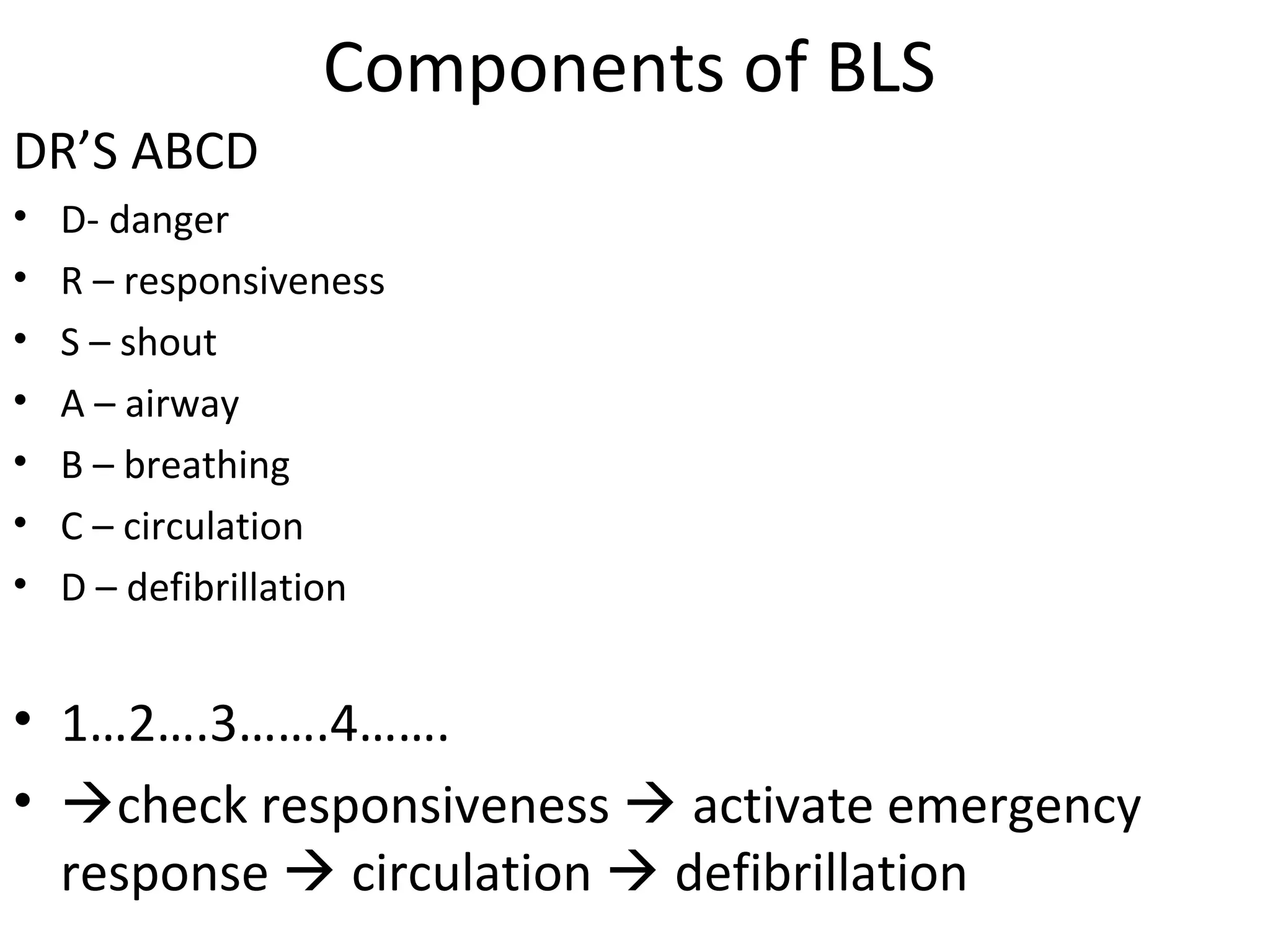
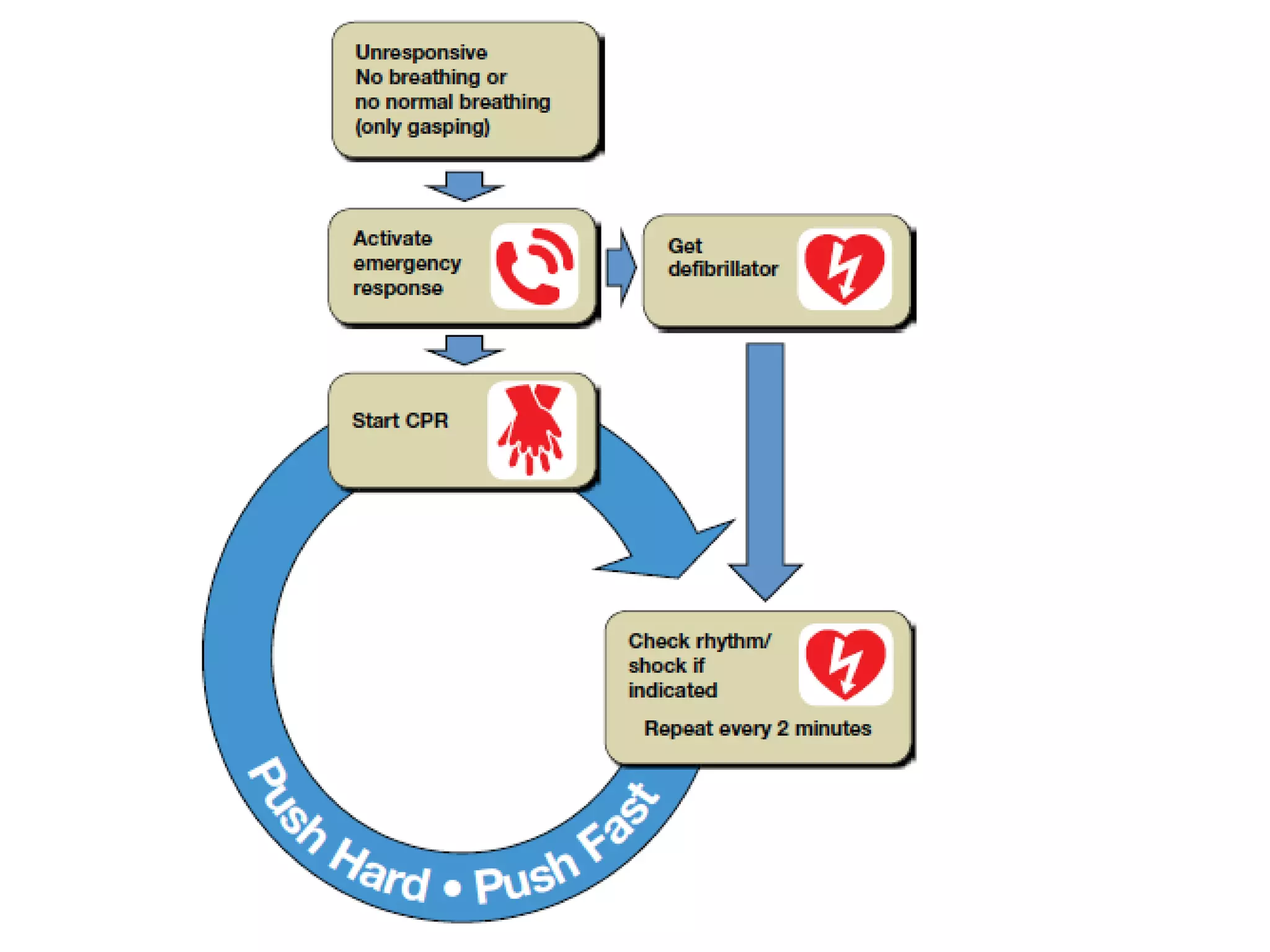
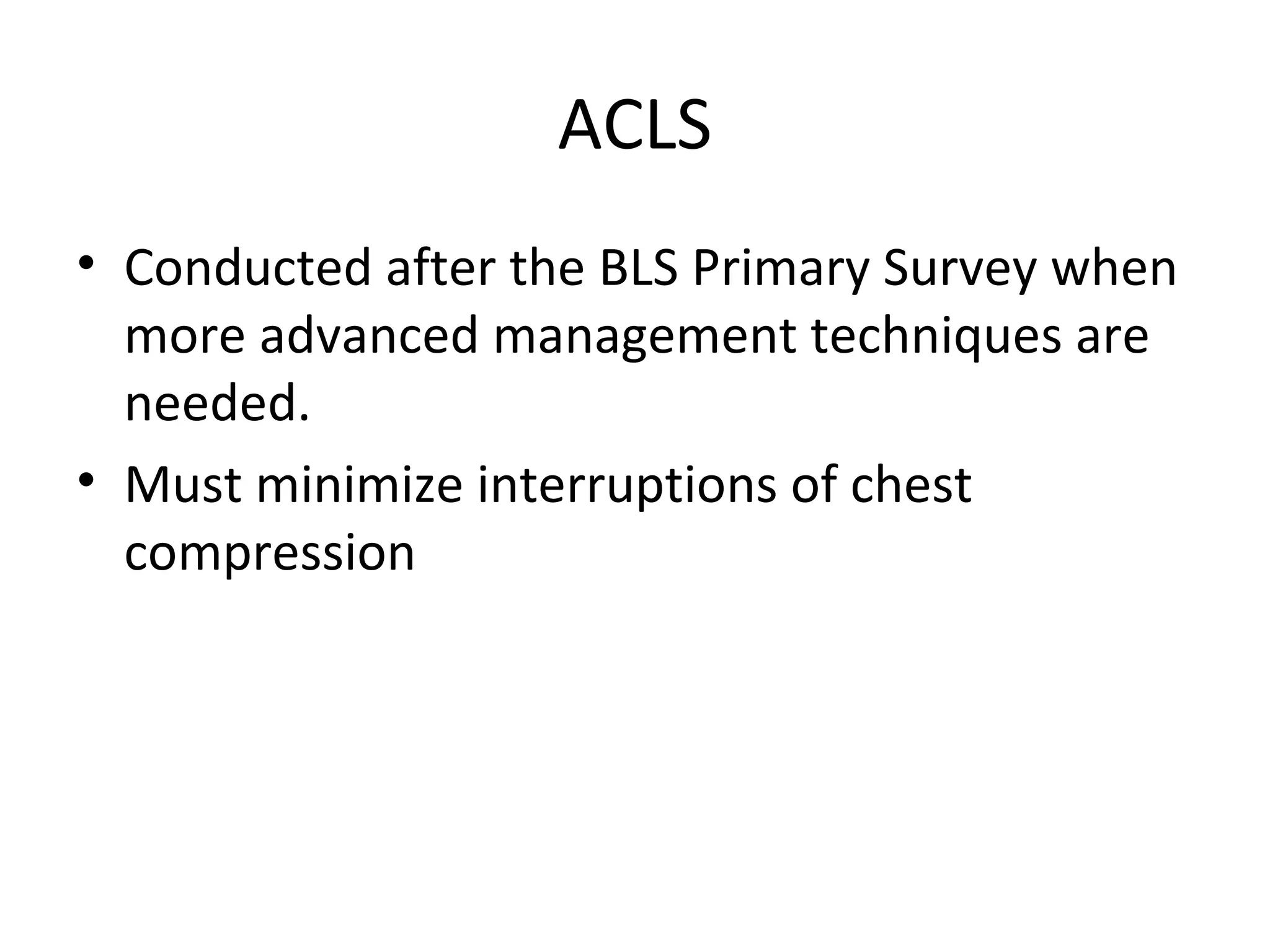
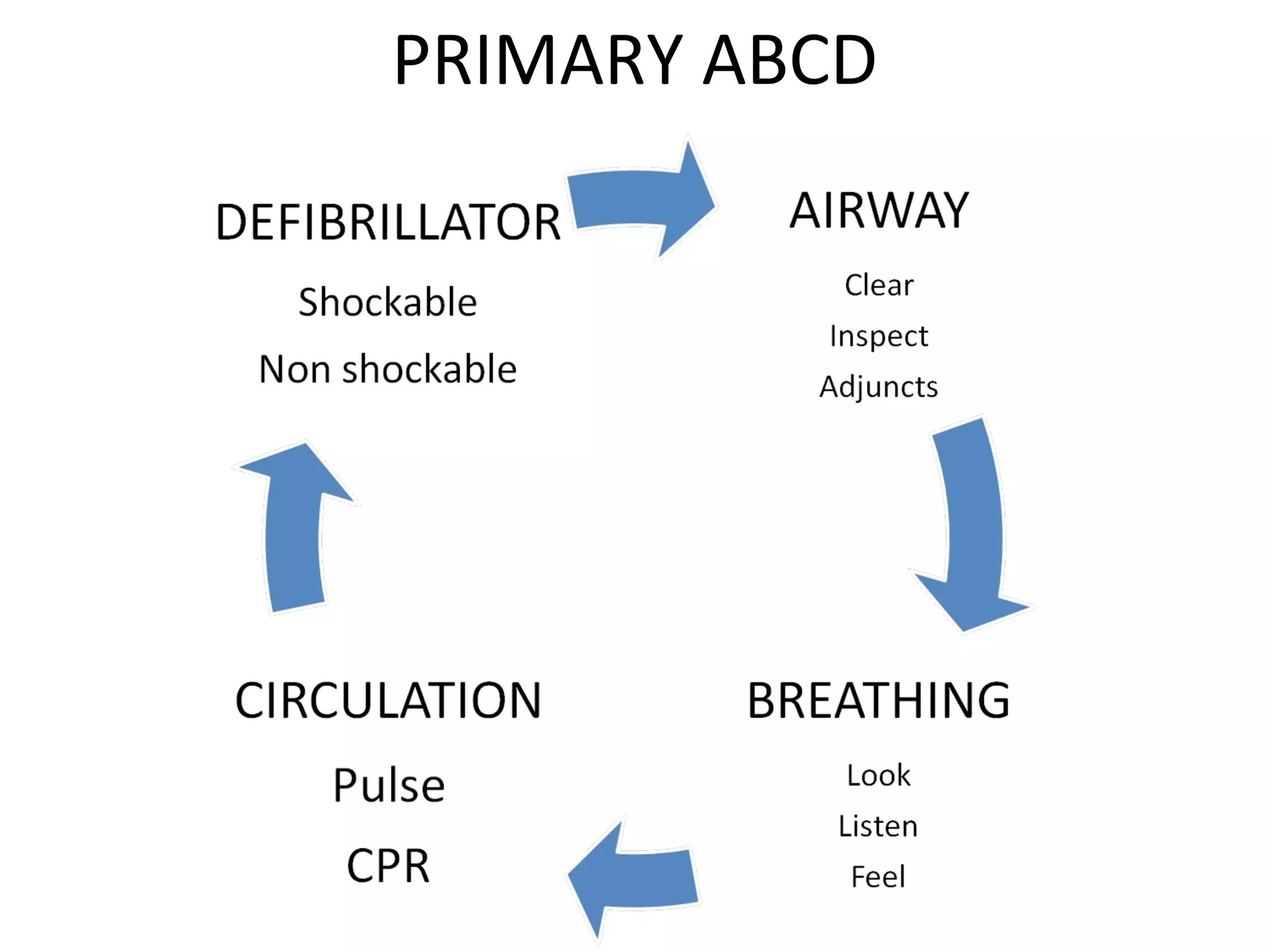
