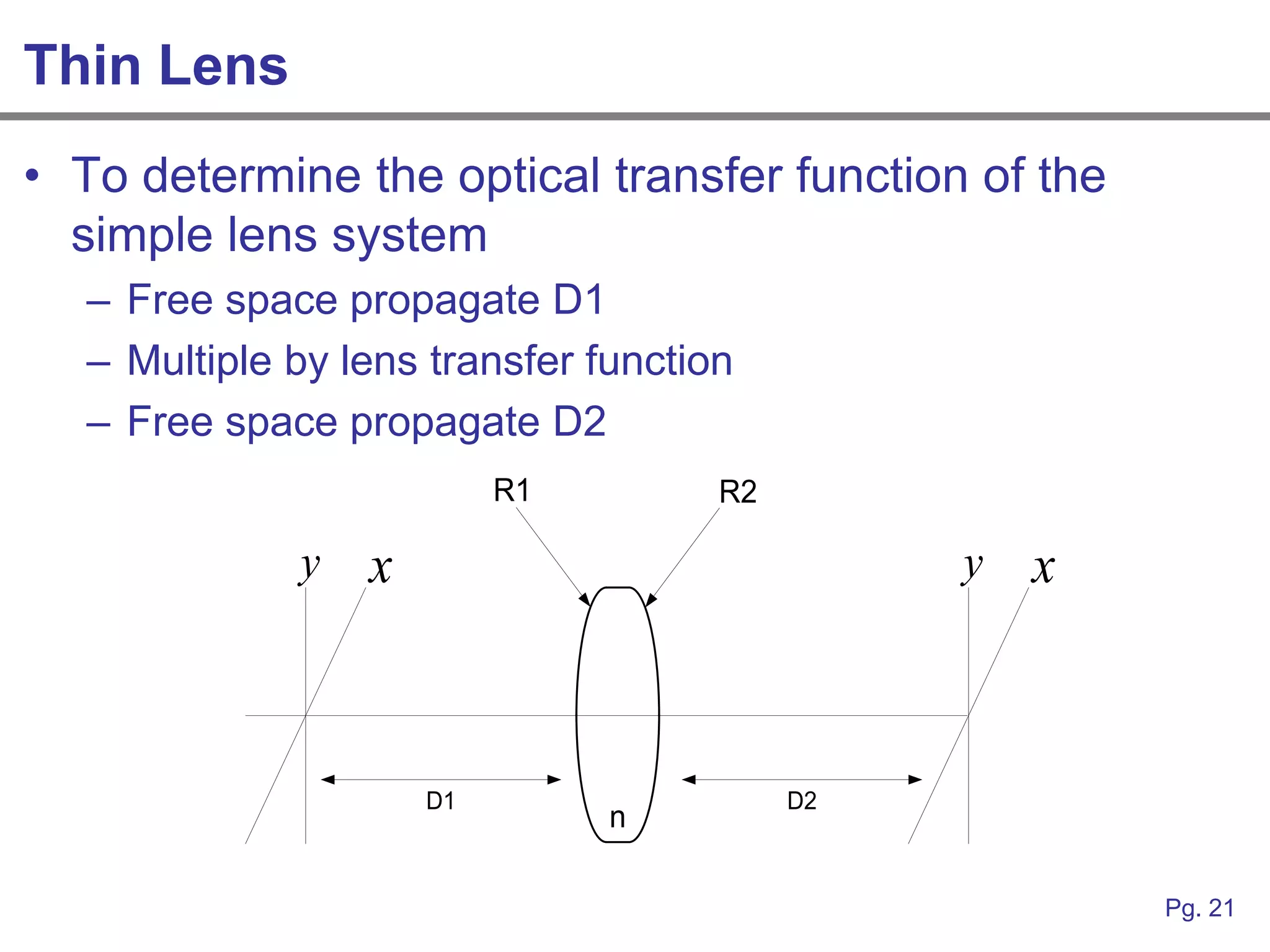
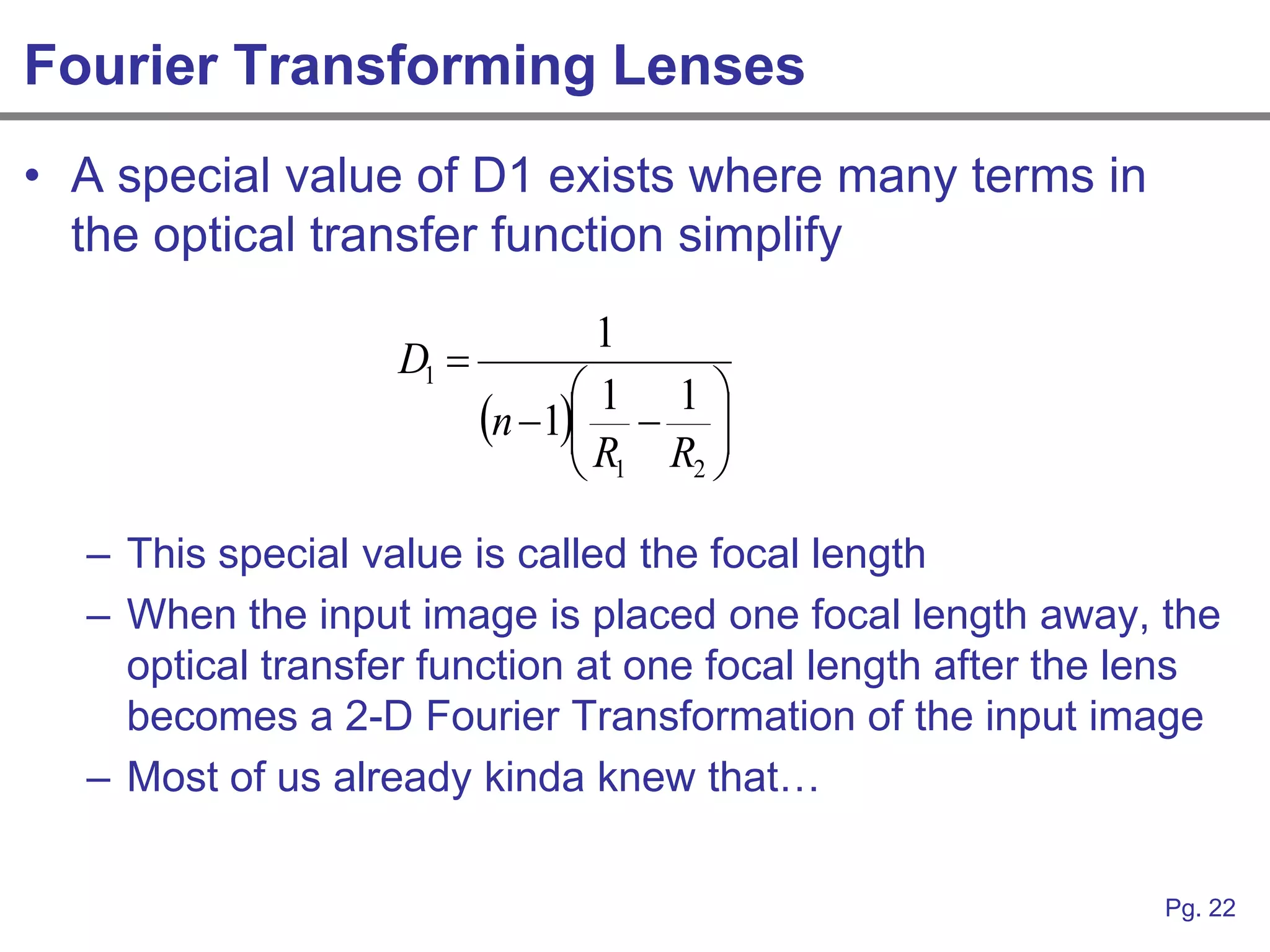
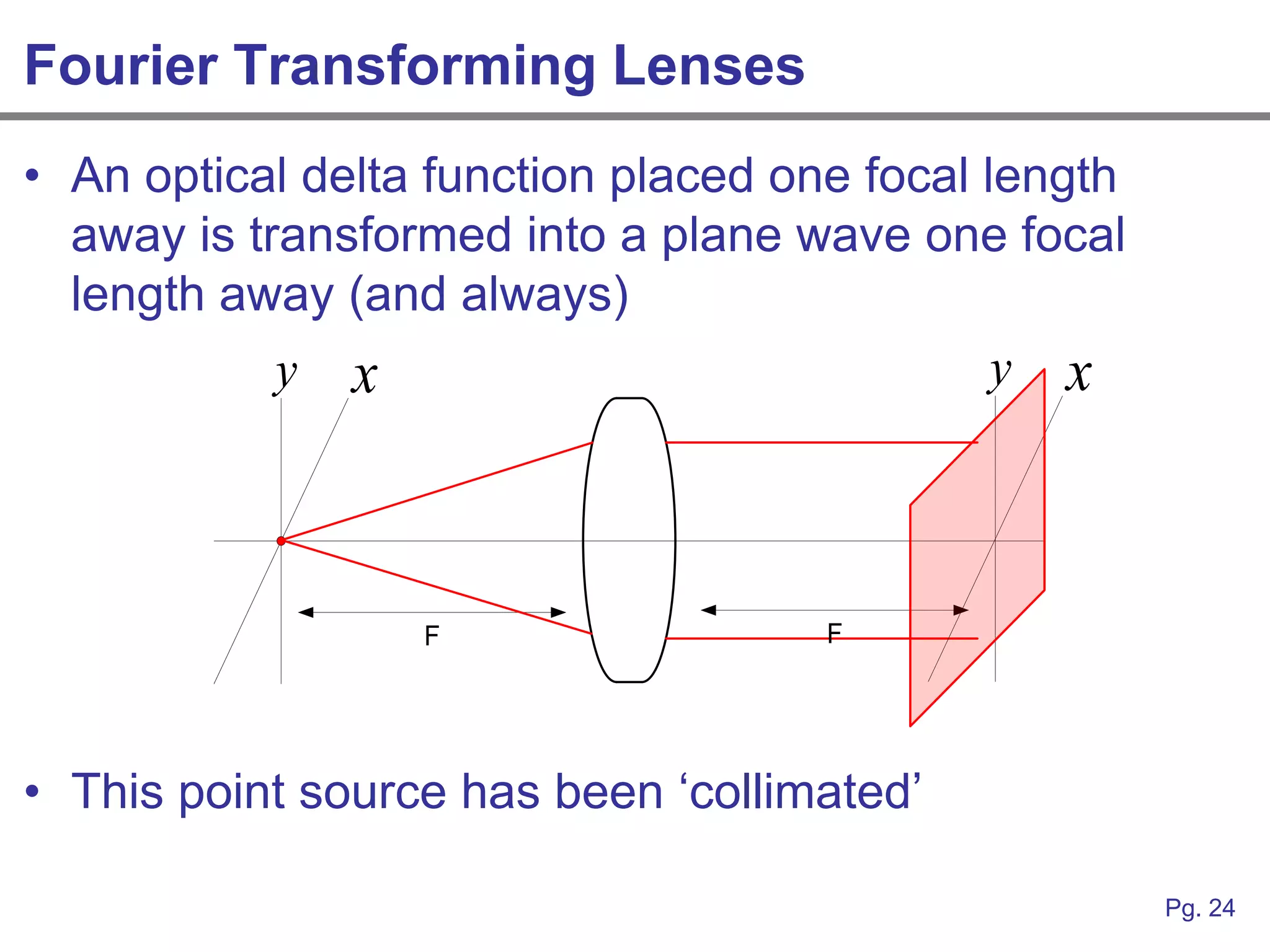
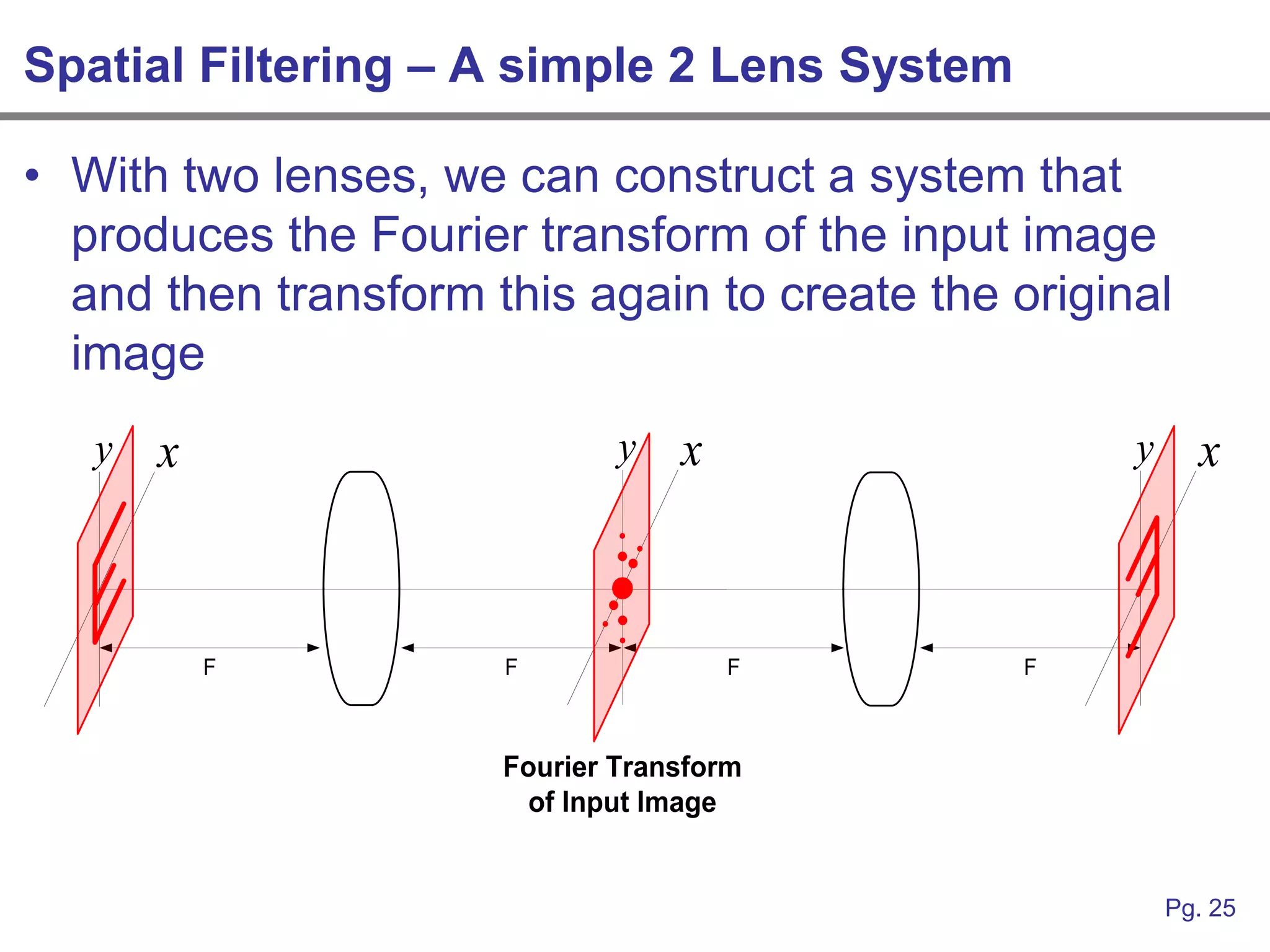
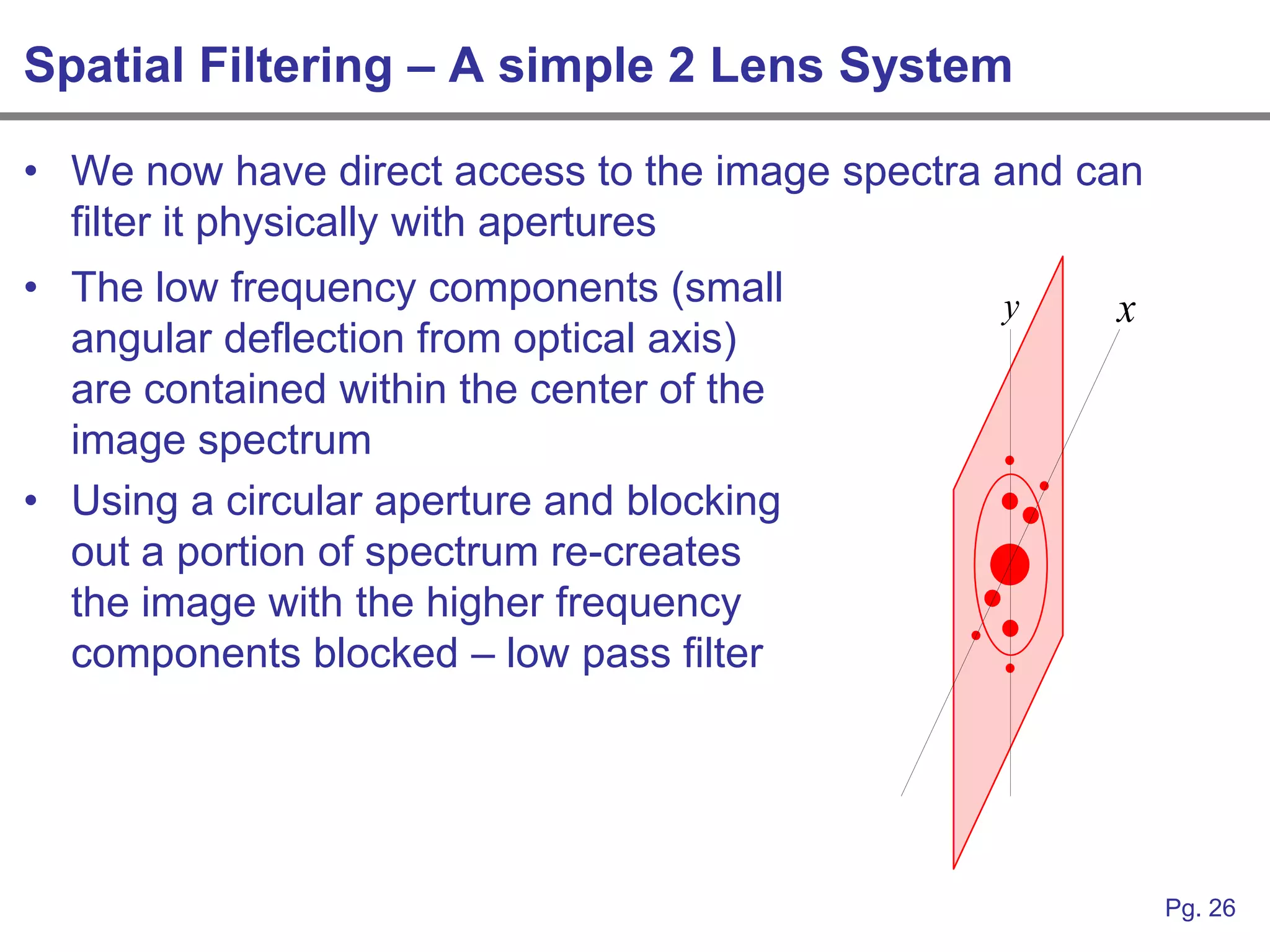
This document provides an overview of how linear systems analysis and Fourier transforms can be applied to analyze 2-dimensional optical images and optical systems. It explains that plane waves serve as the eigenfunctions for linear shift invariant optical systems, just as complex exponentials serve as the eigenfunctions for linear time invariant electrical systems. The Fourier transform can be used to decompose an optical image into its plane wave spectrum, and optical systems can be analyzed by multiplying the image spectrum by the system's optical transfer function and taking the inverse Fourier transform. As an example, it describes how a thin lens can be modeled as a phase shifting device and its optical transfer function calculated.