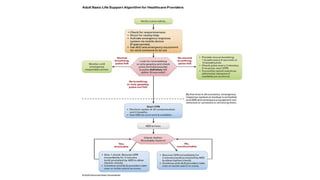
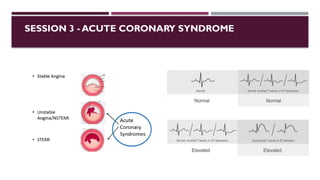
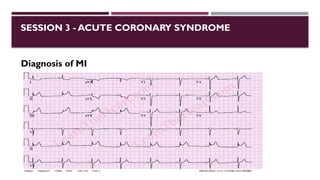
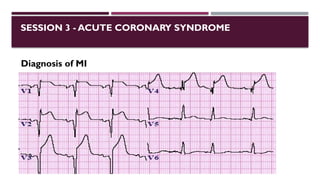
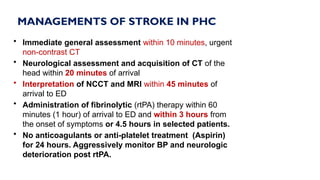
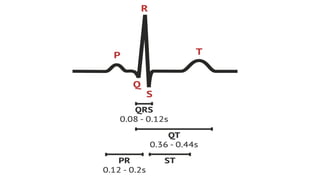
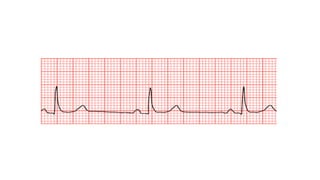
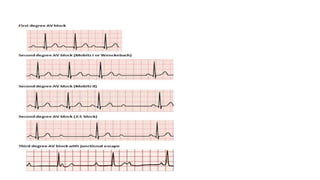
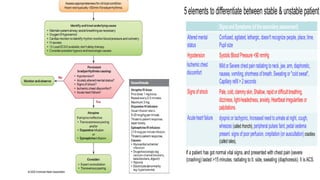
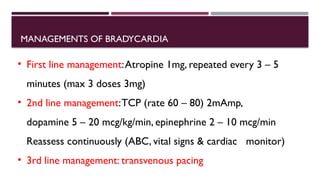
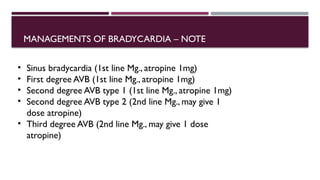
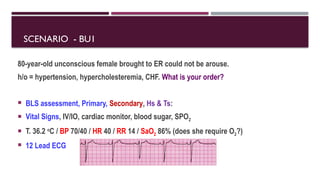
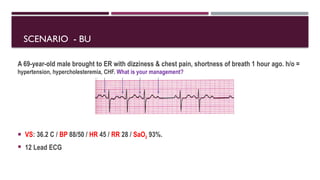
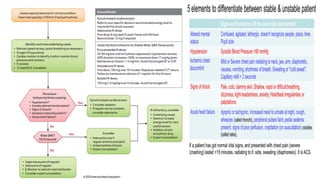
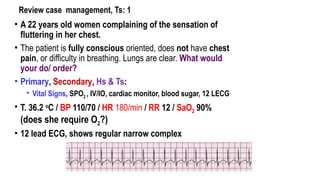
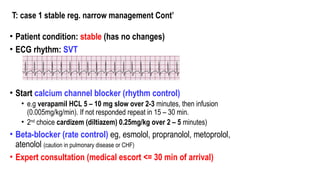
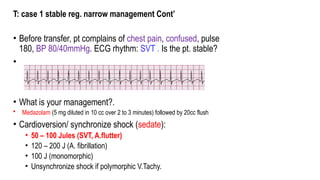
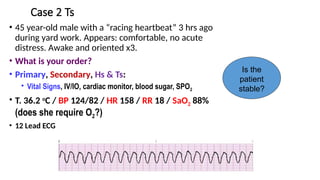
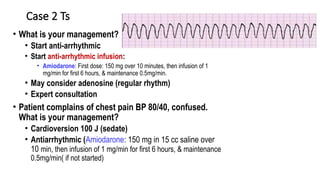
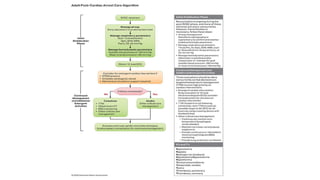
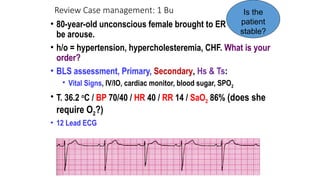
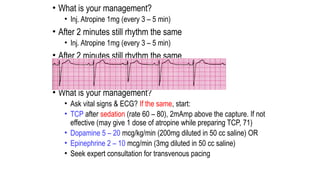
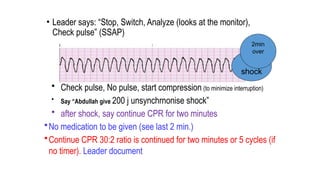
