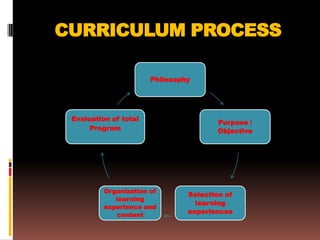
The document outlines the 5 phases of the curriculum process:
1. Formulating the educational philosophy and objectives of the program.
2. Establishing specific purposes and goals to achieve the objectives.
3. Selecting relevant learning experiences, like direct experiences, reading, and observation to meet the objectives.
4. Organizing the selected learning experiences effectively.
5. Evaluating the total curriculum program to ensure the objectives are being met.