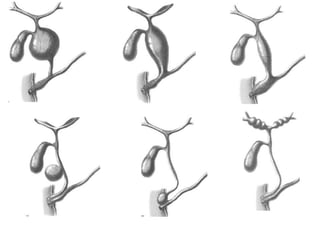
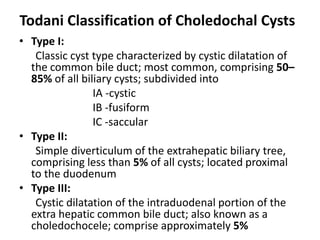
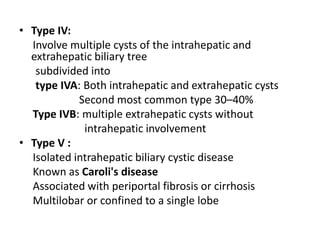
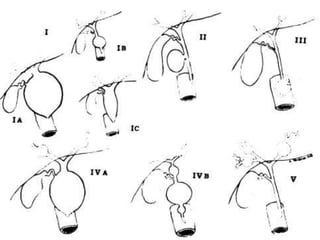
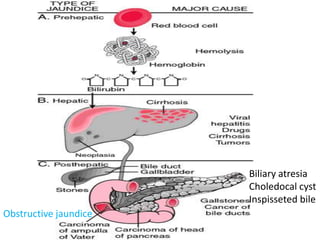
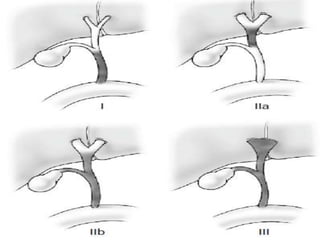
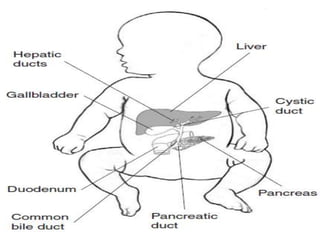
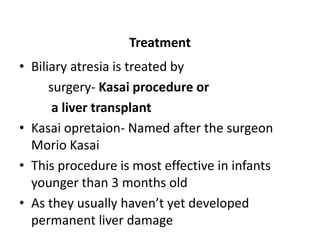
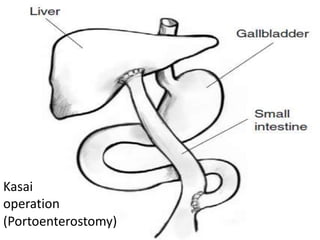
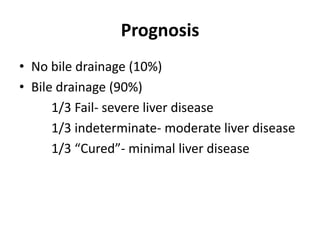
Obstructive jaundice in neonates can be caused by several conditions including biliary atresia, choledochal cysts, and inspissated bile. Biliary atresia, the most common cause, involves obstruction of the bile ducts inside or outside the liver. It is typically treated with the Kasai procedure to reconnect bile flow to the intestine or liver transplantation. Choledochal cysts are rare congenital cysts of the bile ducts that may cause pain, jaundice, and abdominal mass. Surgical excision and reconstruction is the primary treatment. Inspissated bile syndrome can also cause obstructive jaundice in newborns due to thickened bile but sometimes resolves spontaneously




























![Pathologic features
• Frequently include an anomalous junction of
the pancreatic duct and CBD
(pancreaticobiliary malunion [PBMU])
• Intrahepatic bile duct dilatation with or
without downstream stenosis
• Varying degrees of hepatic fibrosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obstructivejaundiceinneonate-ppt-130609005729-phpapp01/85/Obstructive-jaundice-in-neonate-ppt-37-320.jpg)