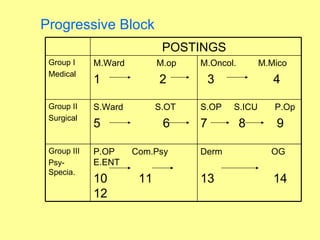
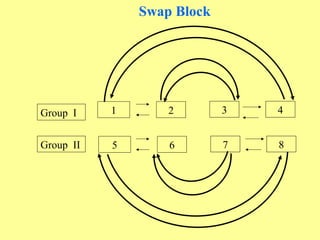
This presentation discusses different patterns for organizing nursing education curriculum and clinical experiences. It covers organizing course content into categories like basic sciences, professional understanding, and nursing sciences. It also discusses distributing content across subjects like humanities, behavioral sciences, and biological sciences. Placement, continuity, sequence, and integration are important principles for organizing learning experiences. Teaching systems can include teaching blocks, study day systems, and daily classes. Patterns of curriculum organization are progressive blocks, swap blocks, and concept blocks, which involve rotating students through different clinical areas over time.