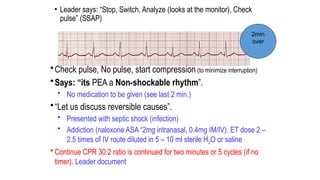
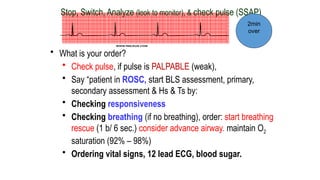
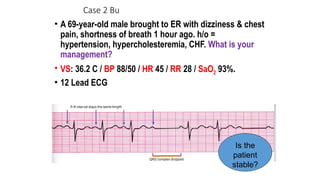
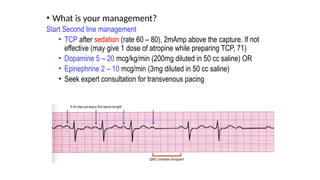
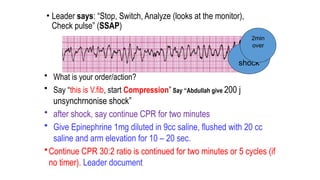
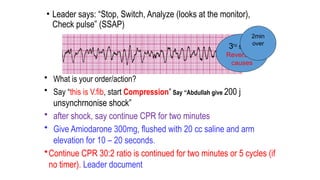
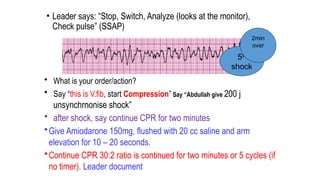
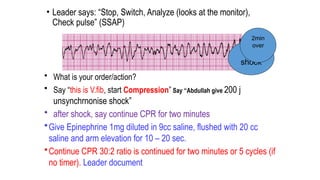
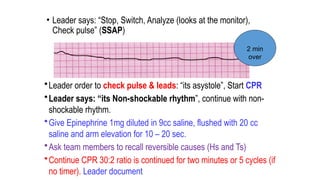
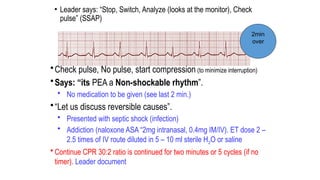
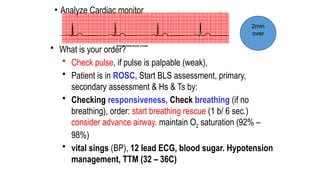
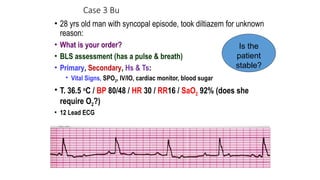
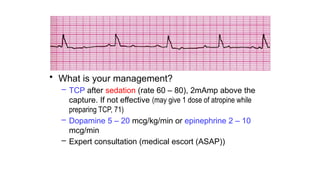
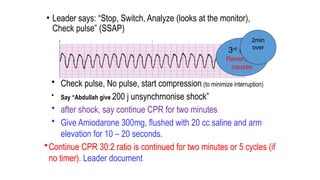
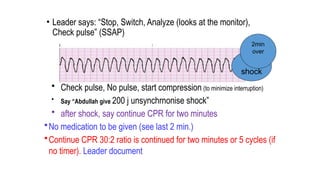
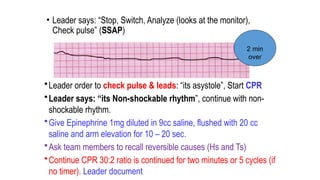
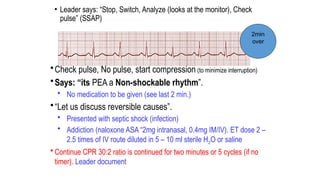
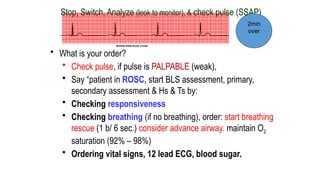
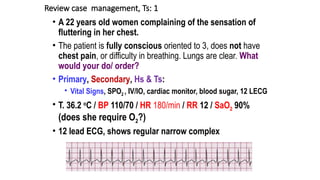
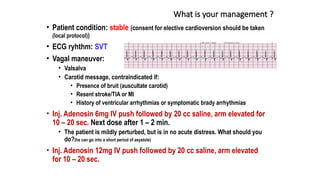
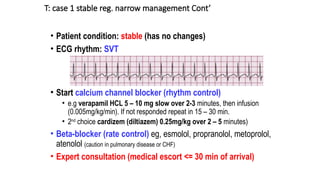
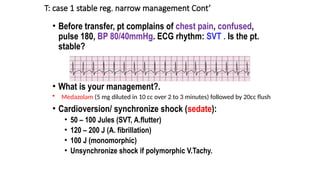
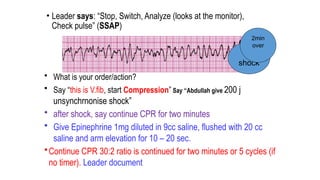
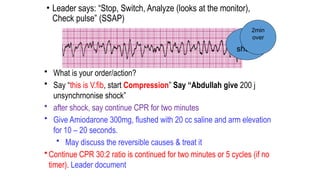
