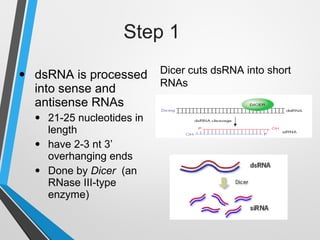
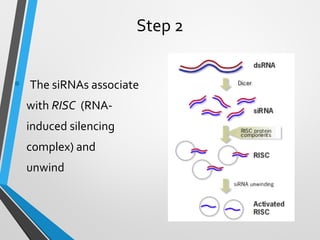
RNA interference (RNAi) is a mechanism for gene silencing by degrading unwanted mRNAs in the cytoplasm, initially discovered in plants and later in C. elegans. The process involves small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) that guide the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to degrade target mRNAs, offering a powerful method to inhibit gene expression. RNAi is valuable for research and has potential applications in crop improvement and functional gene analysis.