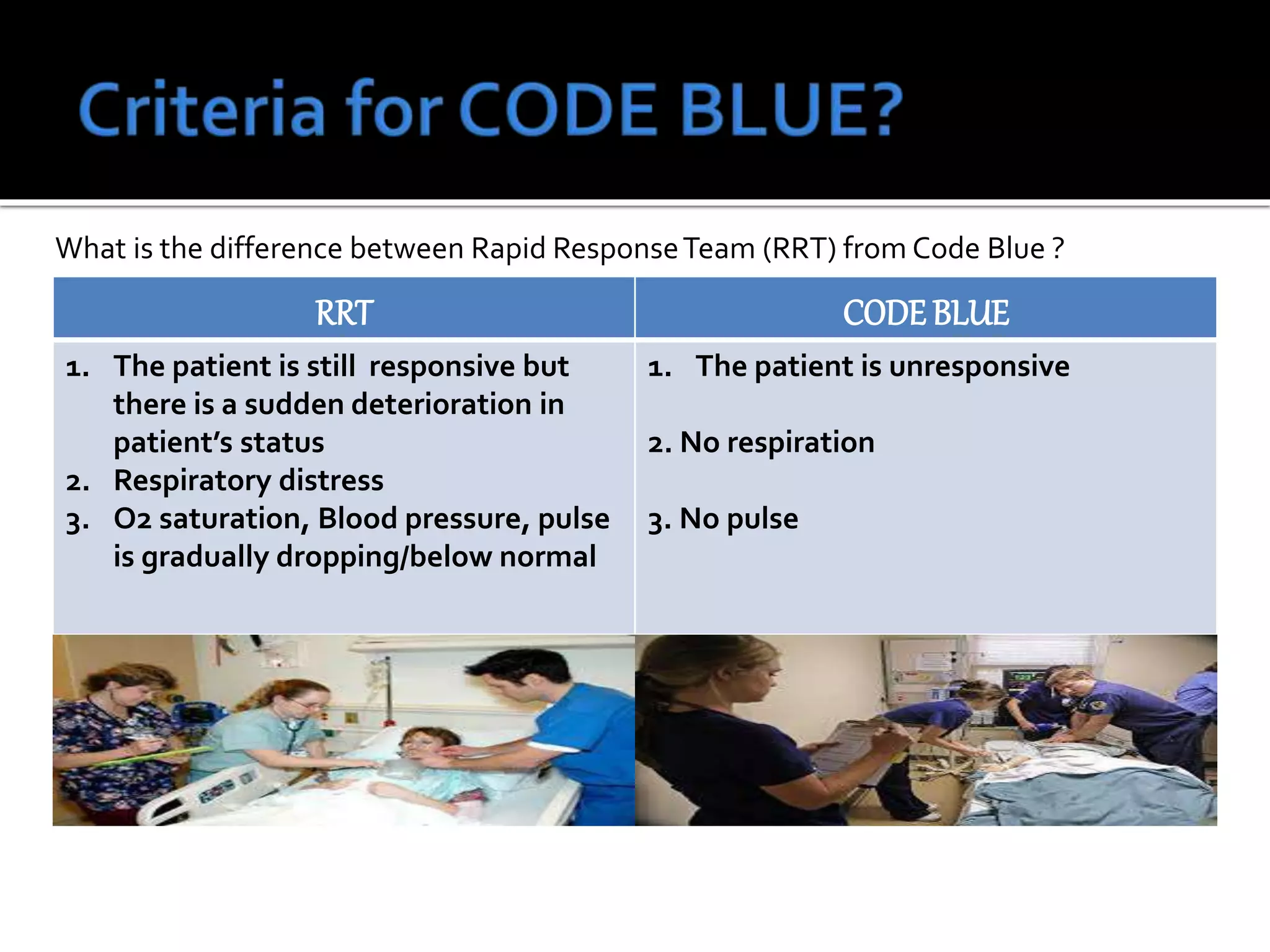
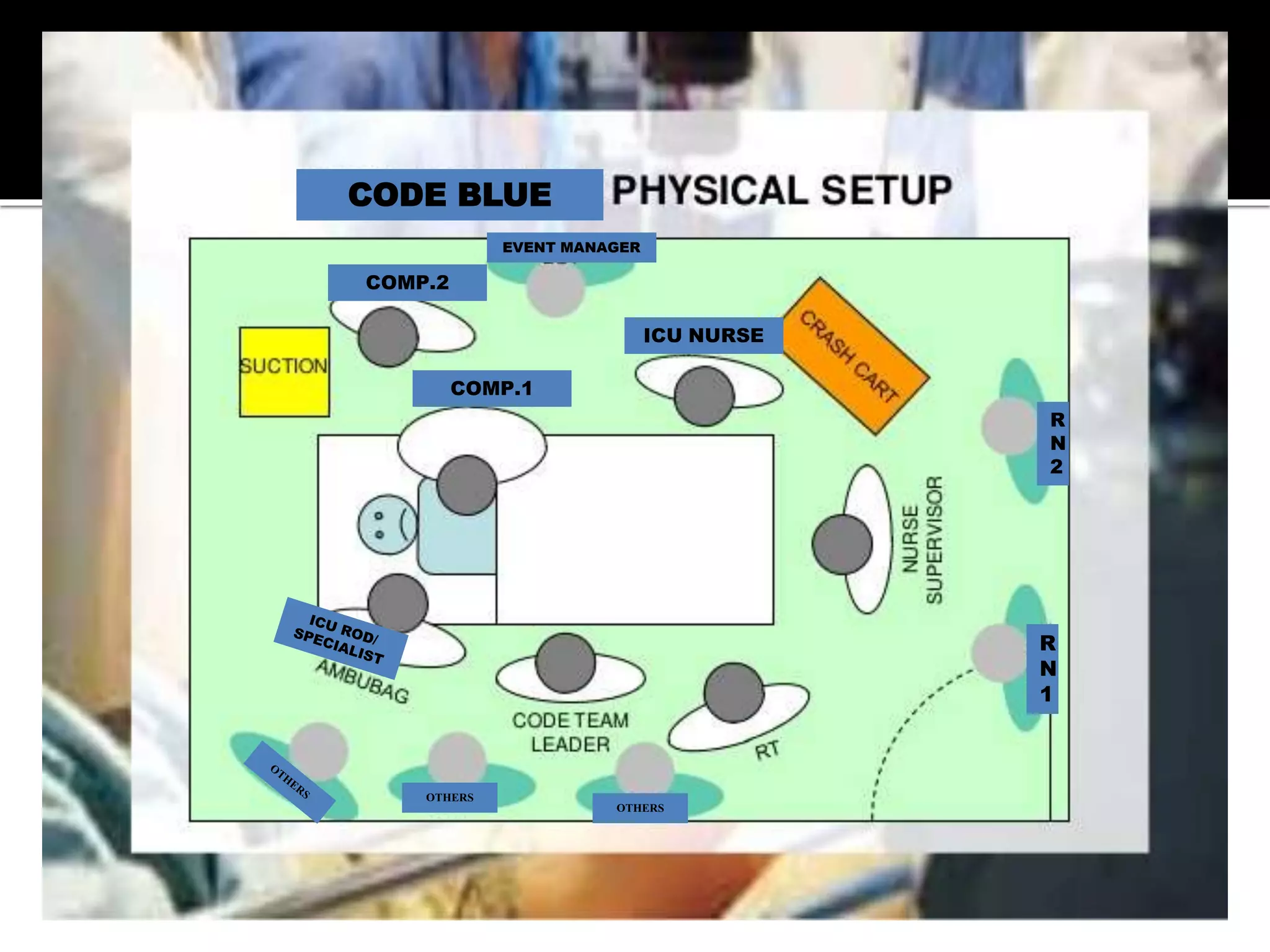
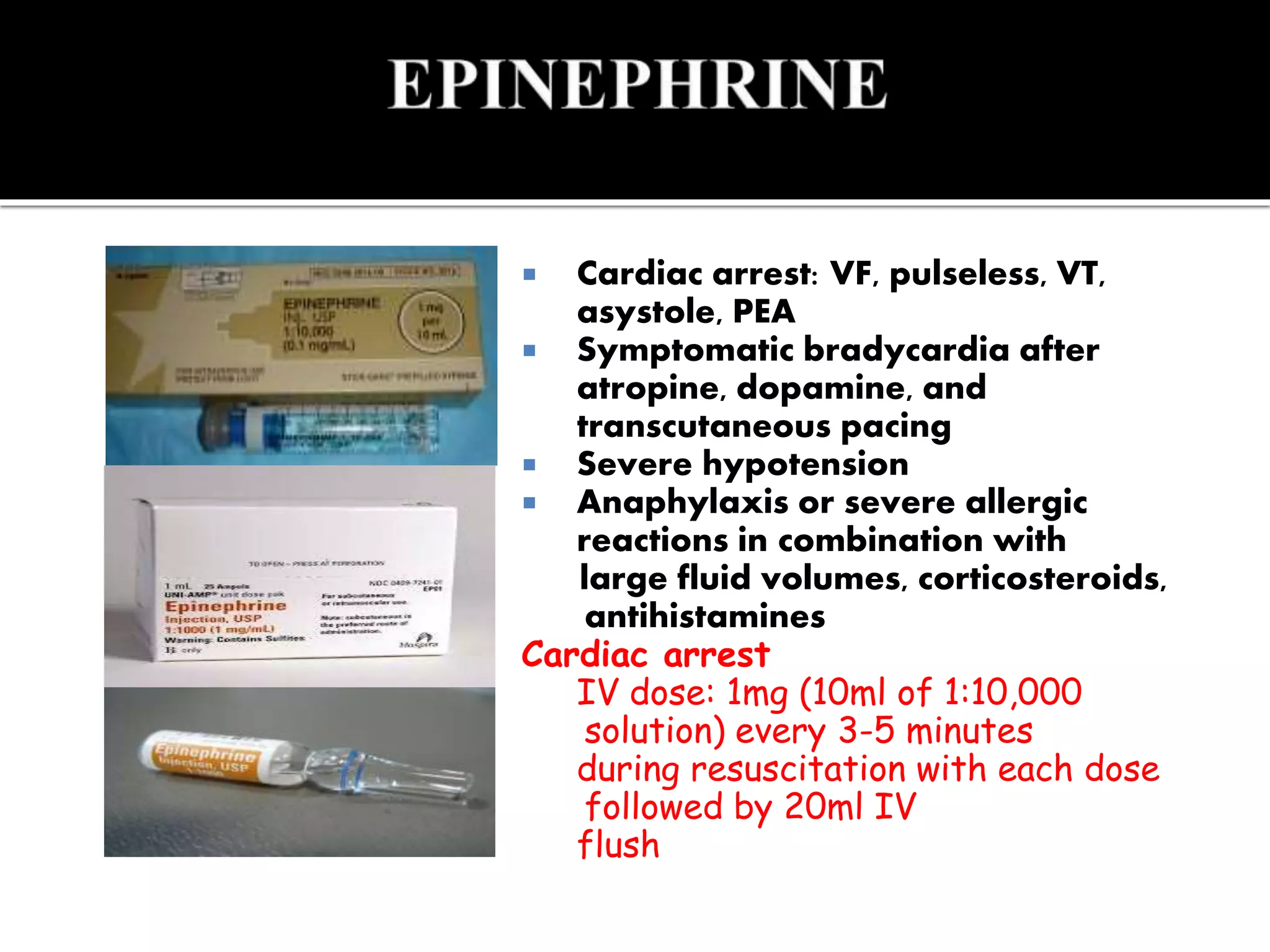
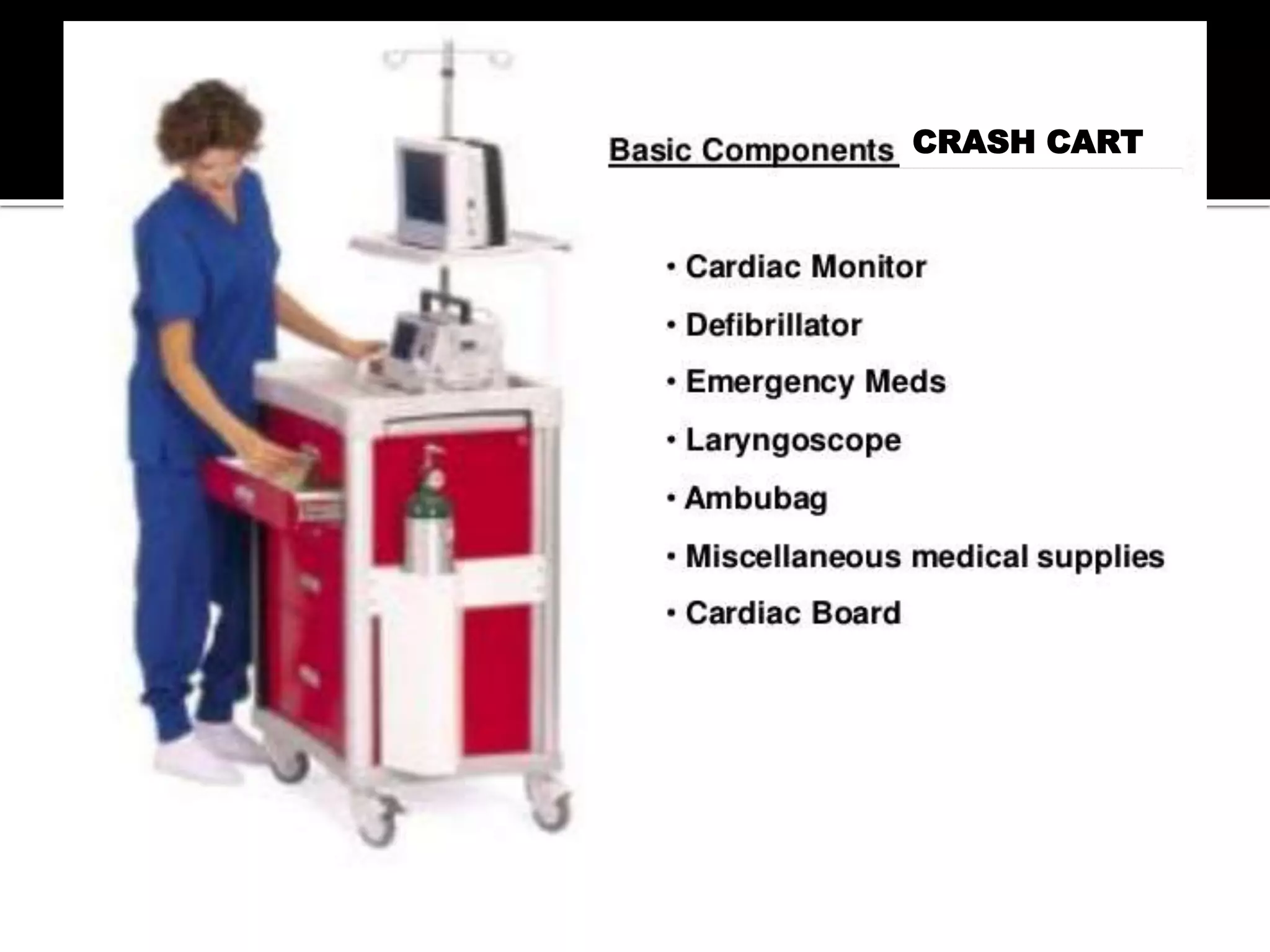
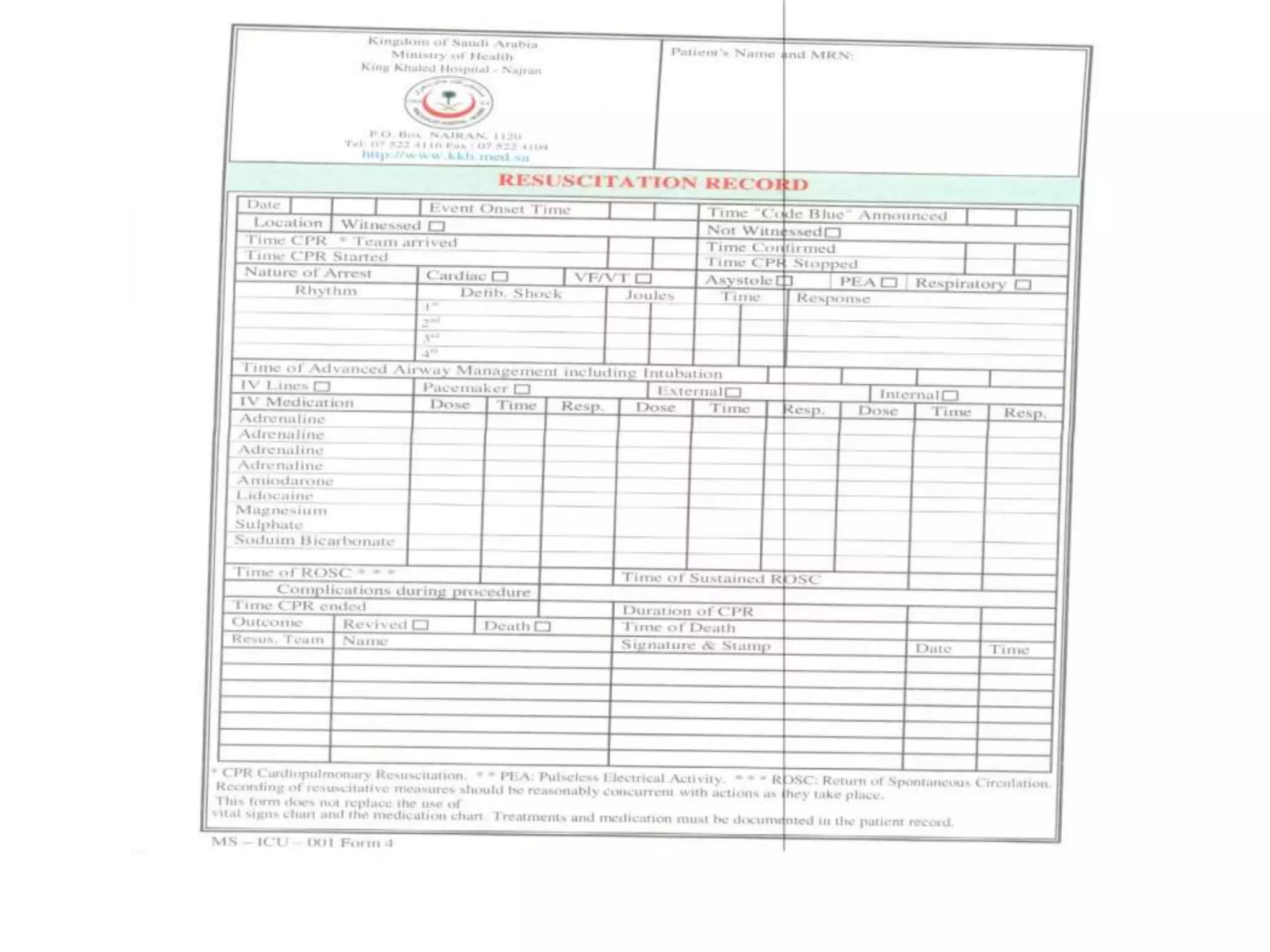
