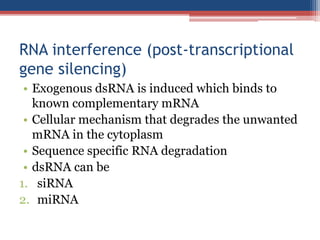
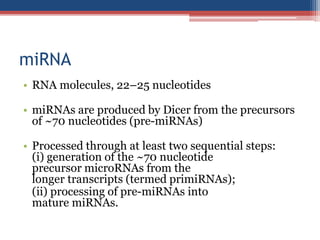
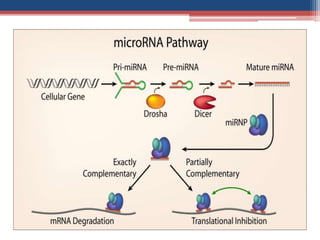
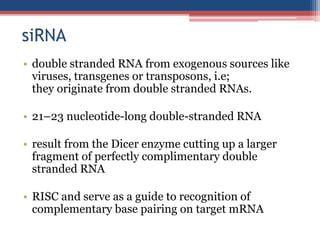
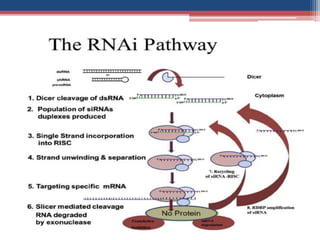
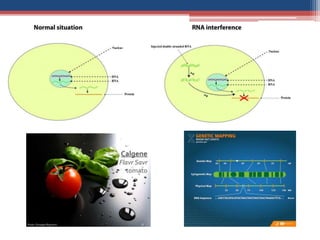
Gene silencing is an epigenetic process that reduces or eliminates the production of a protein from its corresponding gene. There are two main types: transcriptional gene silencing via histone modifications, and post-transcriptional gene silencing by destroying or blocking mRNA. Methods to induce gene silencing include antisense oligonucleotides, ribozymes, and RNA interference using short interfering RNA or microRNA. RNAi leads to sequence-specific degradation of mRNA through the RNA-induced silencing complex. Gene silencing has applications in studying gene function, functional genomics, and medicine, with the goal of downregulating gene expression.