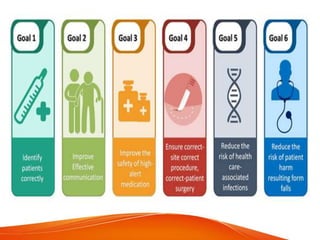
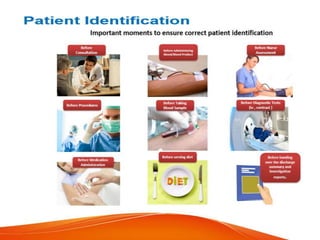
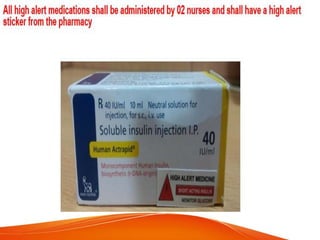
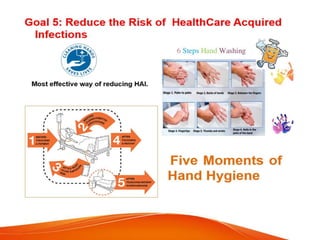
This document outlines several goals and safety measures to reduce patient harm at a hospital. It discusses identifying patients correctly, improving communication, safely managing high-alert medications, preventing wrong-site procedures, reducing healthcare-associated infections, and minimizing falls. Specific strategies are provided, such as conducting vulnerability assessments, monitoring high-risk patients more frequently, using safety checklists, and keeping patients accompanied and call bells within reach. The overall aim is to establish a culture of safety and reporting of any adverse events.