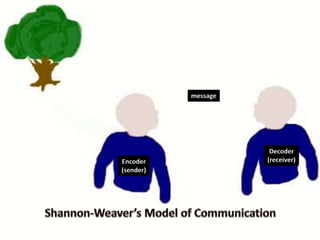
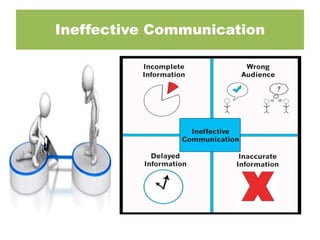
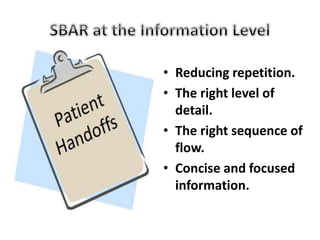
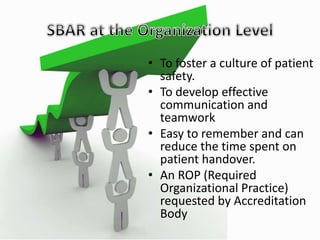
The SBAR technique is a standardized communication framework used in healthcare to communicate critical information effectively and reduce errors. It involves concisely conveying 4 key pieces of information: the Situation, Background, Assessment, and Recommendation. Using SBAR helps ensure the right level of detail is shared, in the proper sequence, to foster a culture of patient safety and effective communication between healthcare providers.