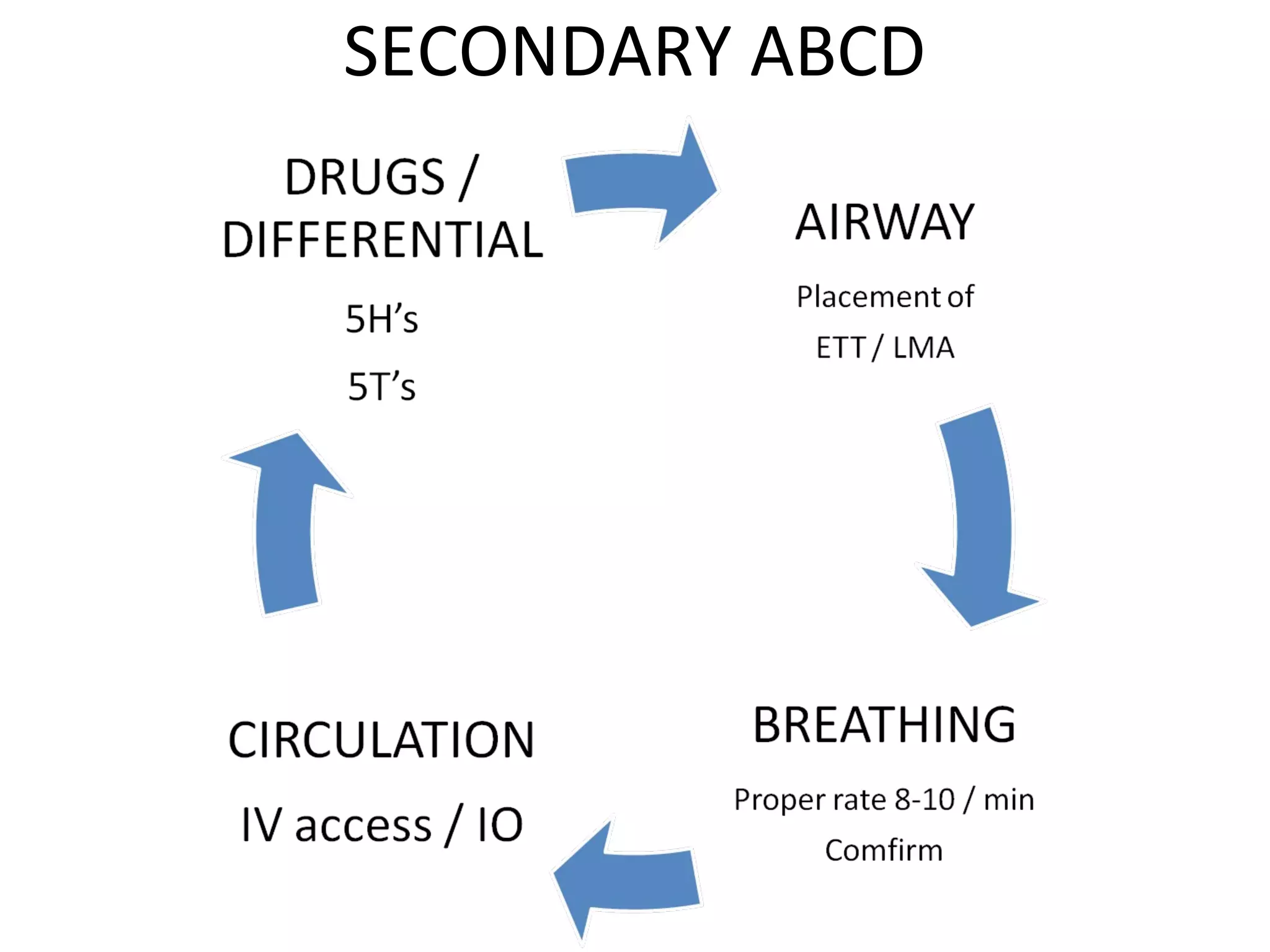
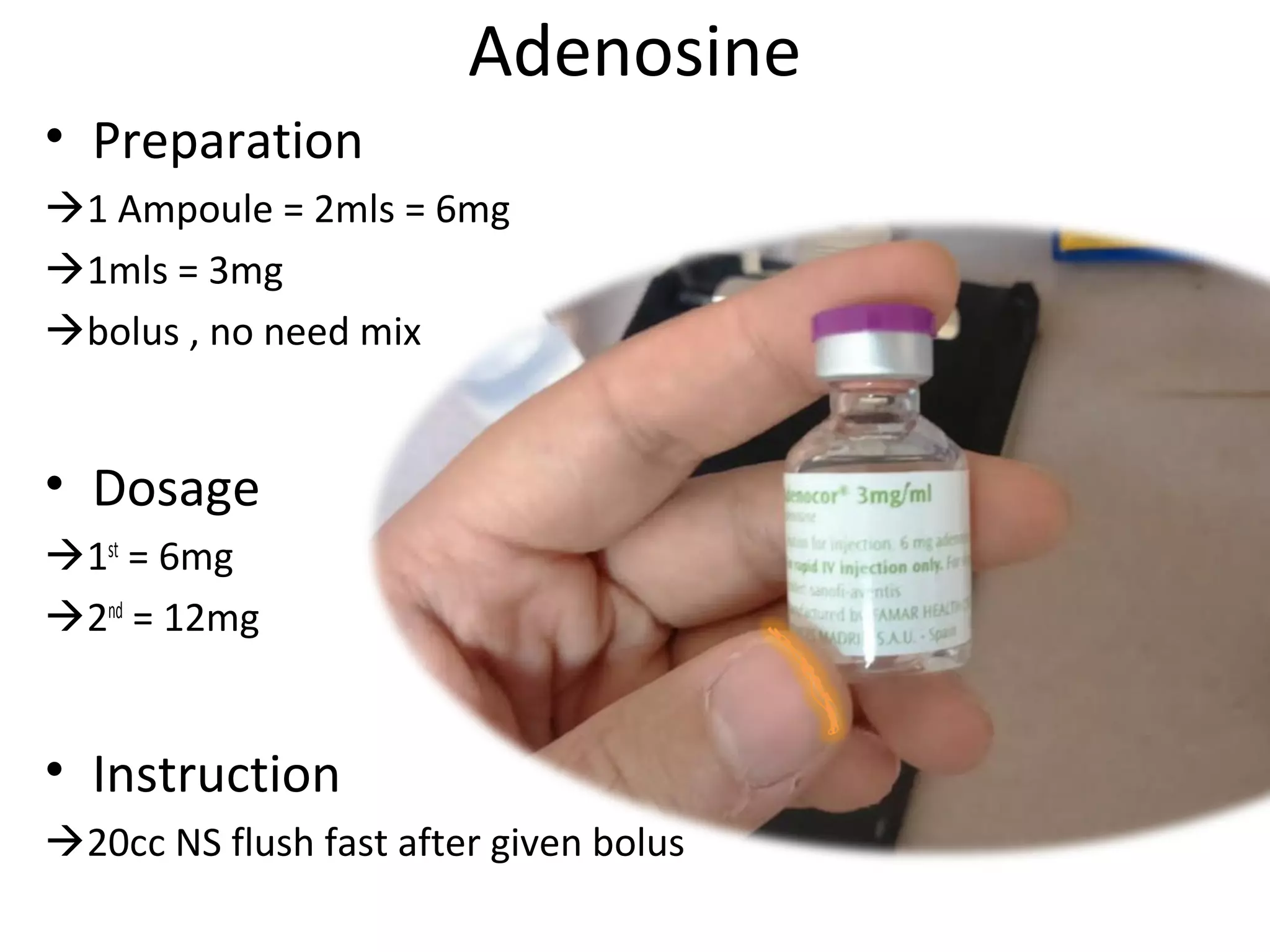
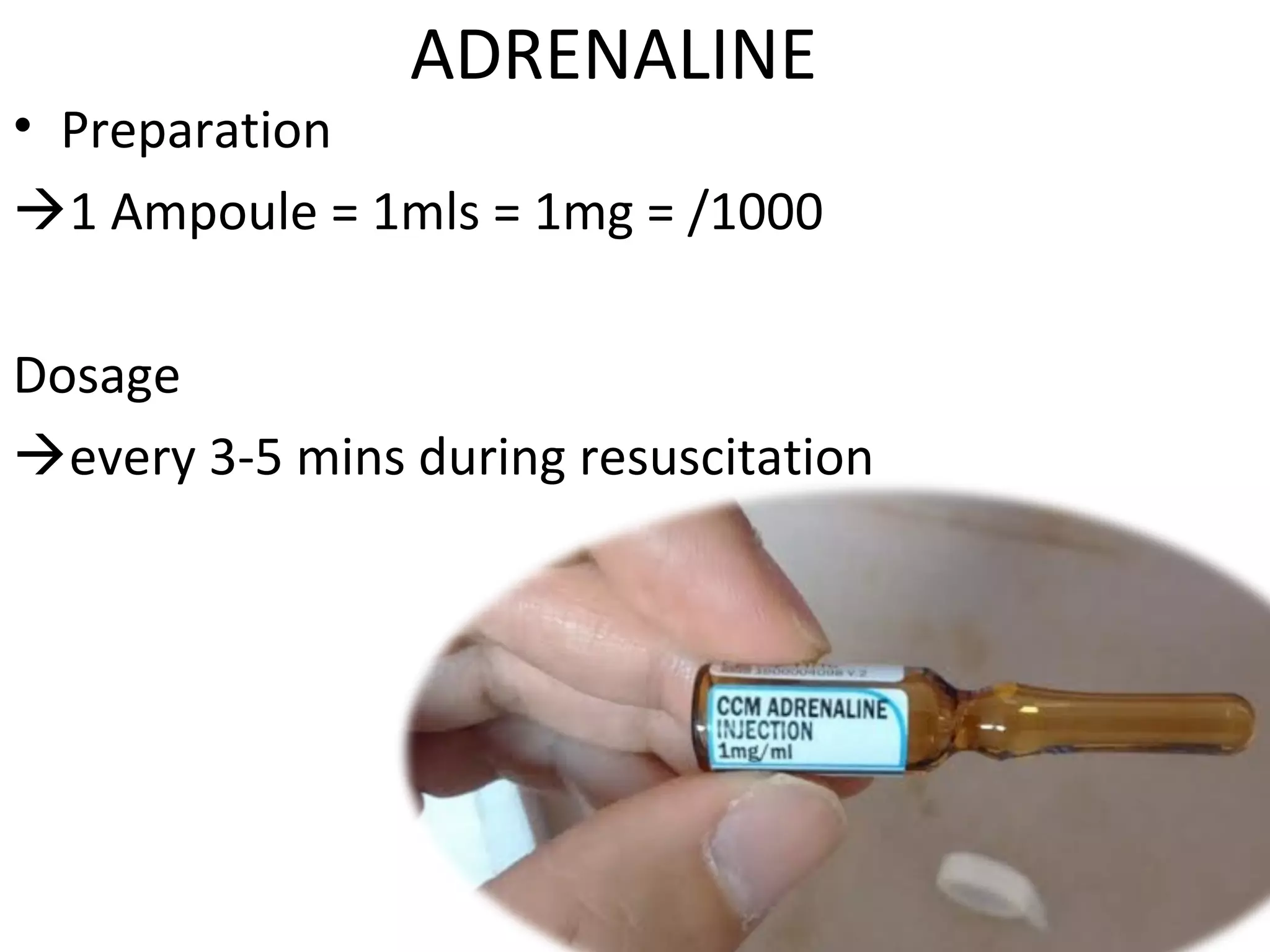
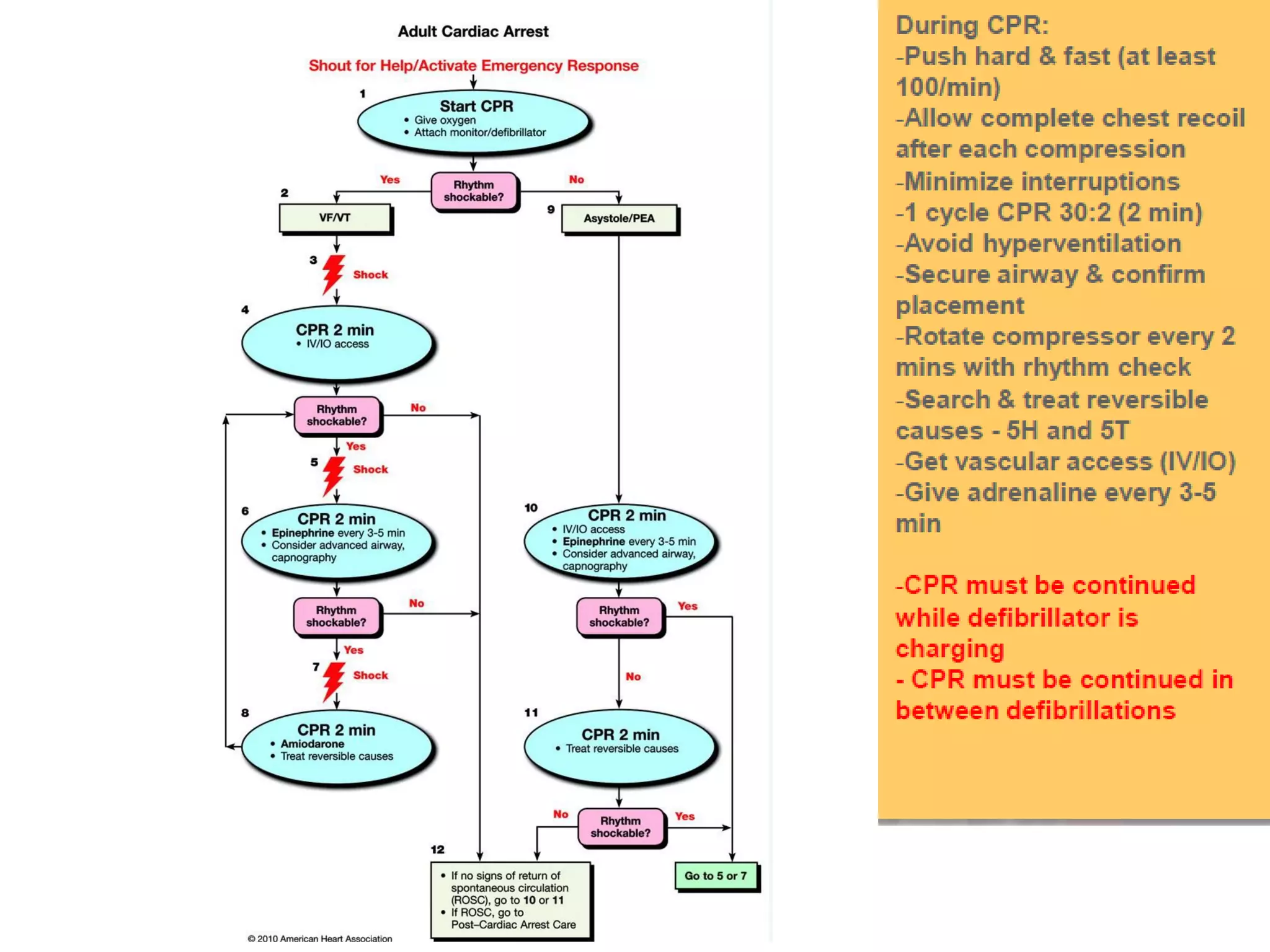
