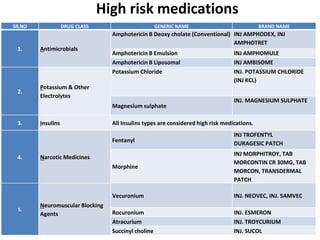
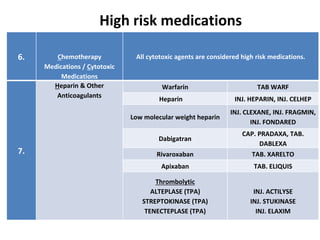
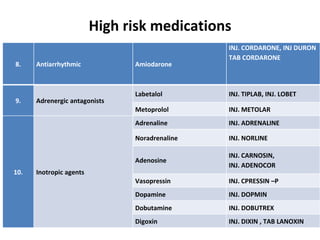
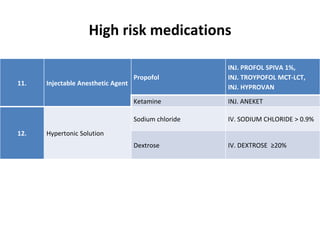
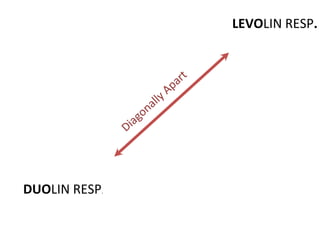
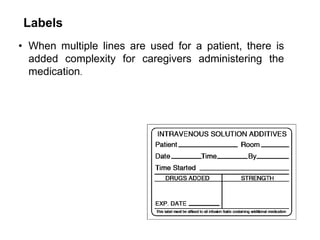
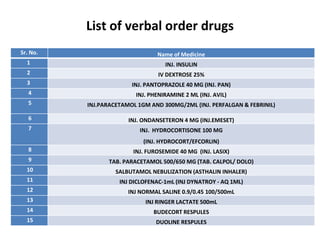
This document discusses the management of high risk medications in a hospital setting. It defines high risk medications as those with an increased risk of harm if misused or used in error. It then lists various classes of high risk medications and provides policies around their safe administration, monitoring, dispensing, and documentation. Specific policies are outlined for narcotics, look-alike/sound-alike drugs, verbal orders, adverse drug reactions, medication errors, and outside medications brought by patients. Monitoring parameters and roles of nursing staff, pharmacists, and physicians are also defined to ensure the appropriate handling of high risk medications.