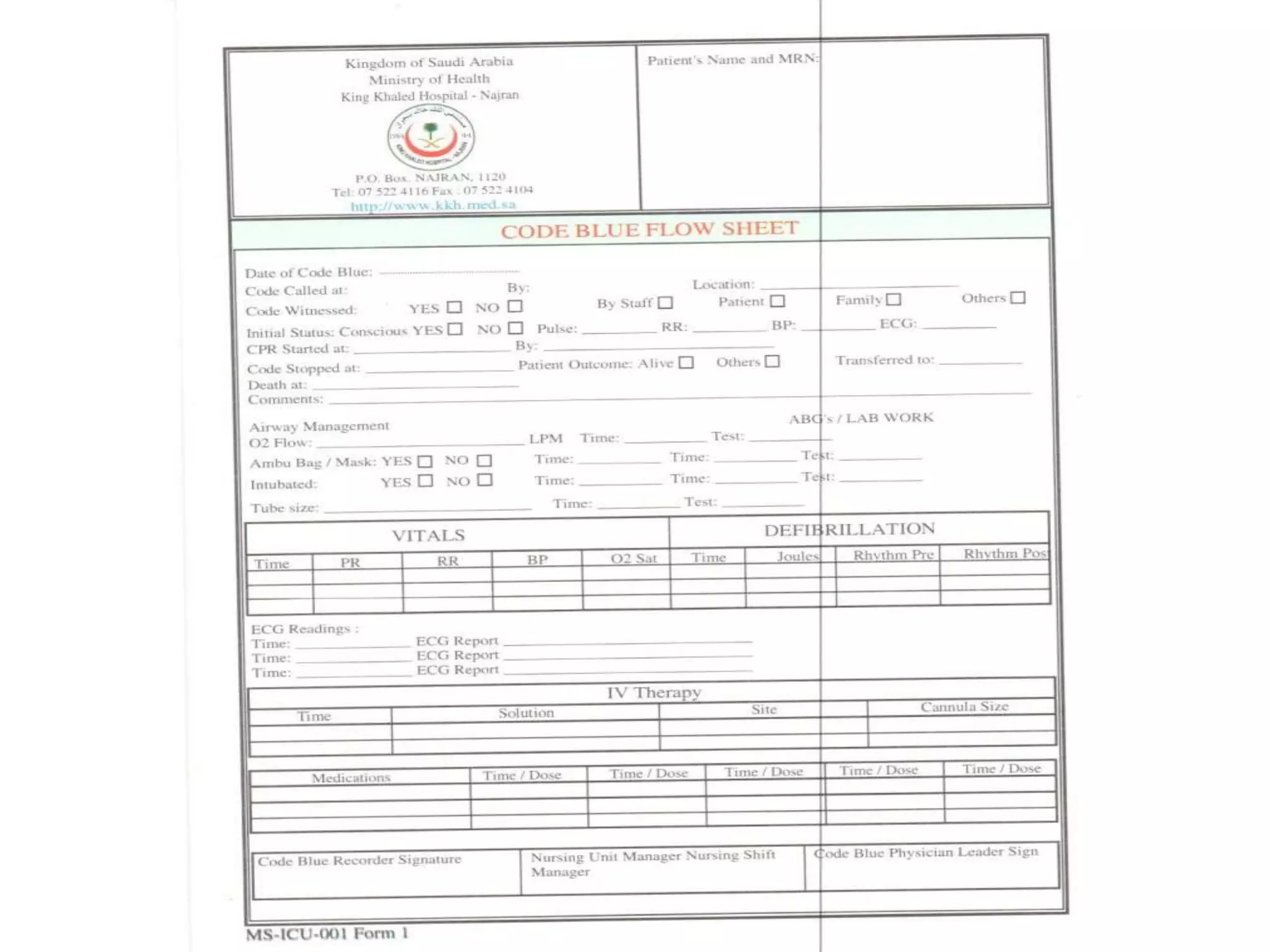
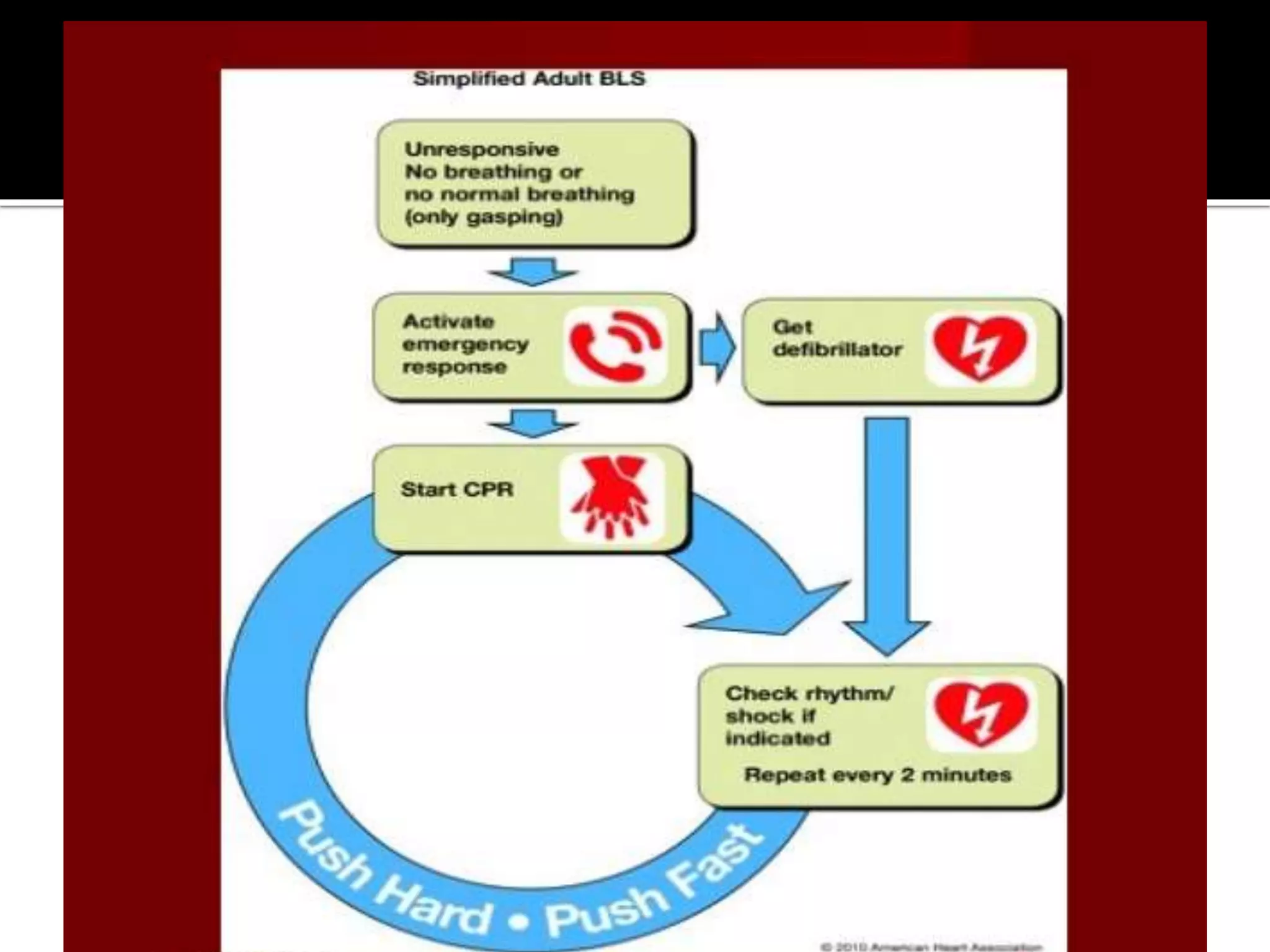
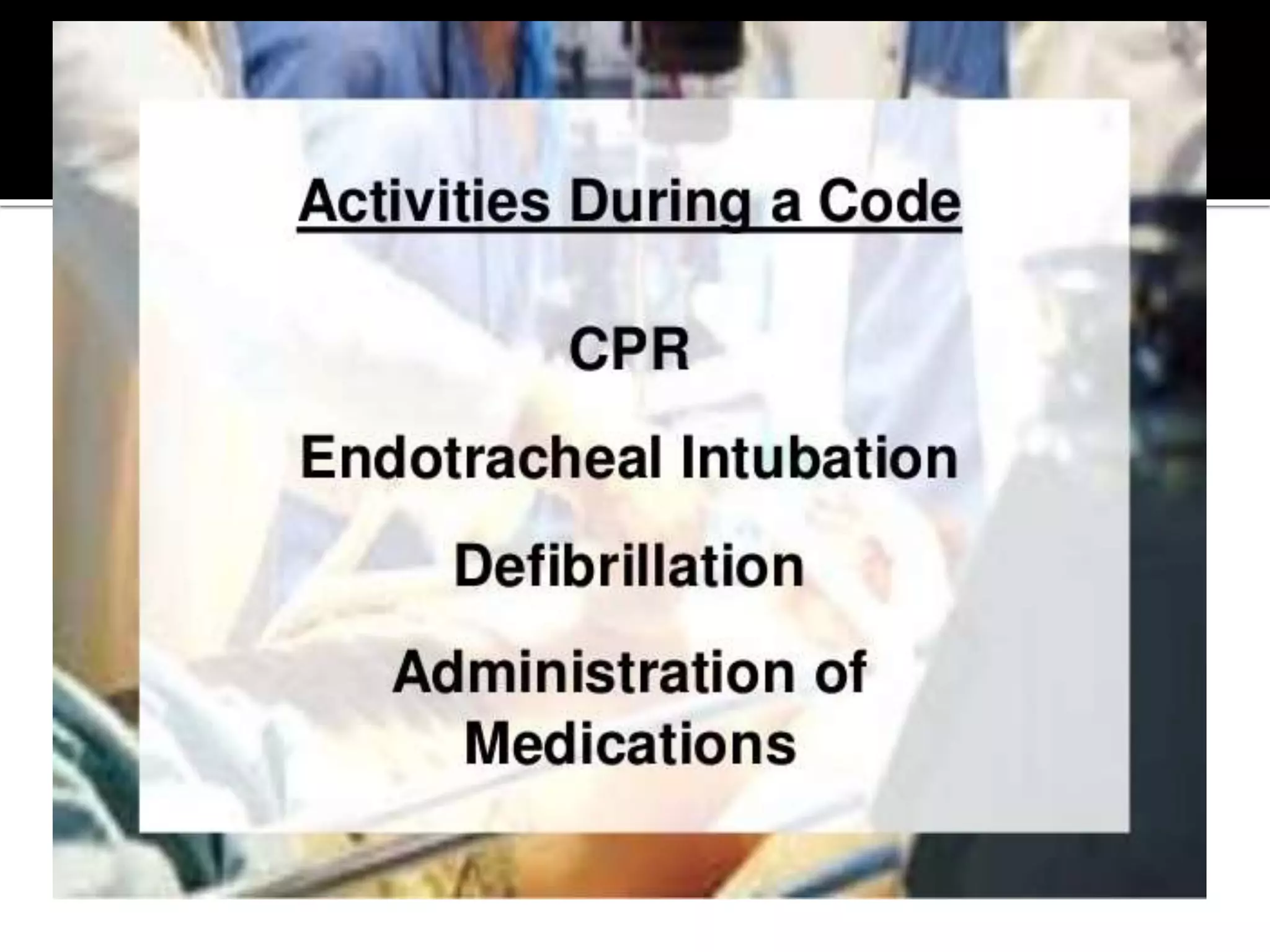
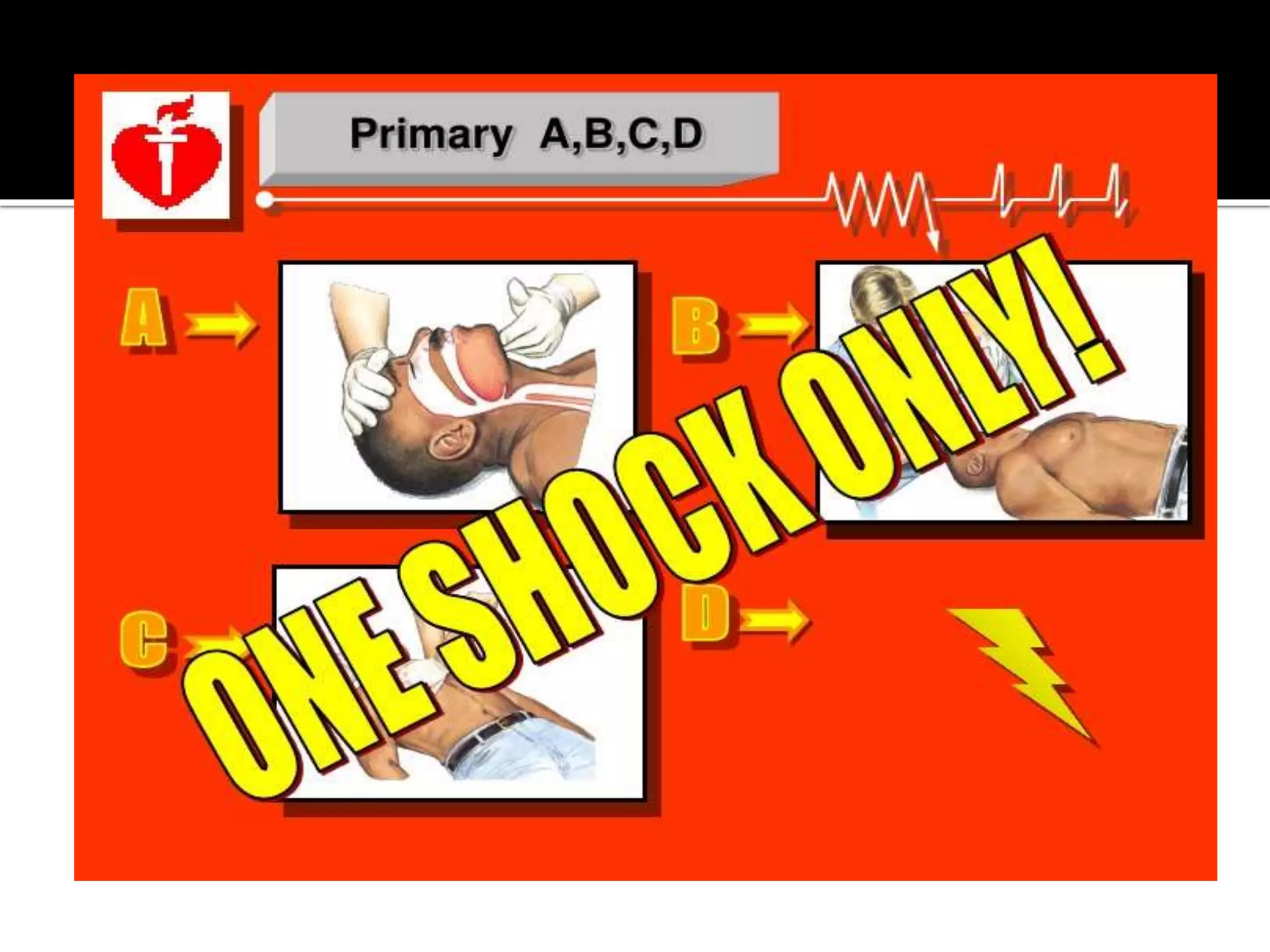
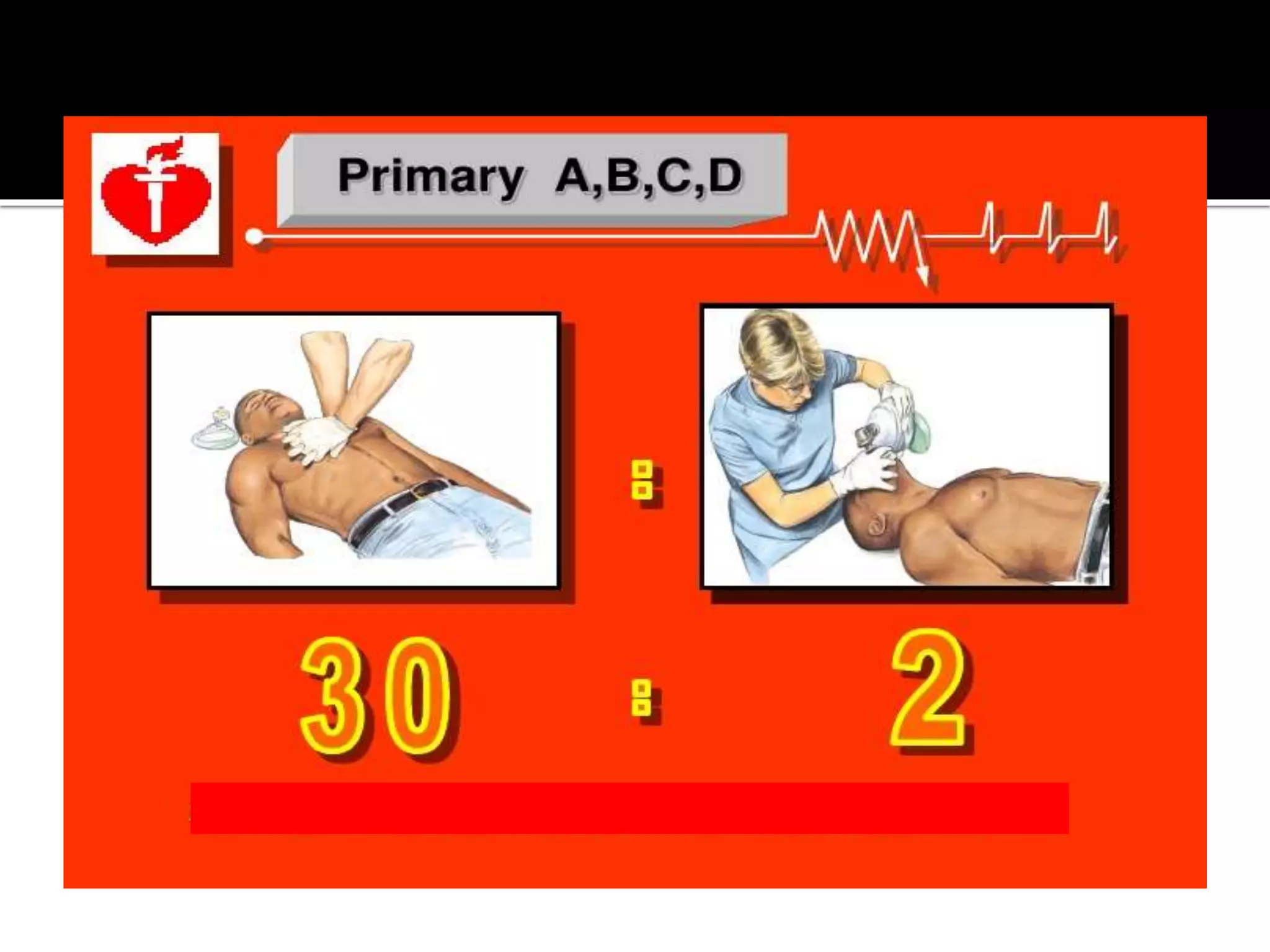
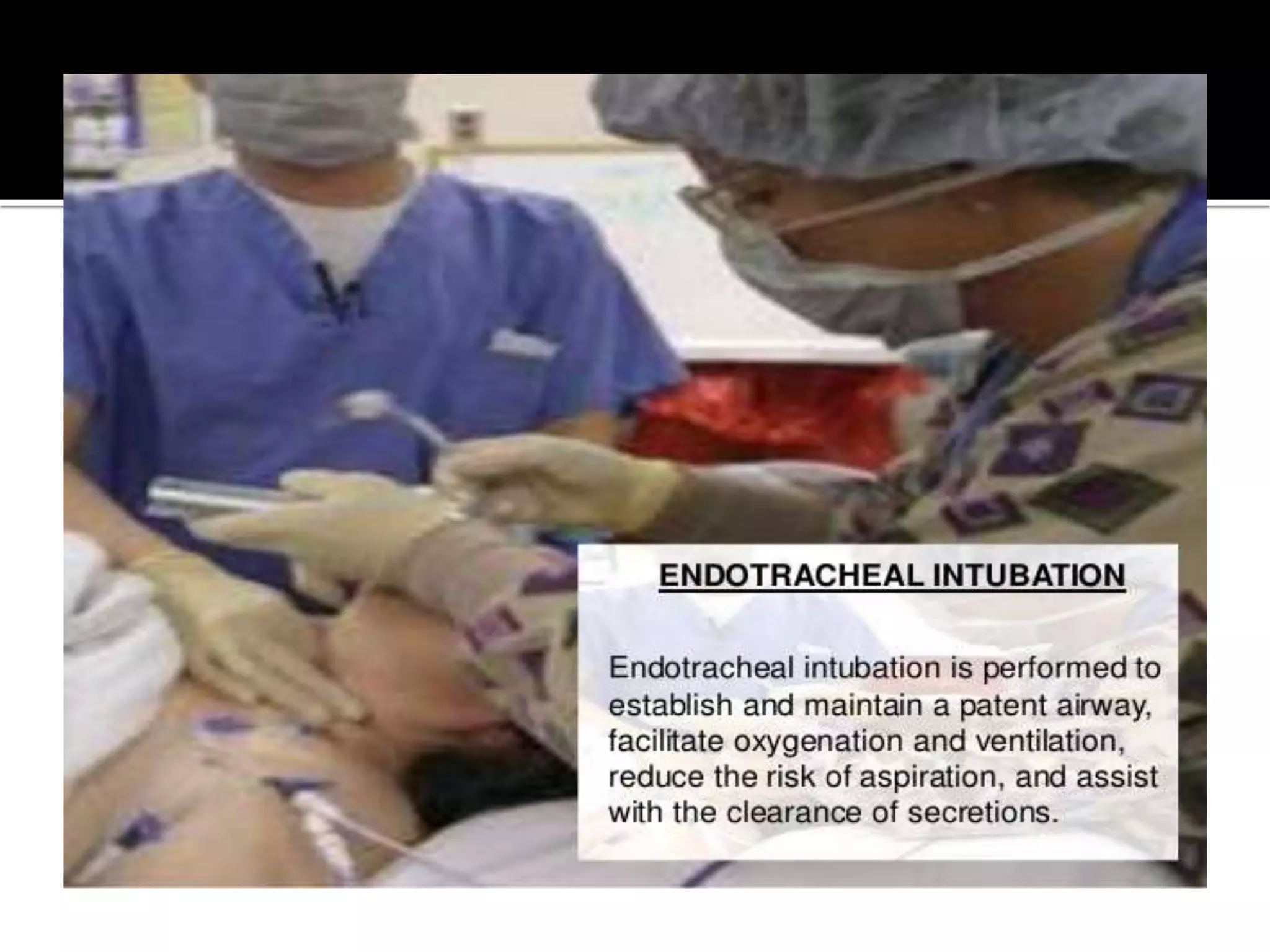
