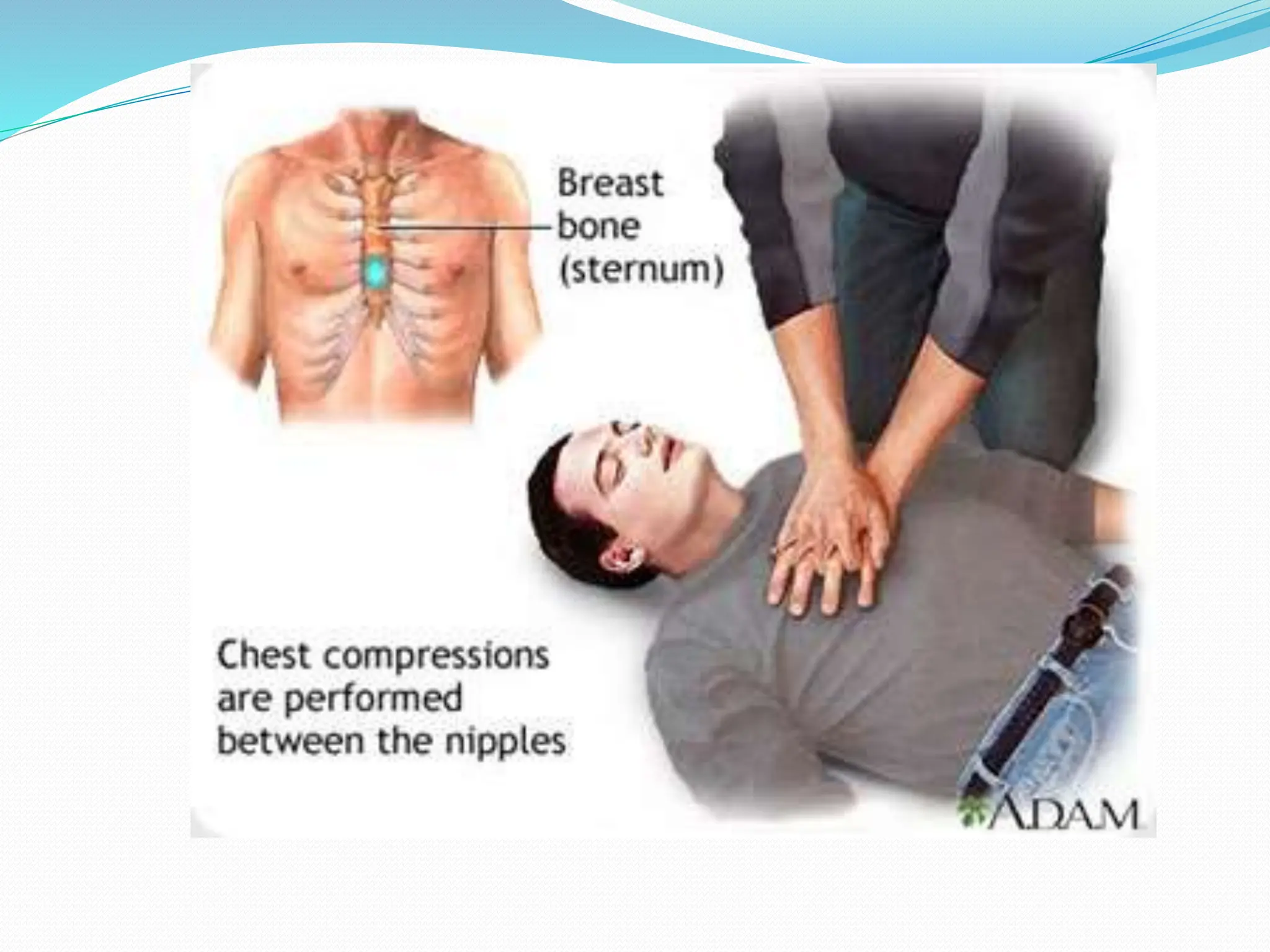
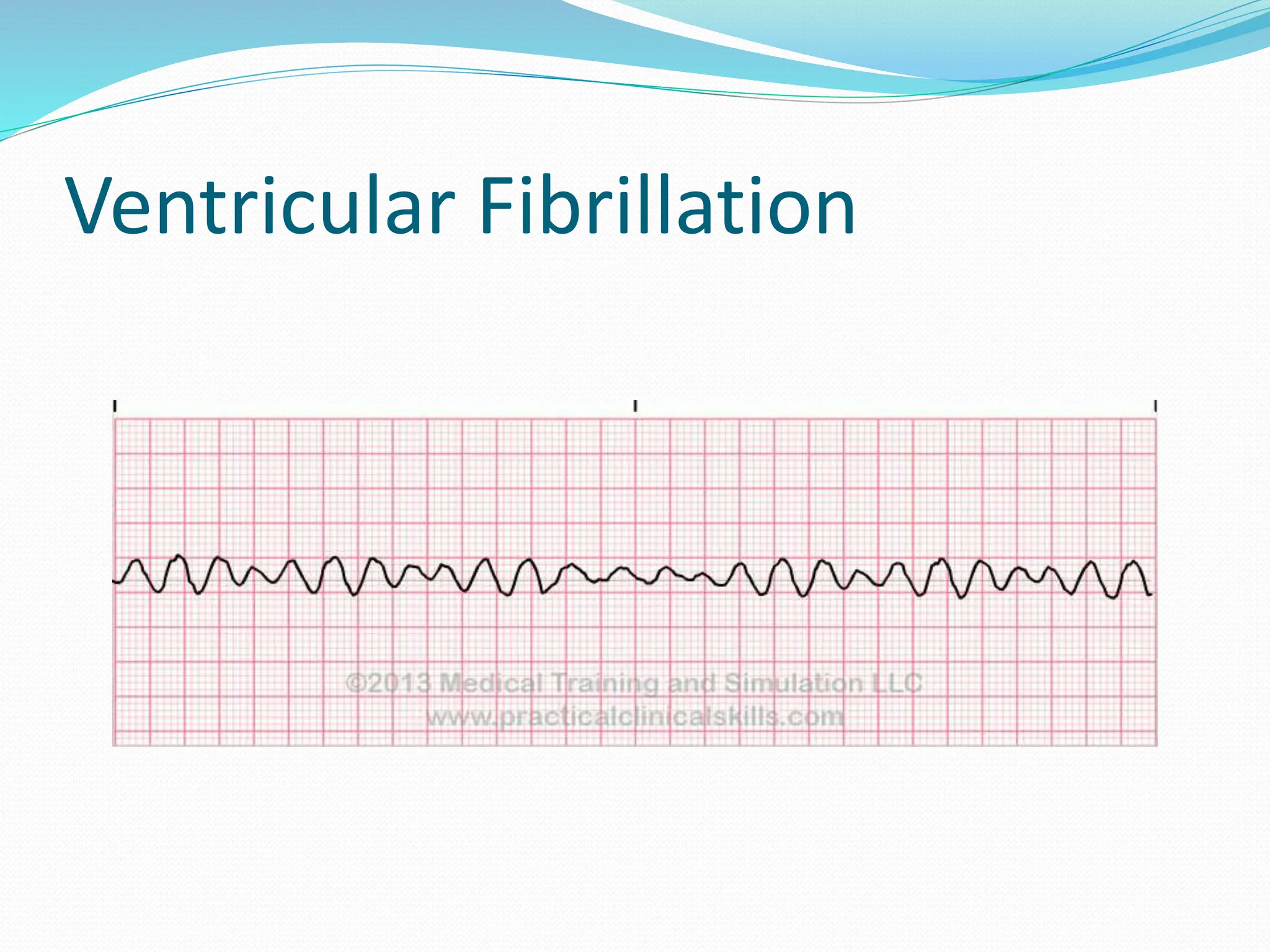
This document provides information on cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and protocols for basic life support (BLS) and advanced cardiac life support (ACLS). It outlines the steps for BLS, including chest compressions, airway management, rescue breathing, and use of an automated external defibrillator. It then describes ACLS, which aims to diagnose the cause of cardiac arrest and provide cause-specific treatment while continuing BLS efforts. Key drugs and procedures covered in ACLS are also summarized, such as defibrillation, intubation, vasopressors like epinephrine, and antiarrhythmics like amiodarone and lidocaine. The document emphasizes the importance of high-quality C