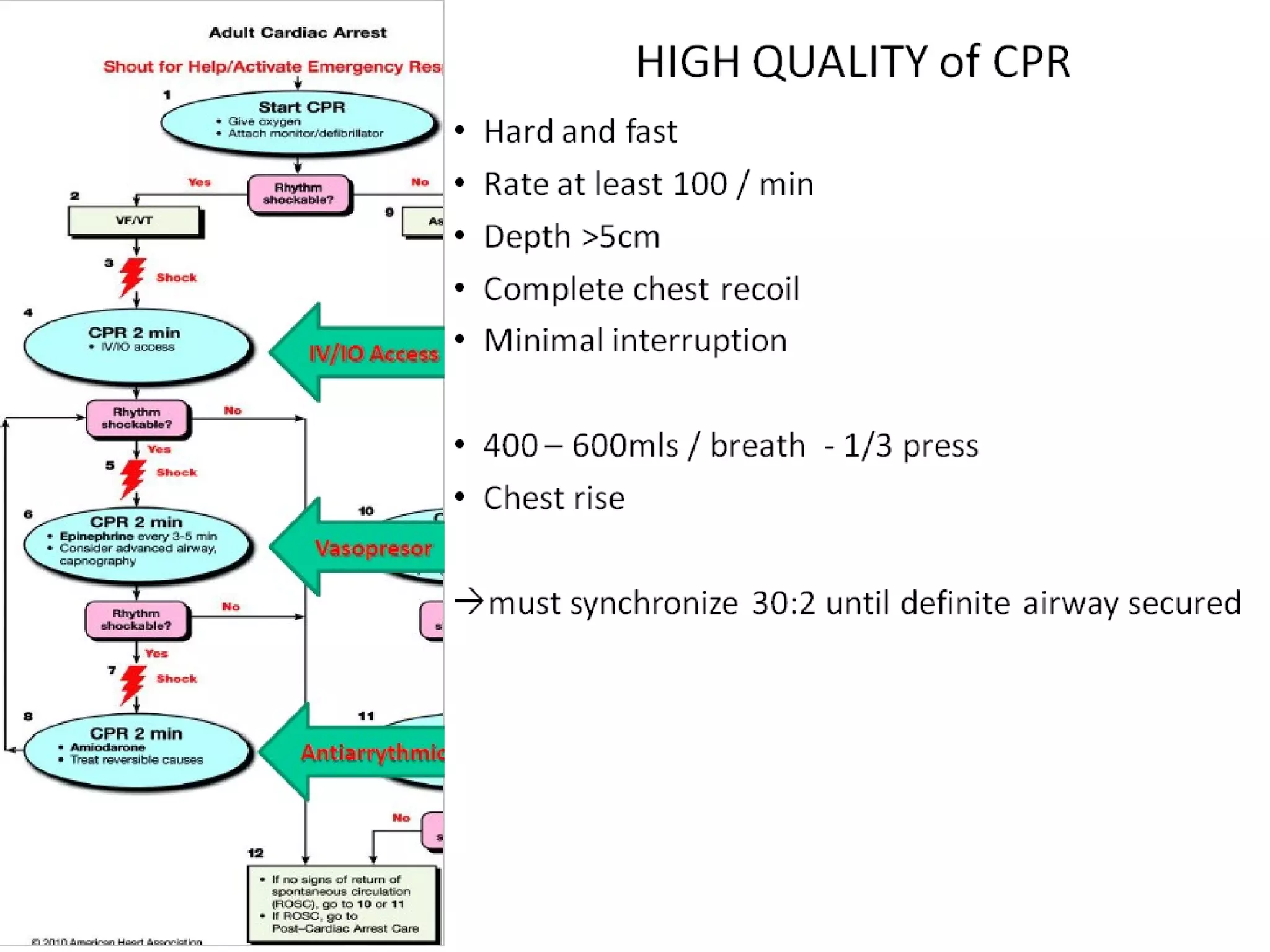
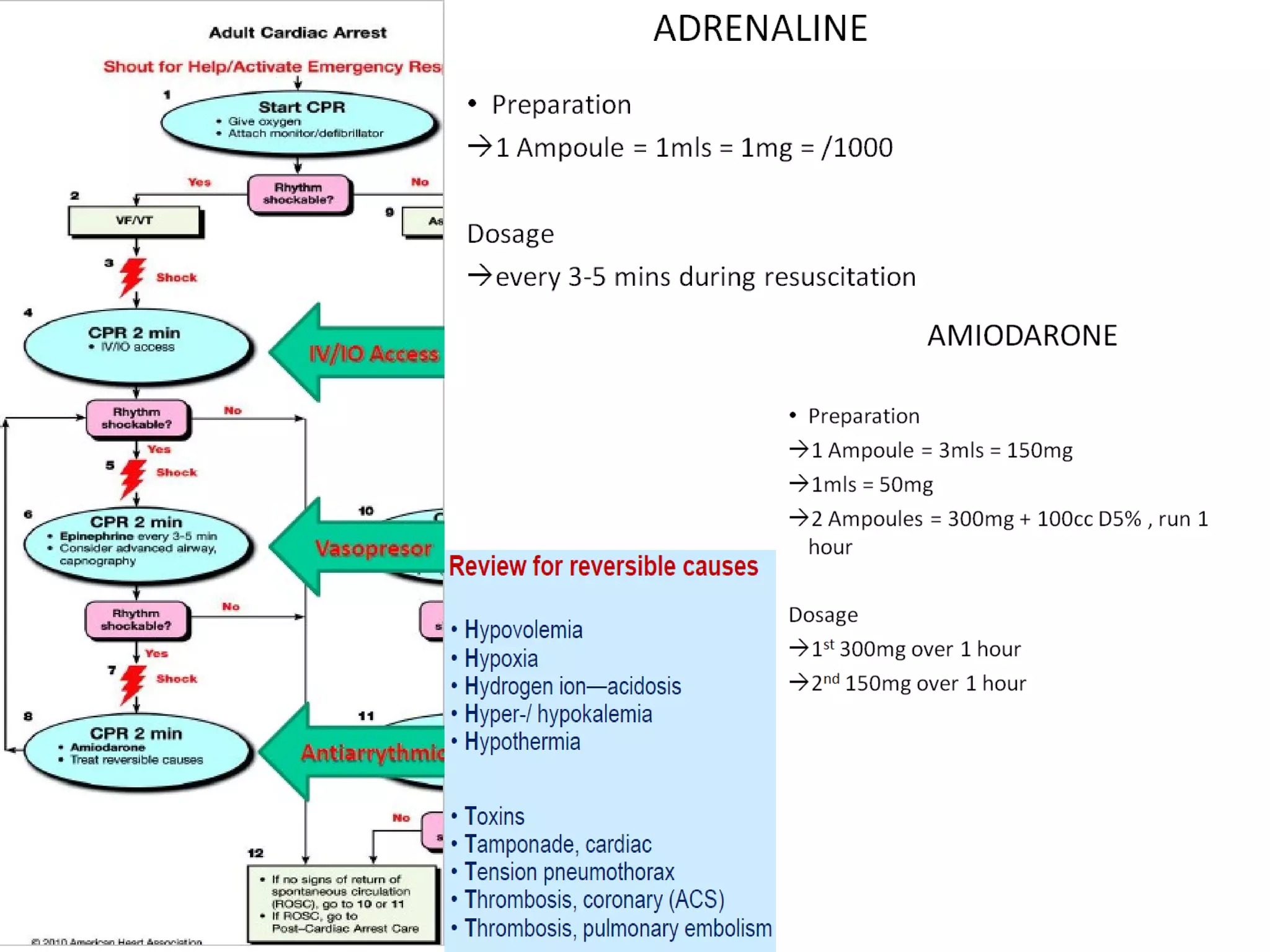
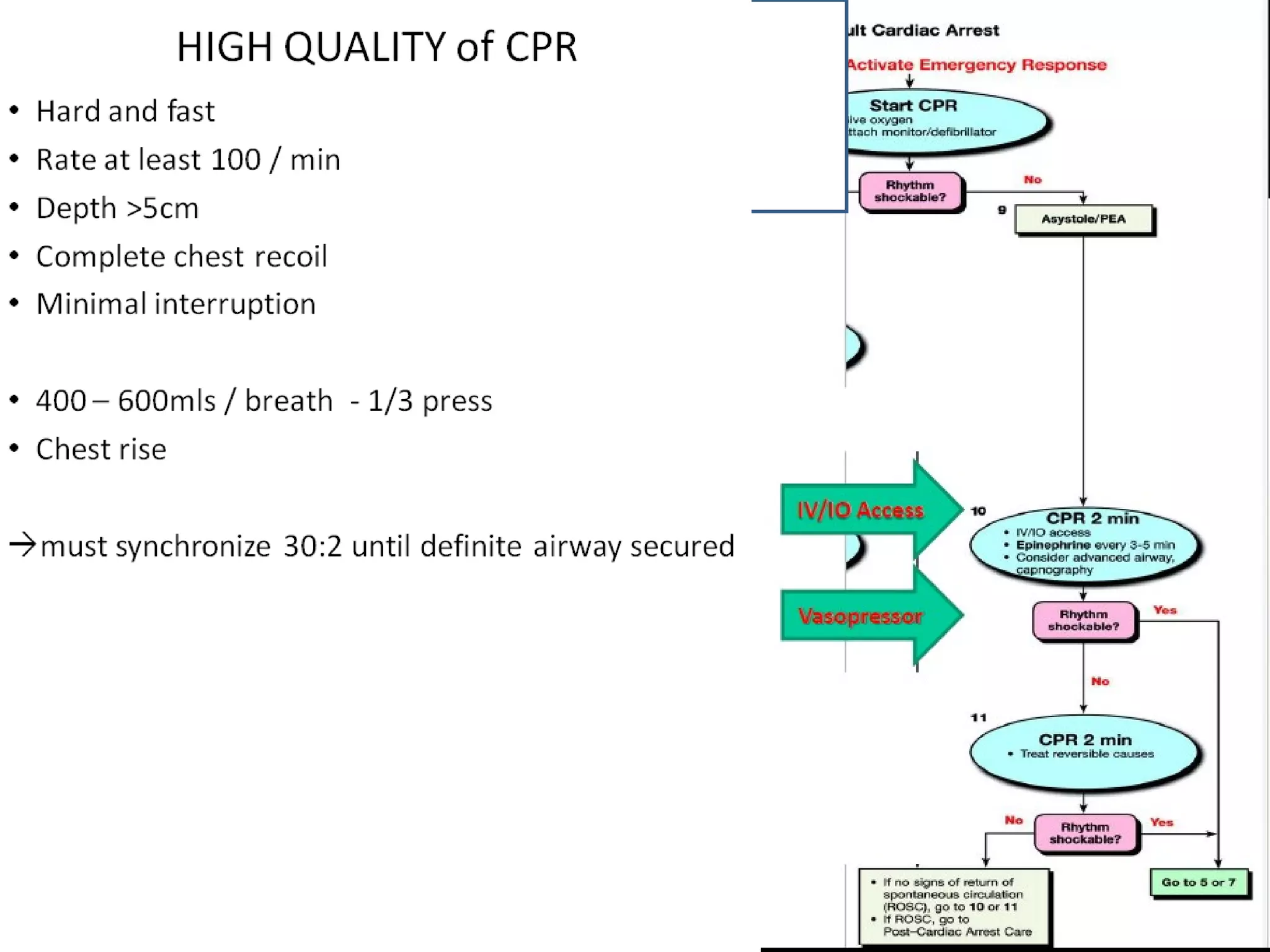