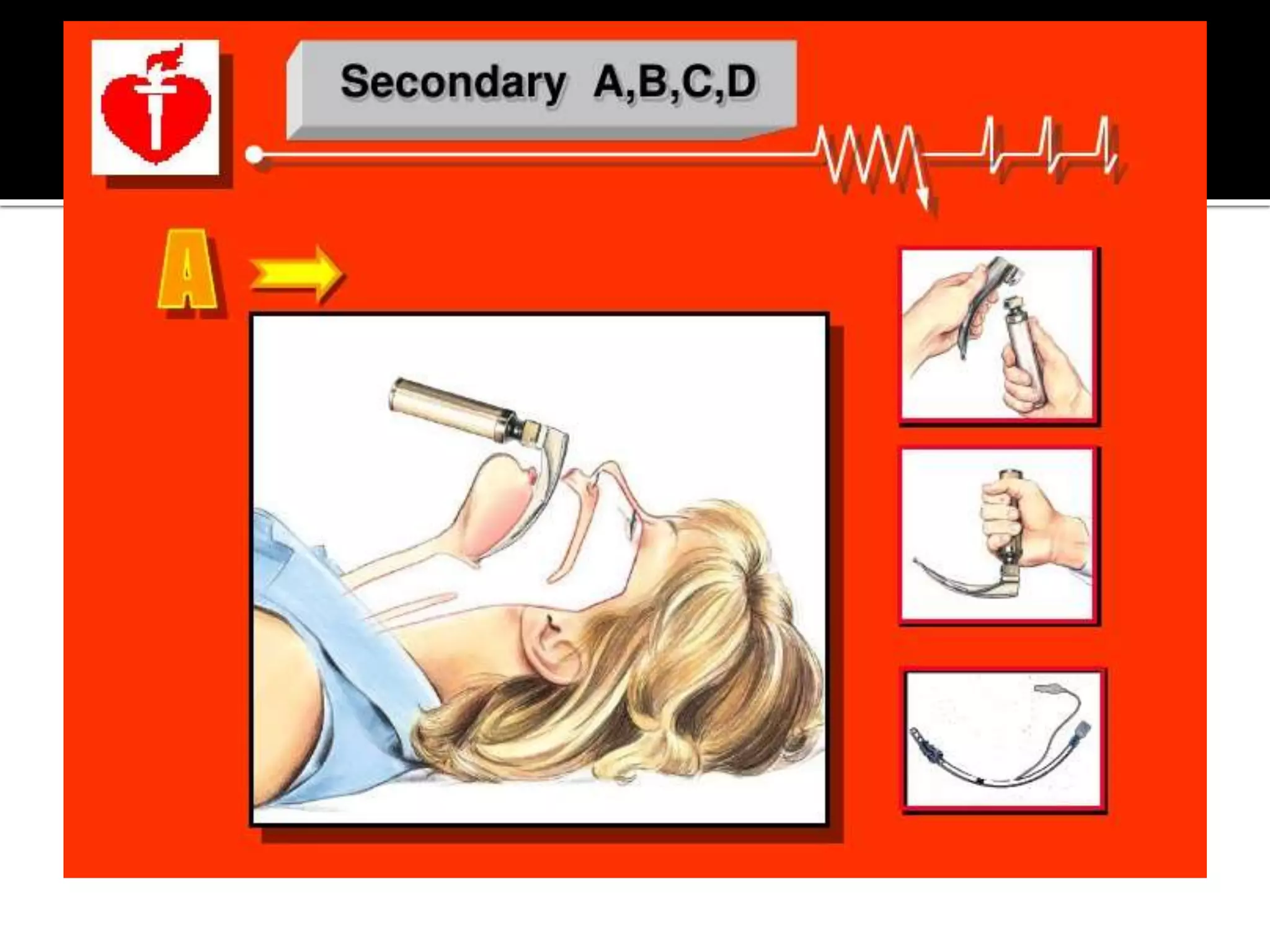
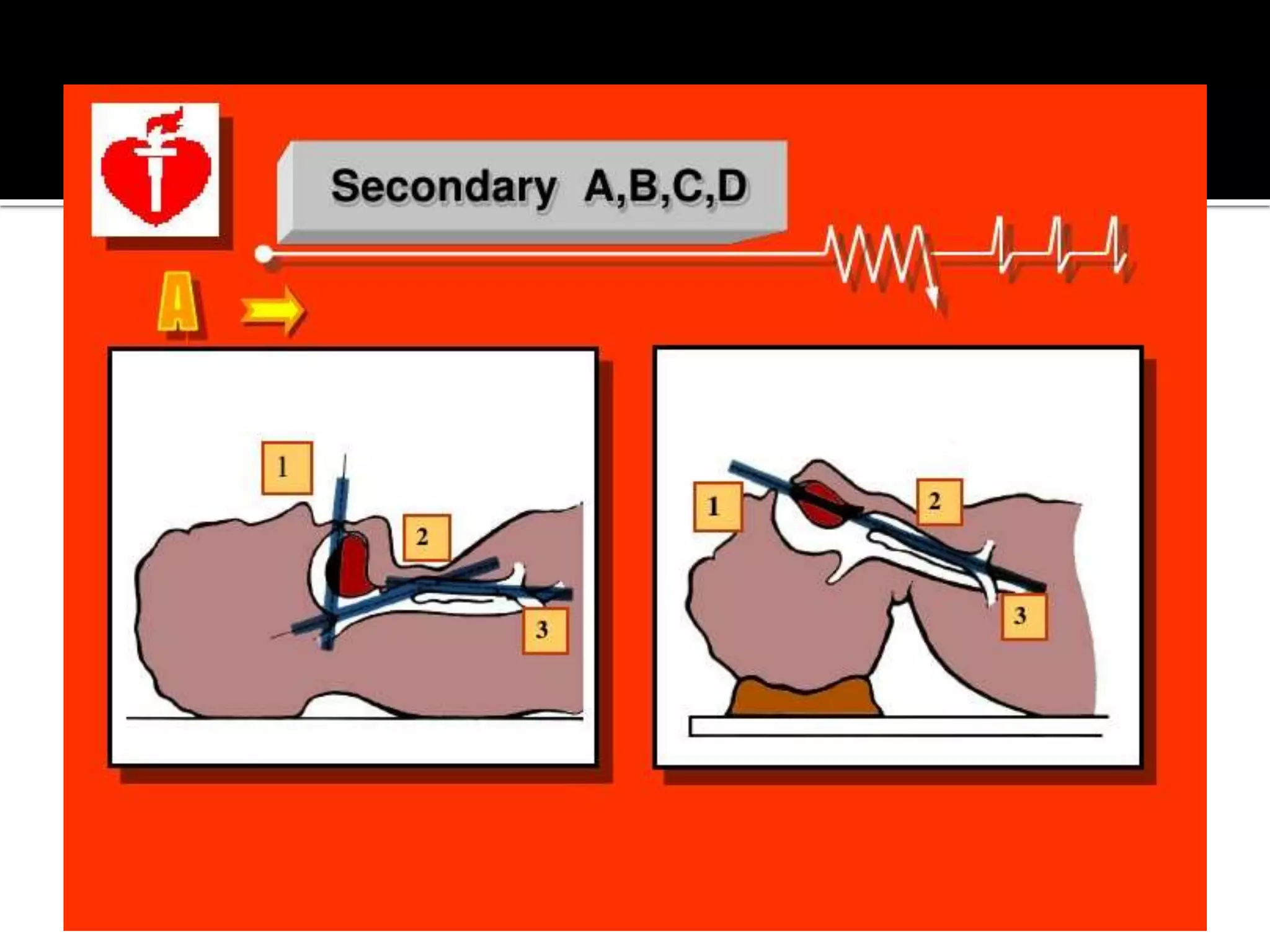
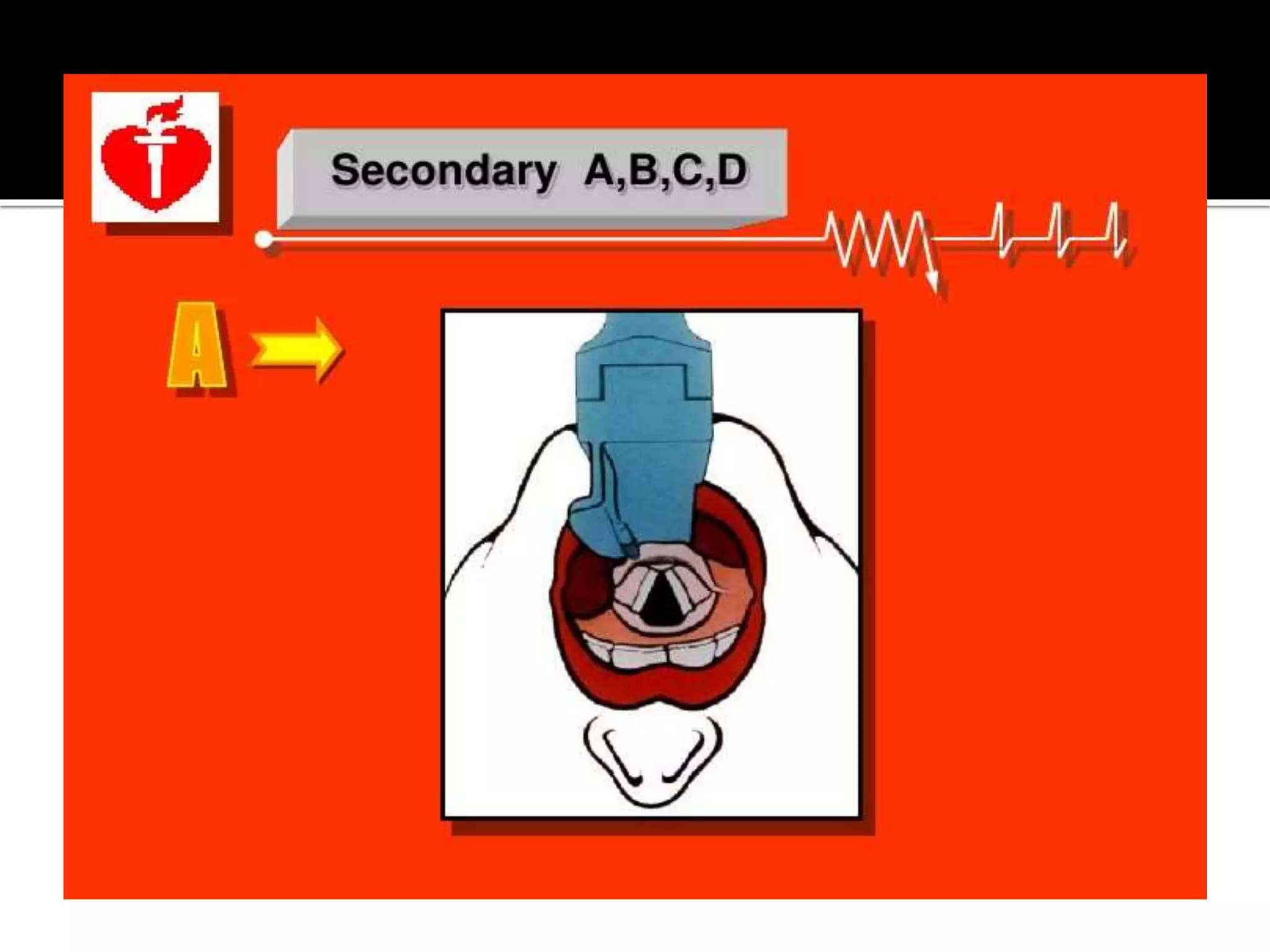
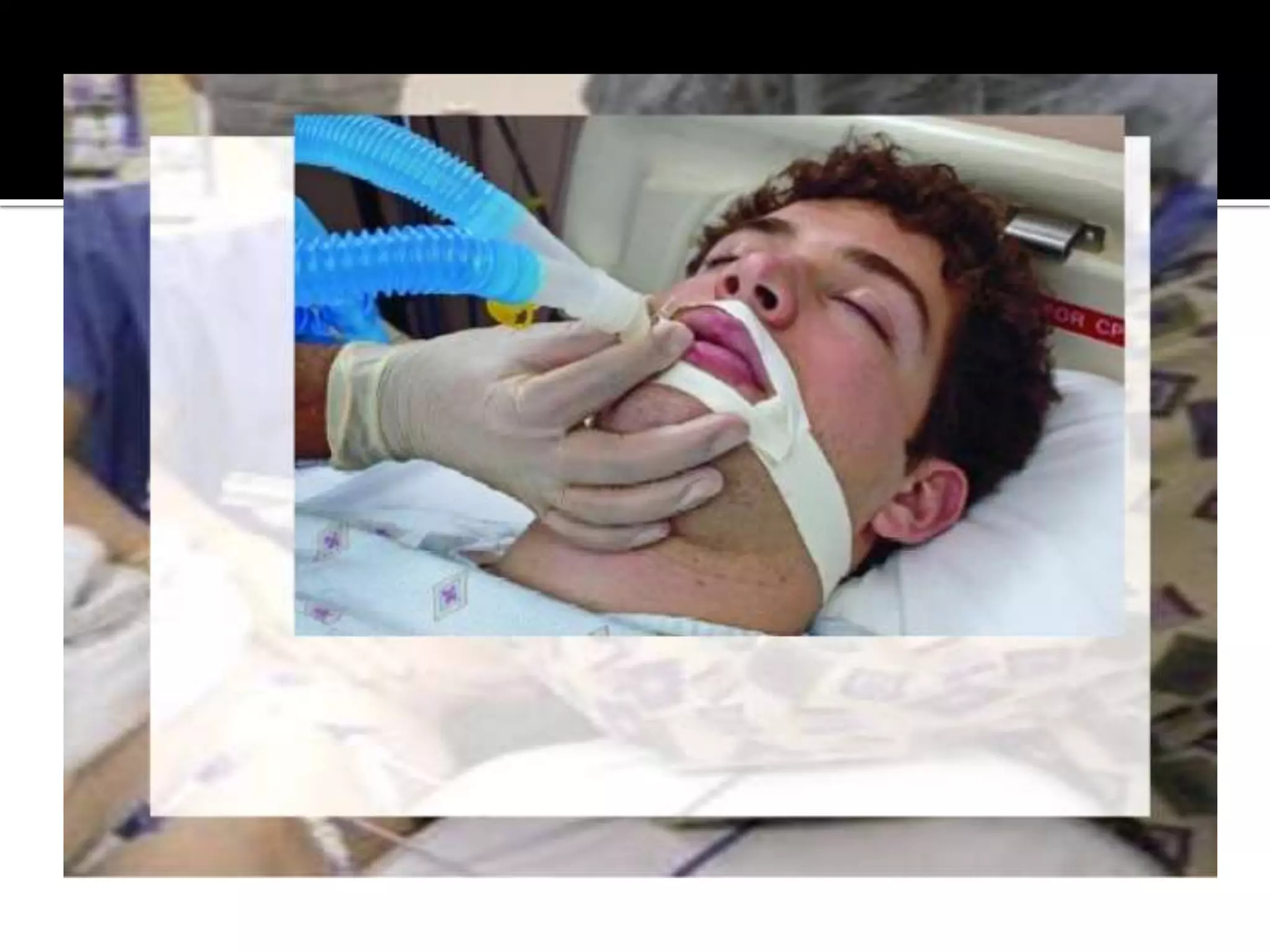
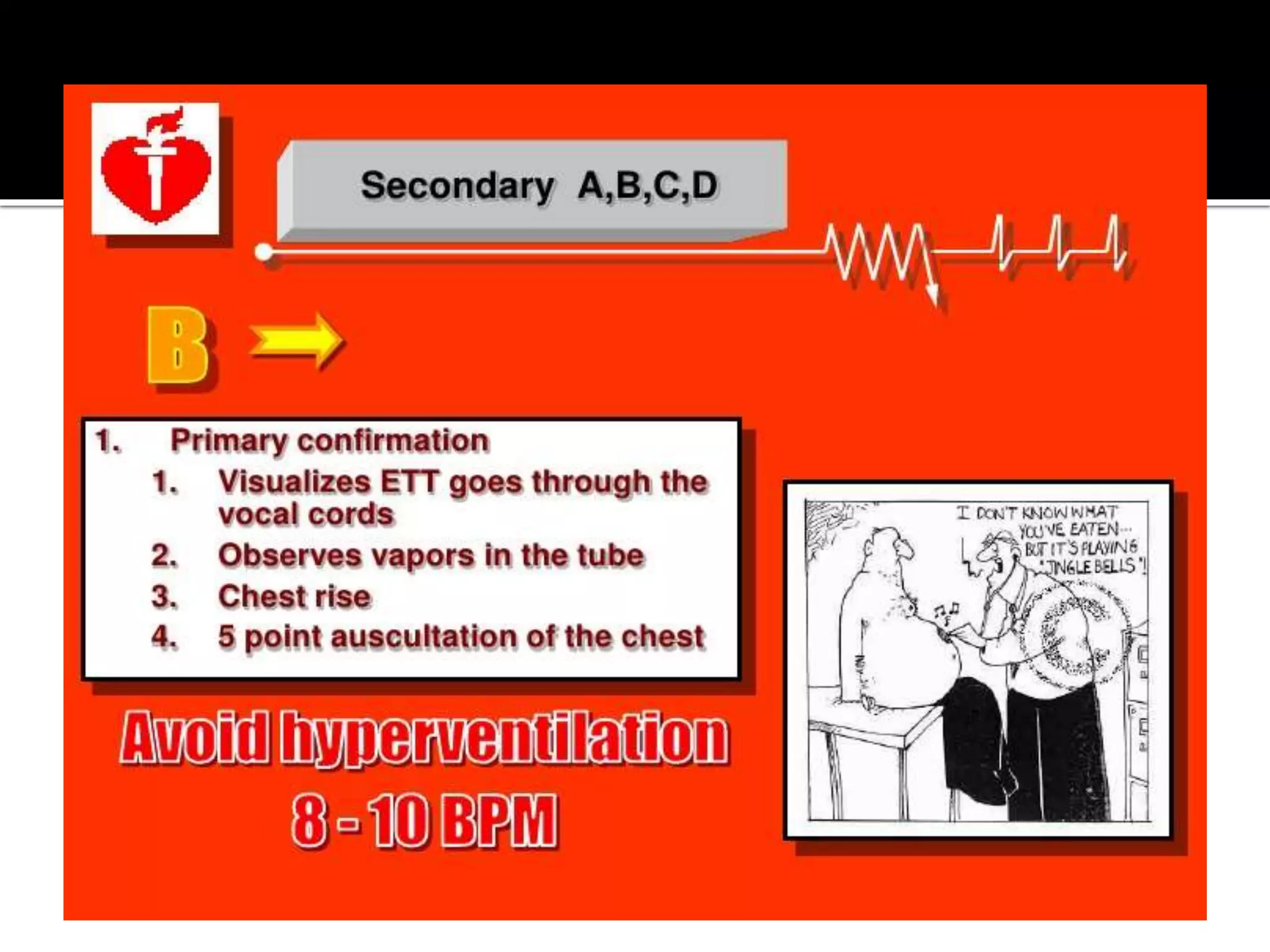
