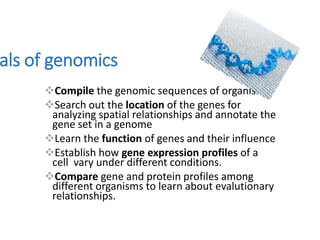
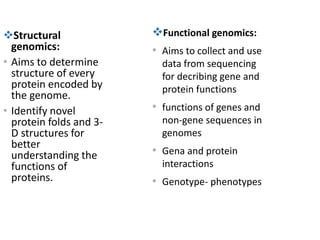
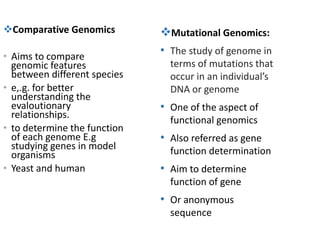
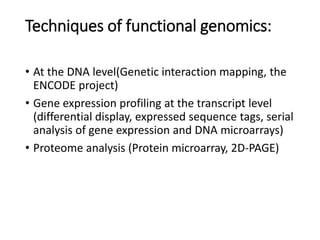
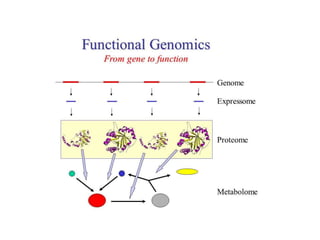
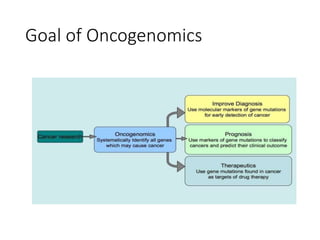
The document discusses several types of genomics: structural genomics aims to determine the 3D structure of every protein encoded in a genome. Functional genomics determines the biological functions of genes and their products. Mutational genomics characterizes mutation-associated genes and links genotypes to transcriptional states. Comparative genomics compares genomic features between species to study evolution and identify conserved and unique genes.