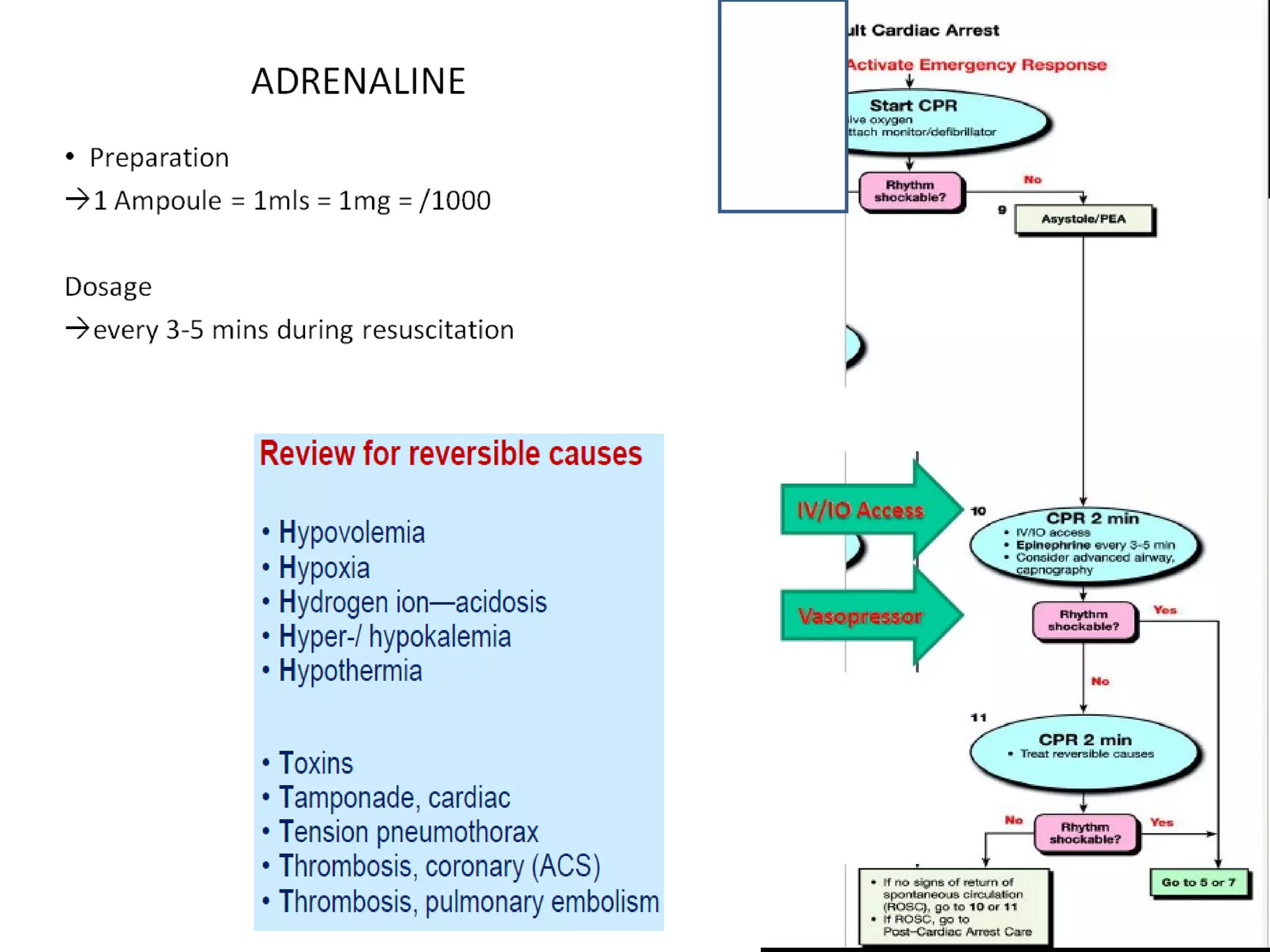
This document provides an overview of basic life support (BLS) and advanced cardiac life support (ACLS). The goals of BLS are to provide early CPR, early defibrillation, and support oxygenation and circulation until more advanced ACLS interventions can be initiated. BLS components follow the DR ABC approach of assessing danger, responsiveness, shouting for help, opening the airway, checking breathing, and performing chest compressions. ACLS is conducted after BLS and involves more advanced airway management techniques and drug administration to treat cardiac issues while minimizing interruptions in chest compressions. The document reviews cardiac drugs, defibrillator use, high quality CPR techniques, and cases commonly addressed in ACLS.