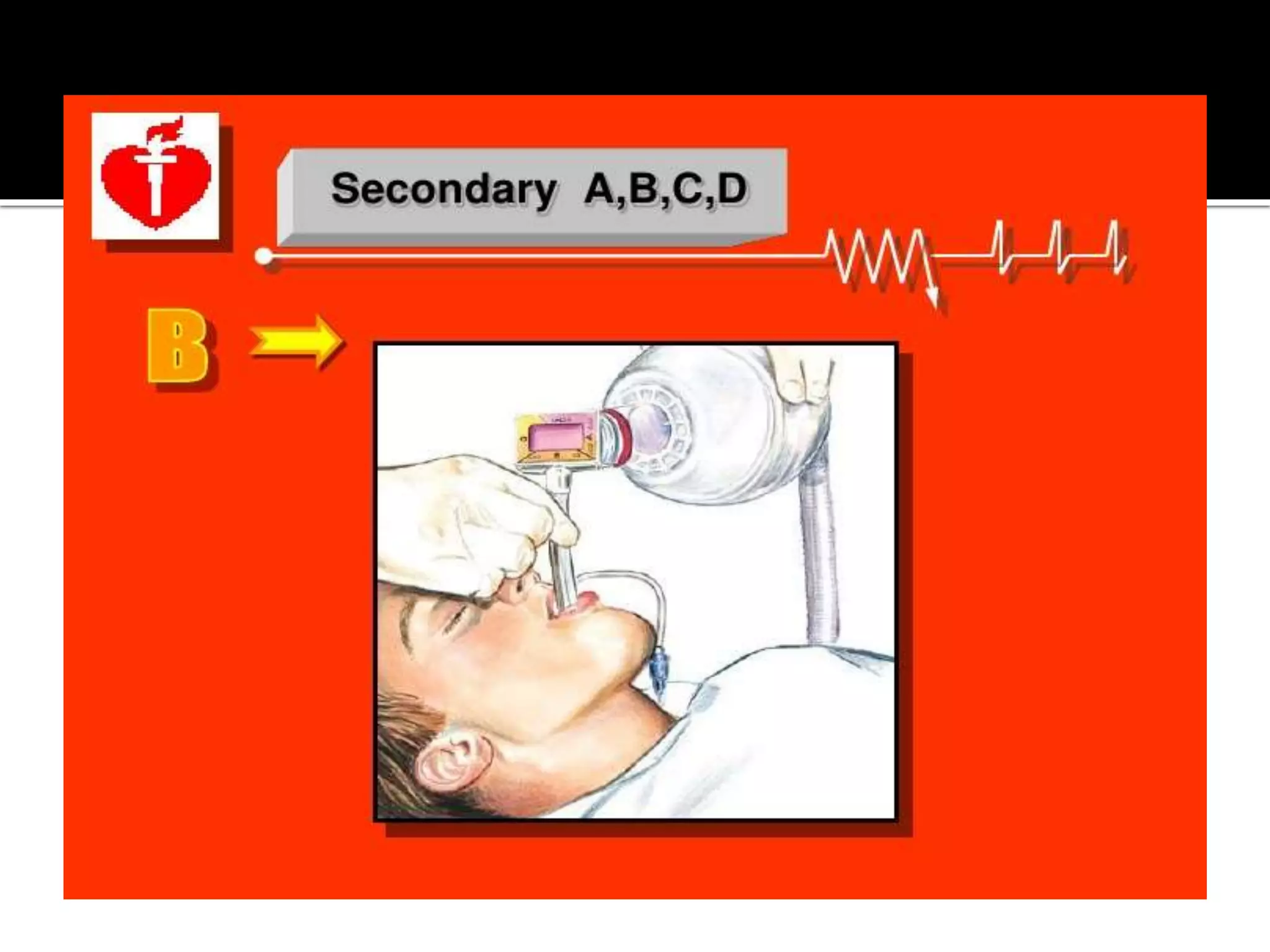
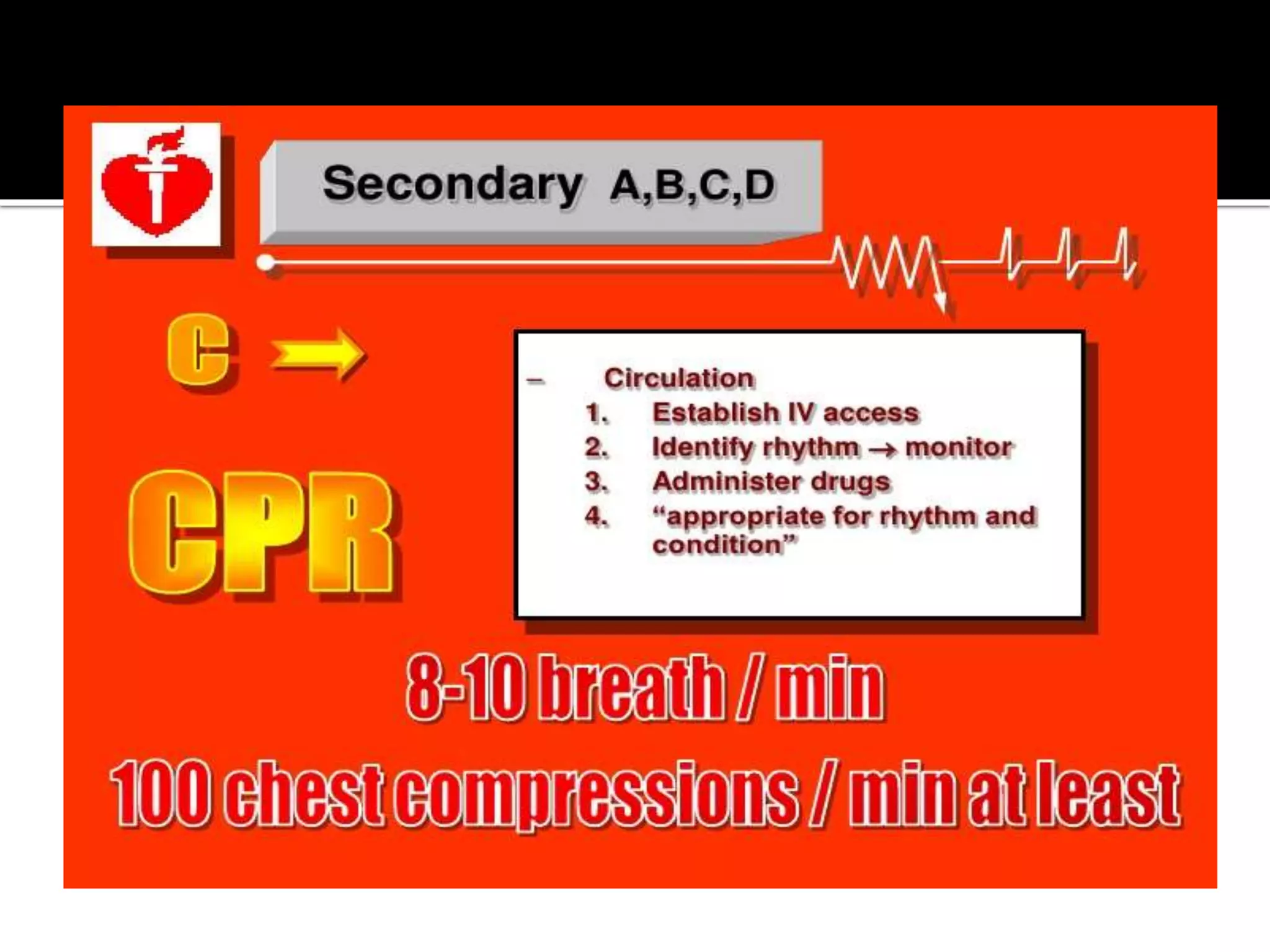
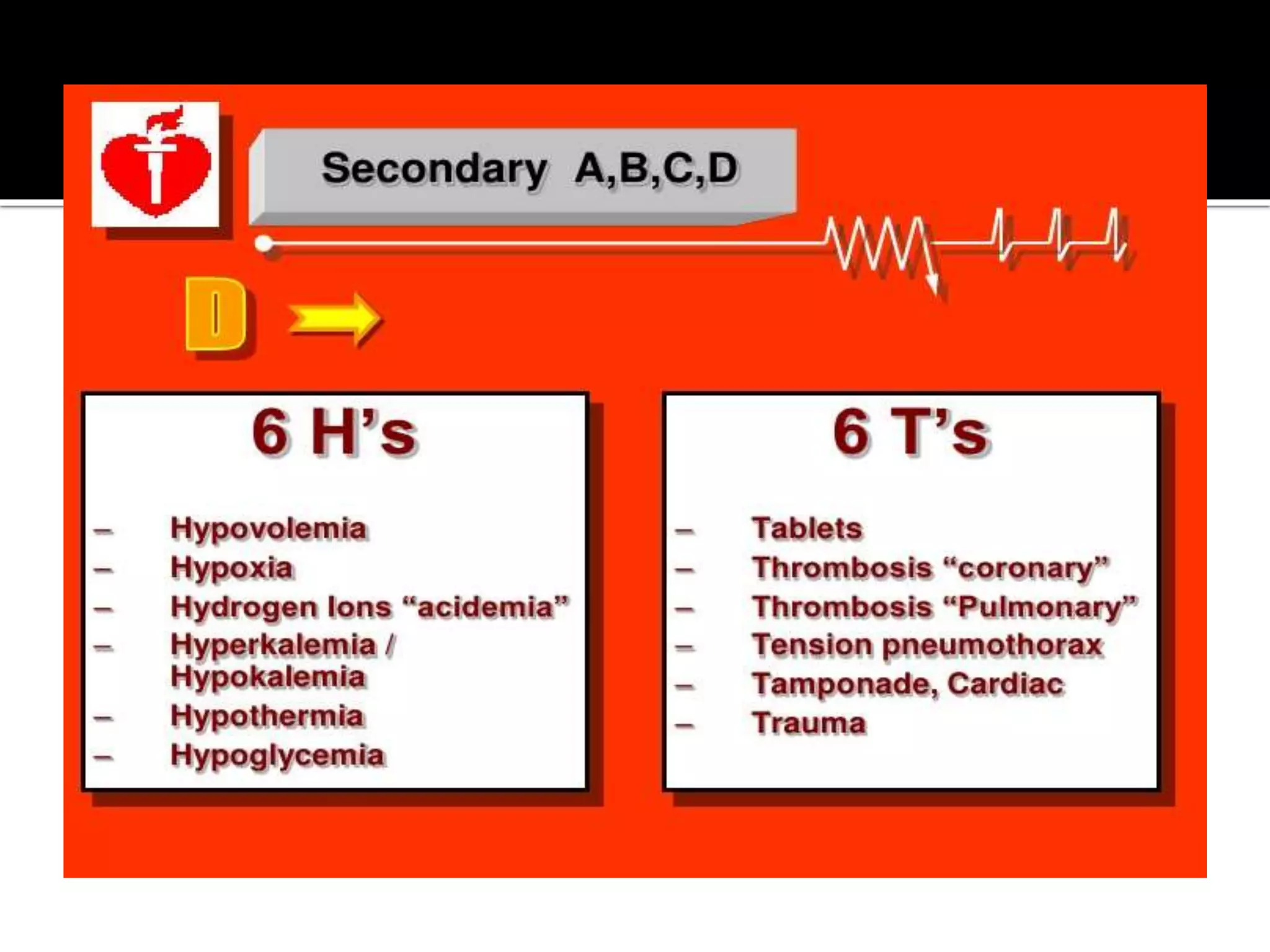
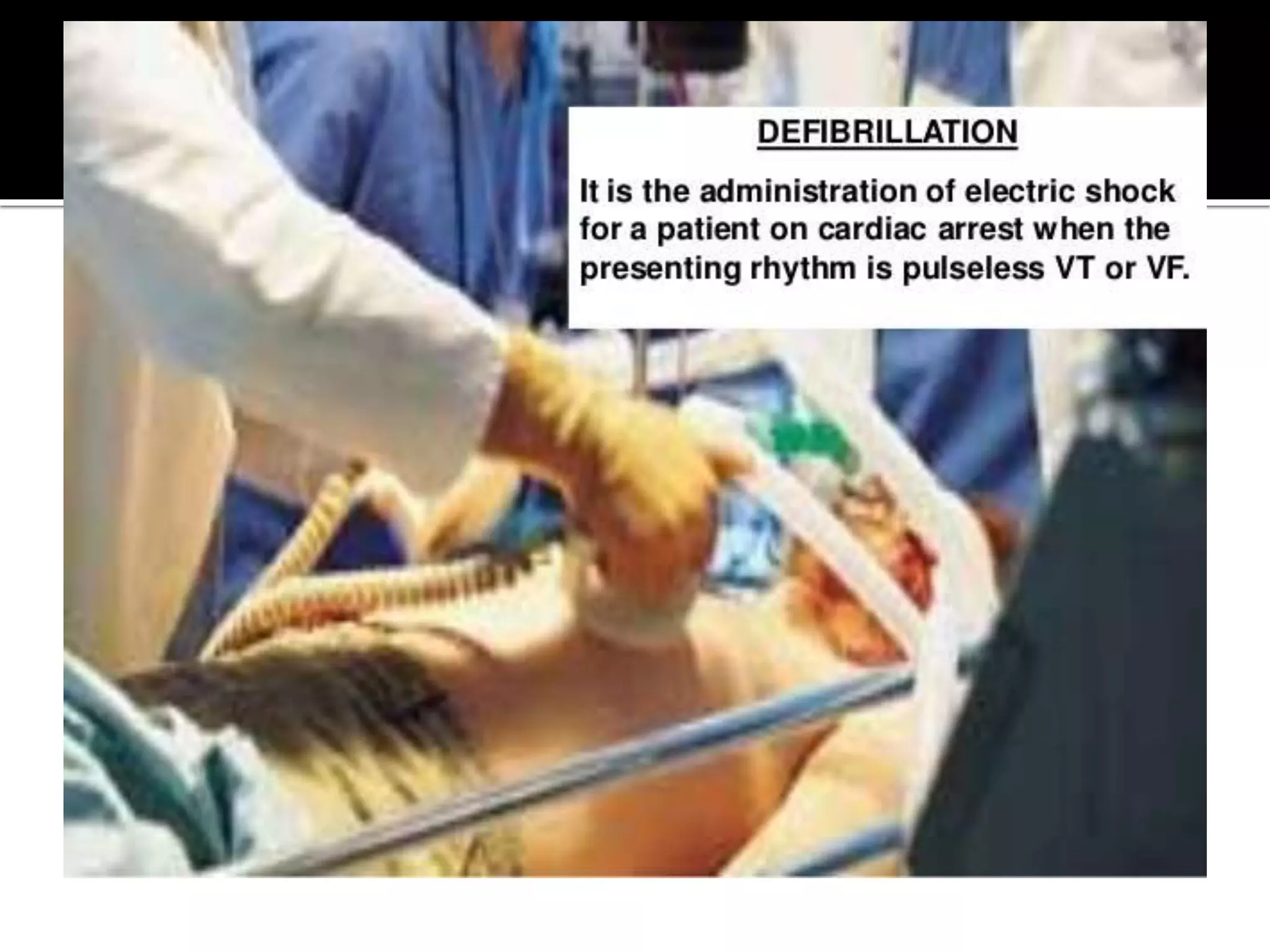
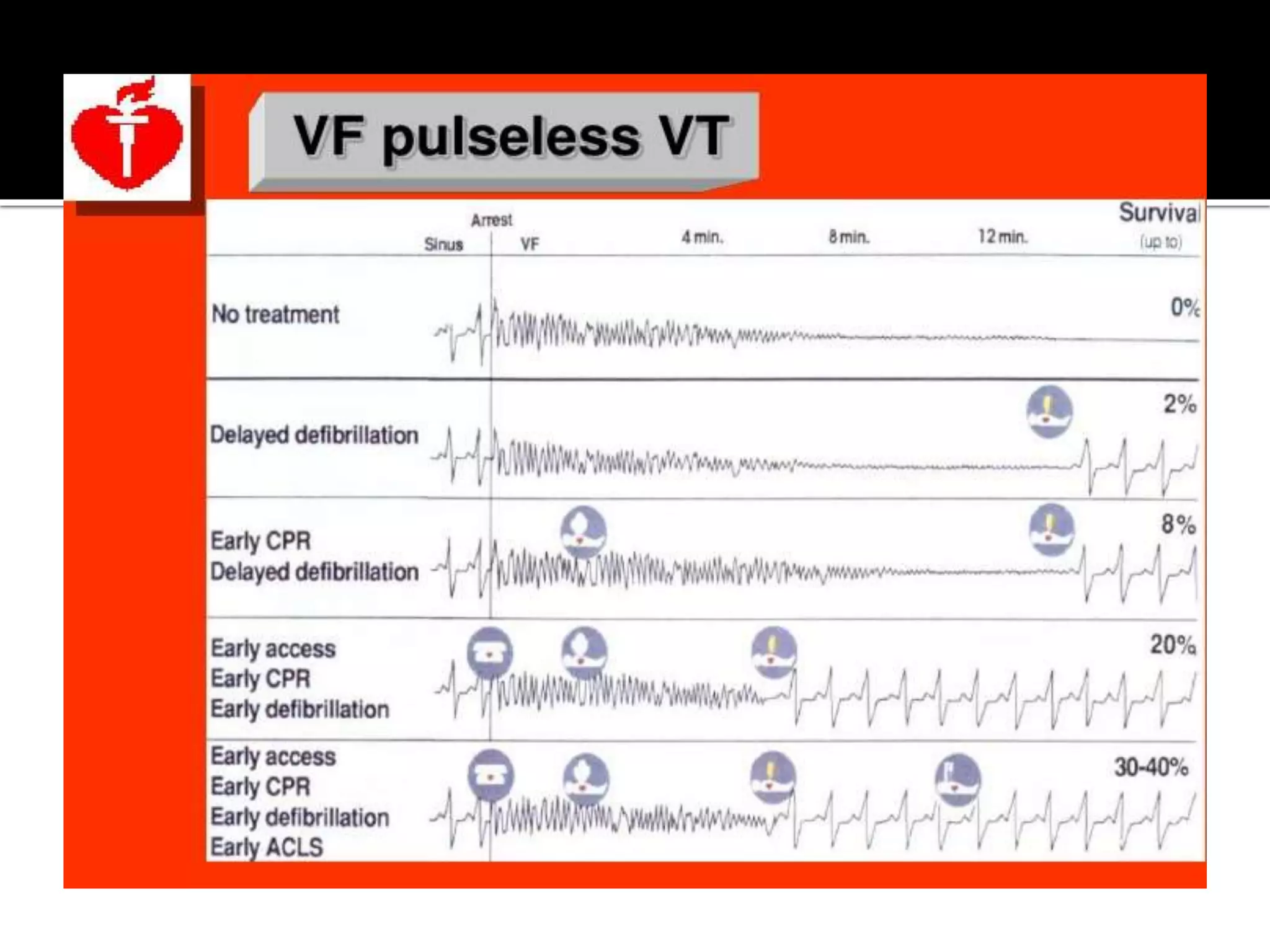
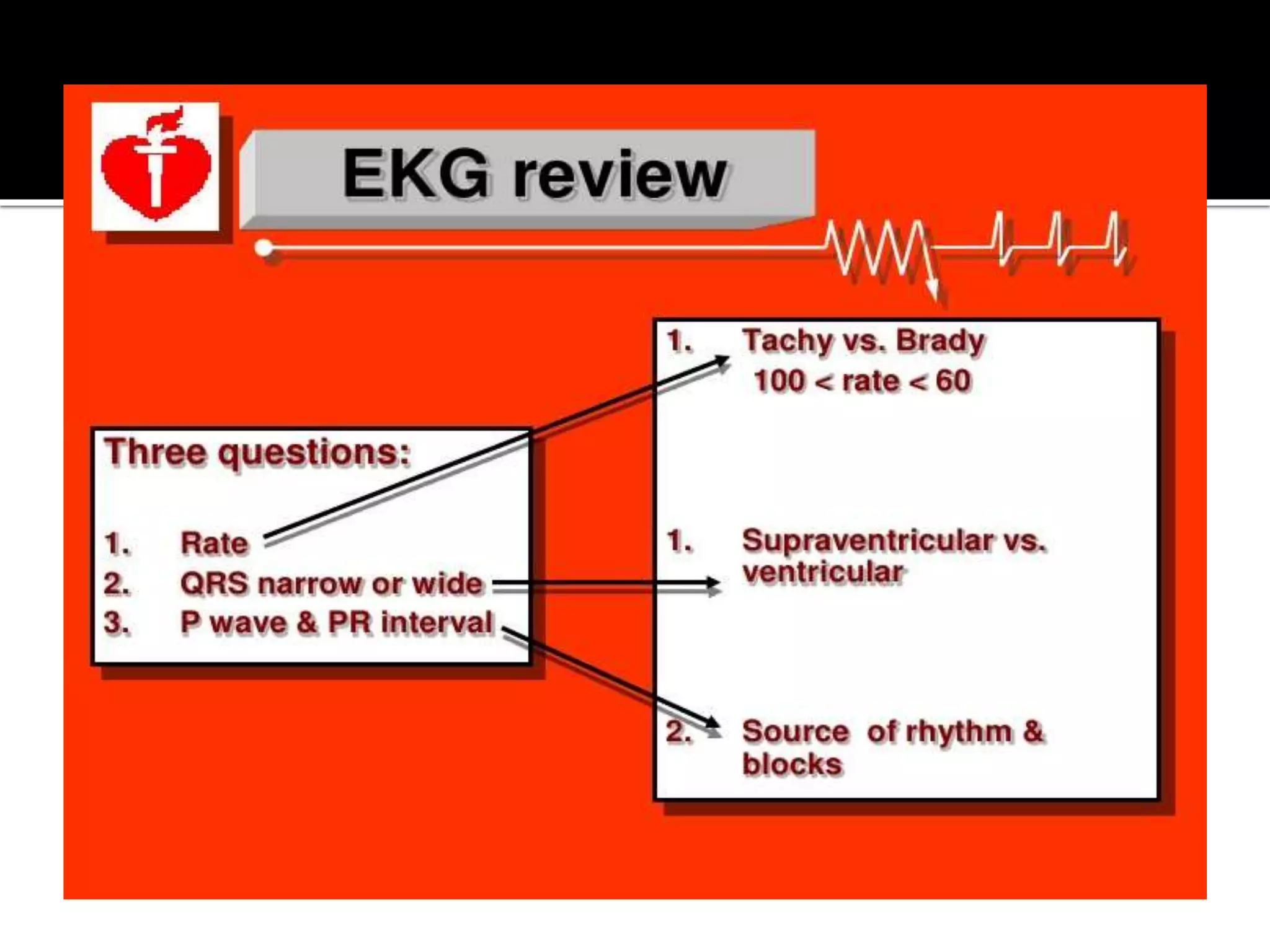