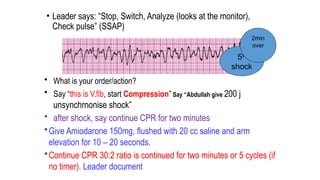
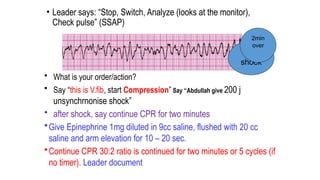
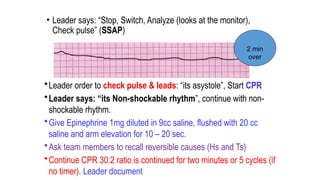
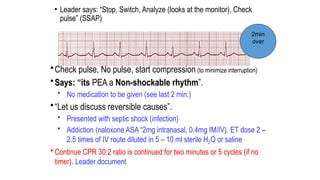
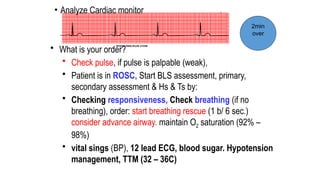
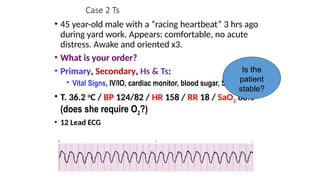
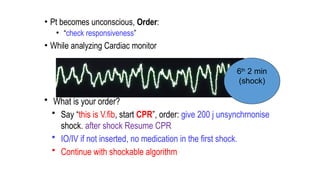
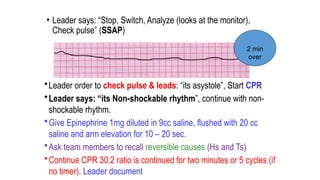
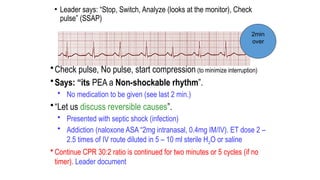
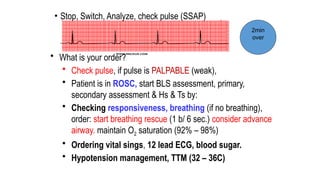
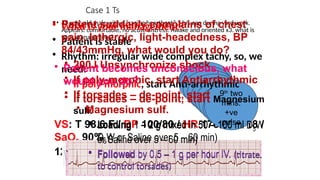
The document outlines advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS) practices, including sessions on adult and infant basic life support (BLS), management of acute coronary syndrome, and stroke care protocols. It details the management of various cardiac rhythms such as bradycardia and tachycardia, including medication dosages and procedures for cardioversion. Additionally, it provides case scenarios for practical application of ACLS principles in emergency situations.