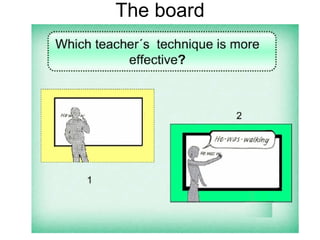
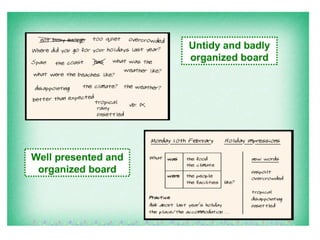
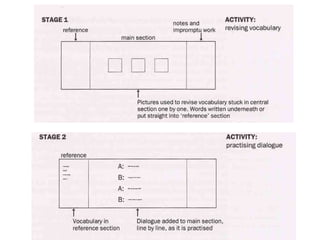
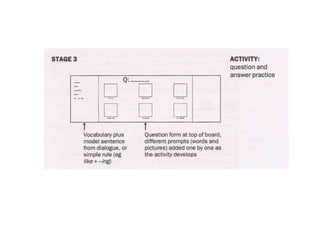
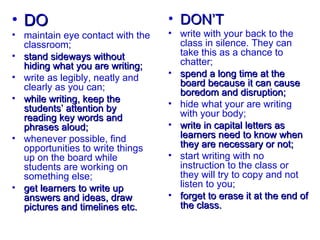
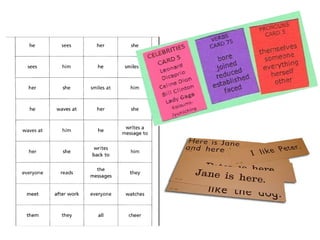
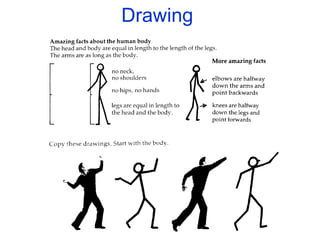
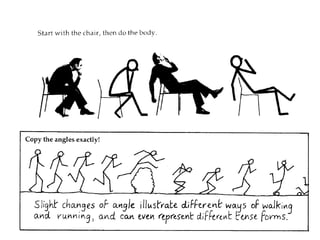
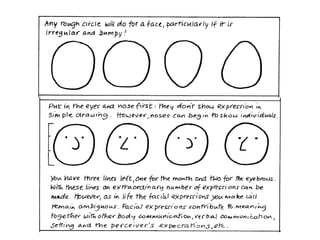
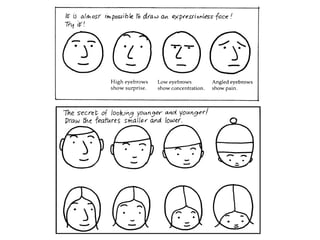
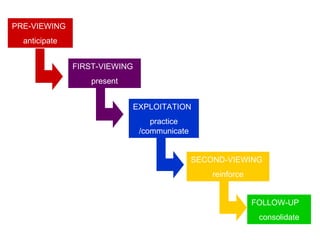
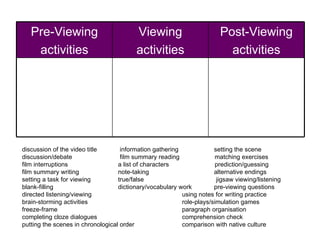
The document discusses various teaching resources and materials that can be used in the classroom, including coursebooks, the board, visual aids, technology, and alternatives when resources are limited. It provides advice on using different resources effectively, such as maintaining eye contact when writing on the board and including pre, during, and post viewing activities for videos. The document also considers the benefits and drawbacks of relying heavily on coursebooks for teaching.