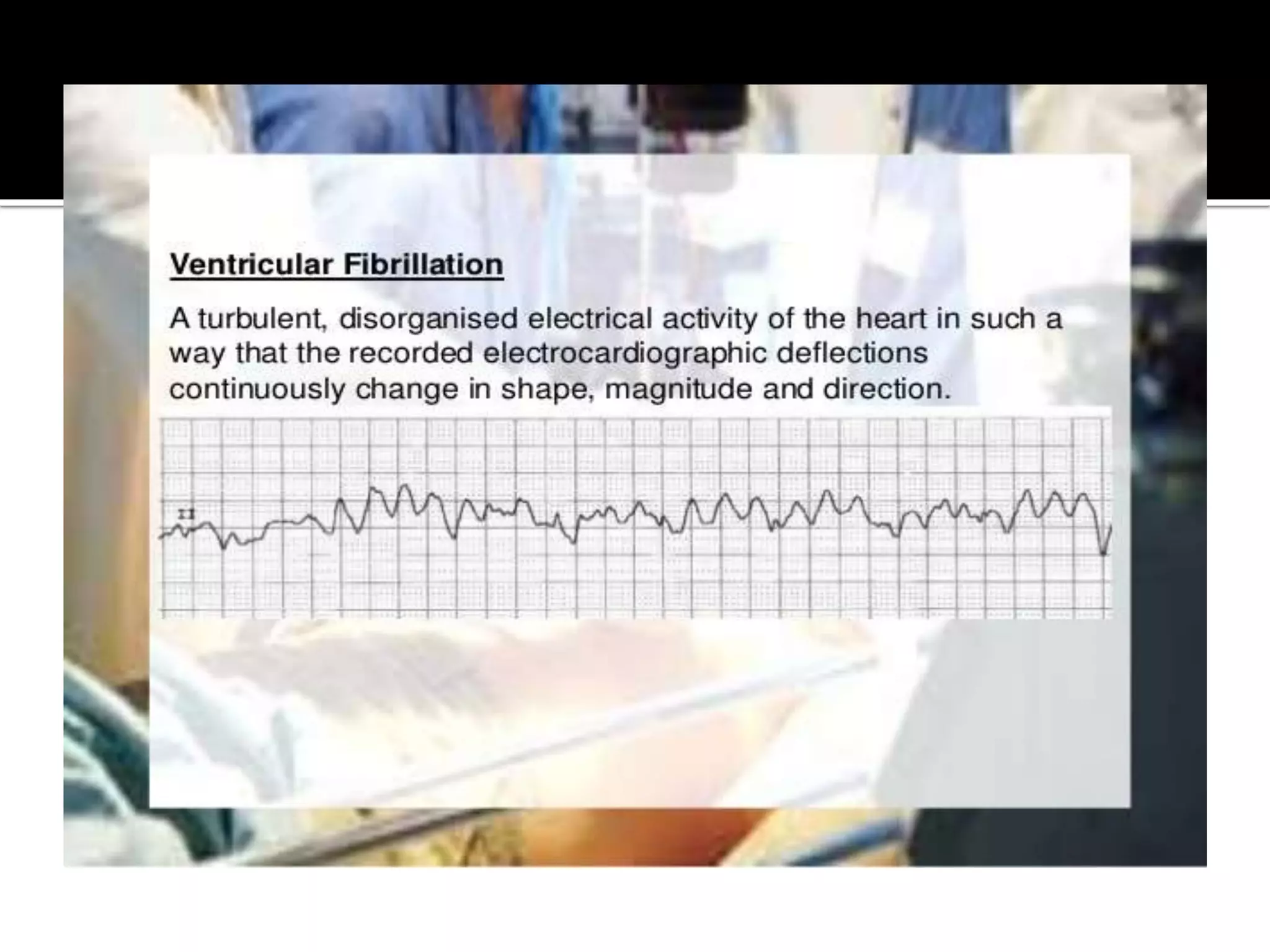
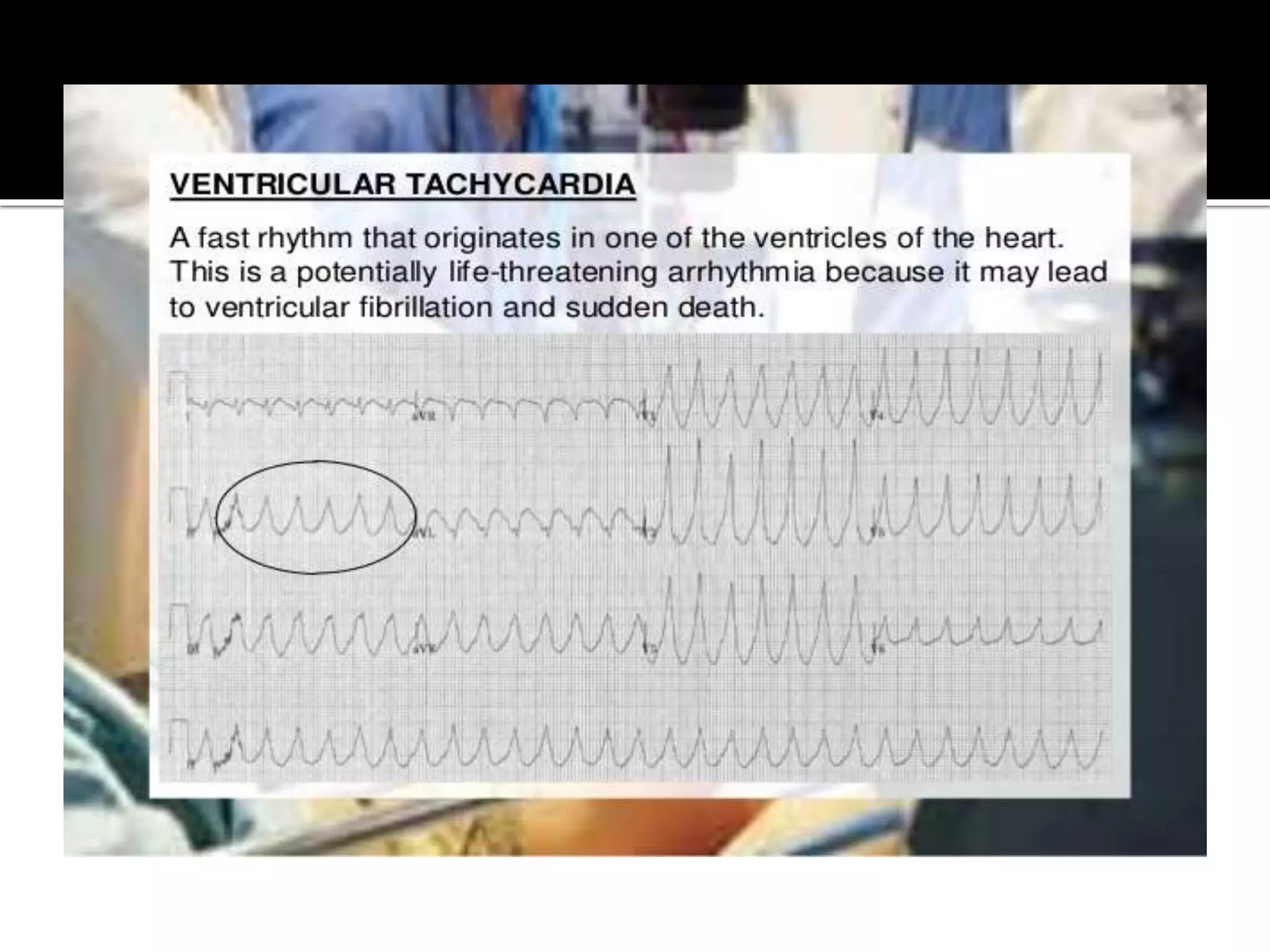
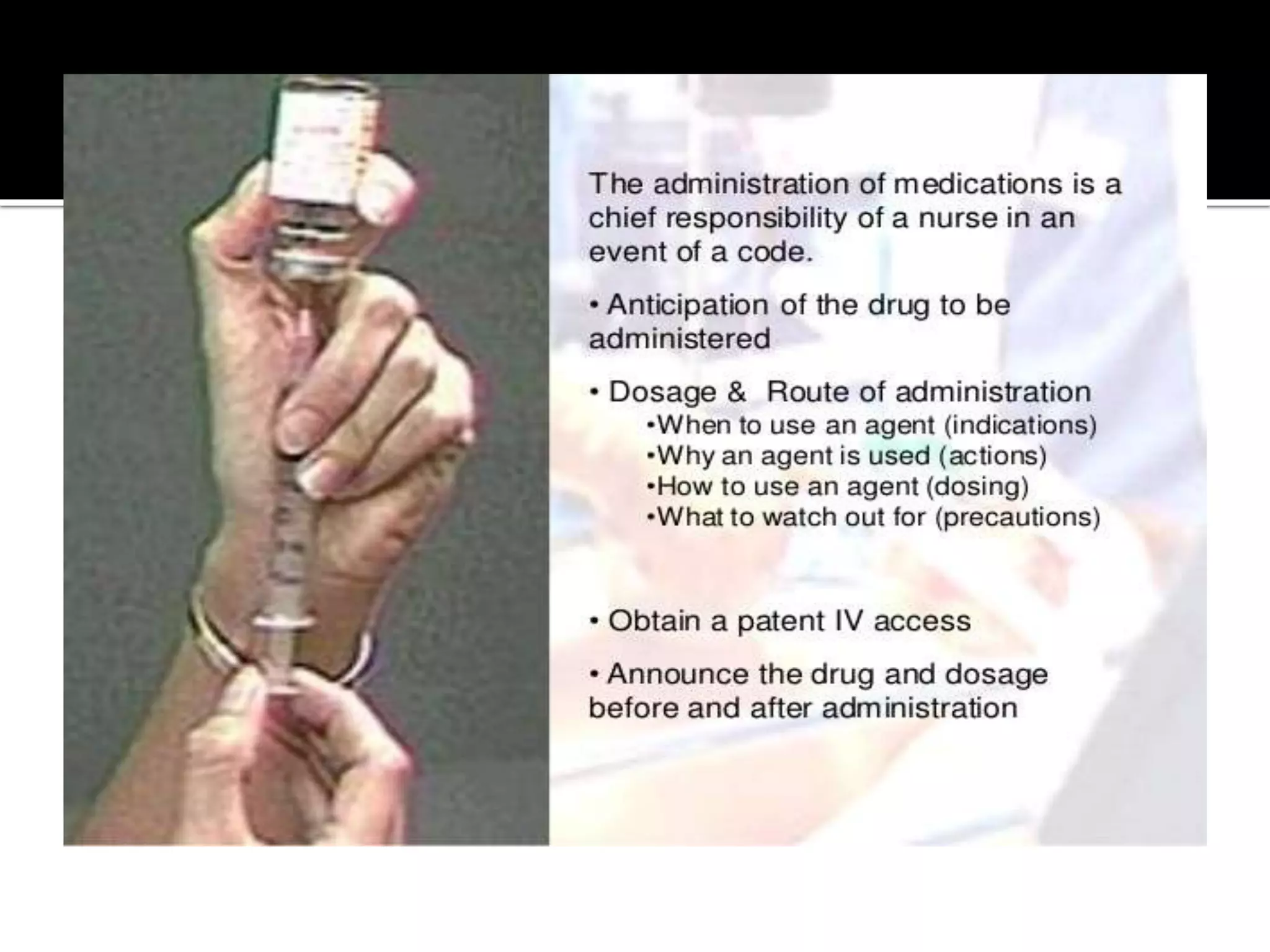
This document provides information and guidelines regarding code blue protocols at King Khalid Hospital in Najran, Saudi Arabia. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the code blue team members, including physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists and others. It describes how a code blue is initiated when cardiac arrest occurs, including notifying the switchboard to announce the code over the PA system. It provides guidance on termination of resuscitation efforts and responsibilities after the code. Key points covered include adopting standards from the Saudi Heart Association for BCLS and ACLS, requirements for certification in life support protocols, and ensuring the code blue team and crash cart are available 24/7.