Embed presentation
Downloaded 104 times



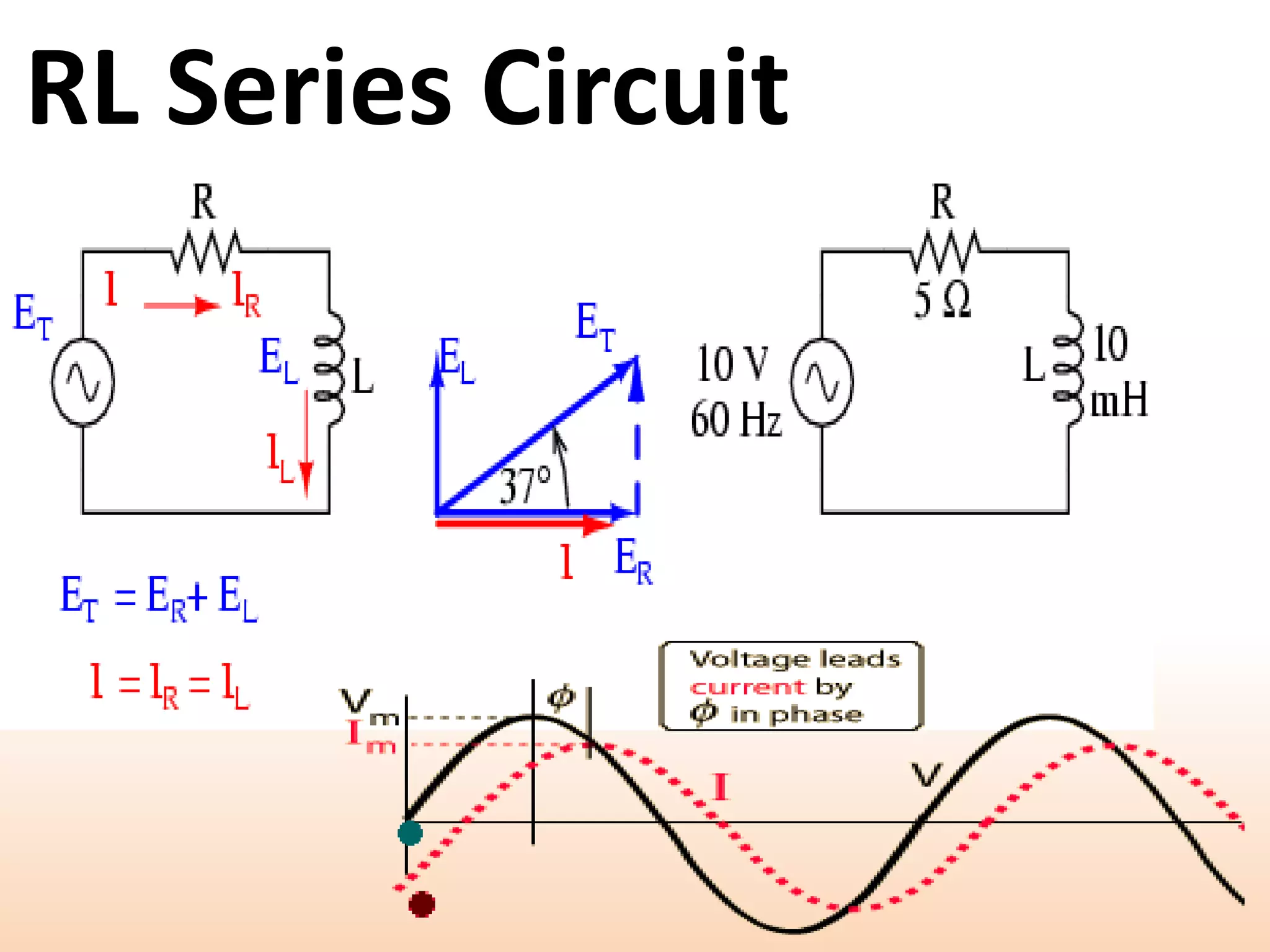
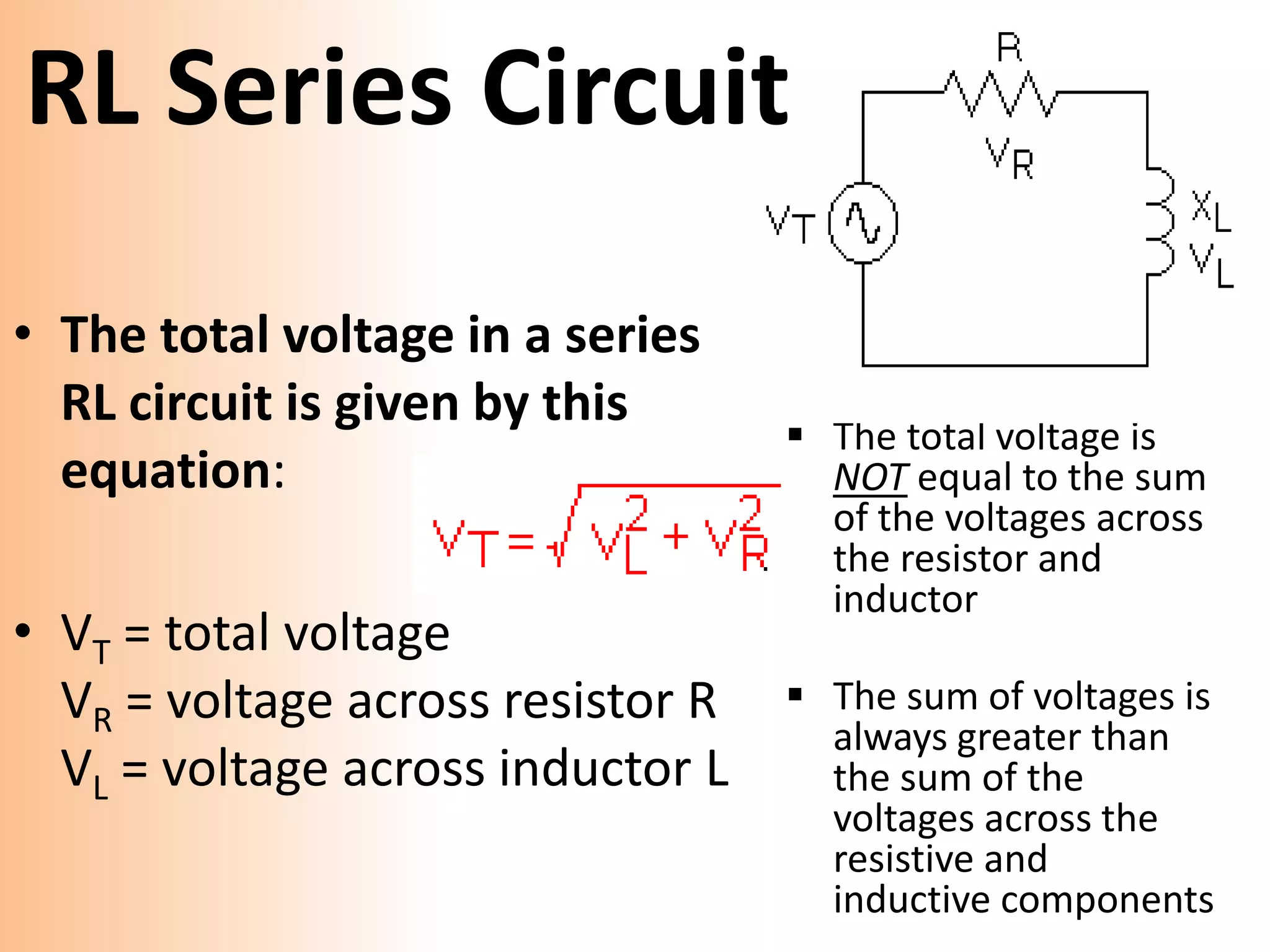
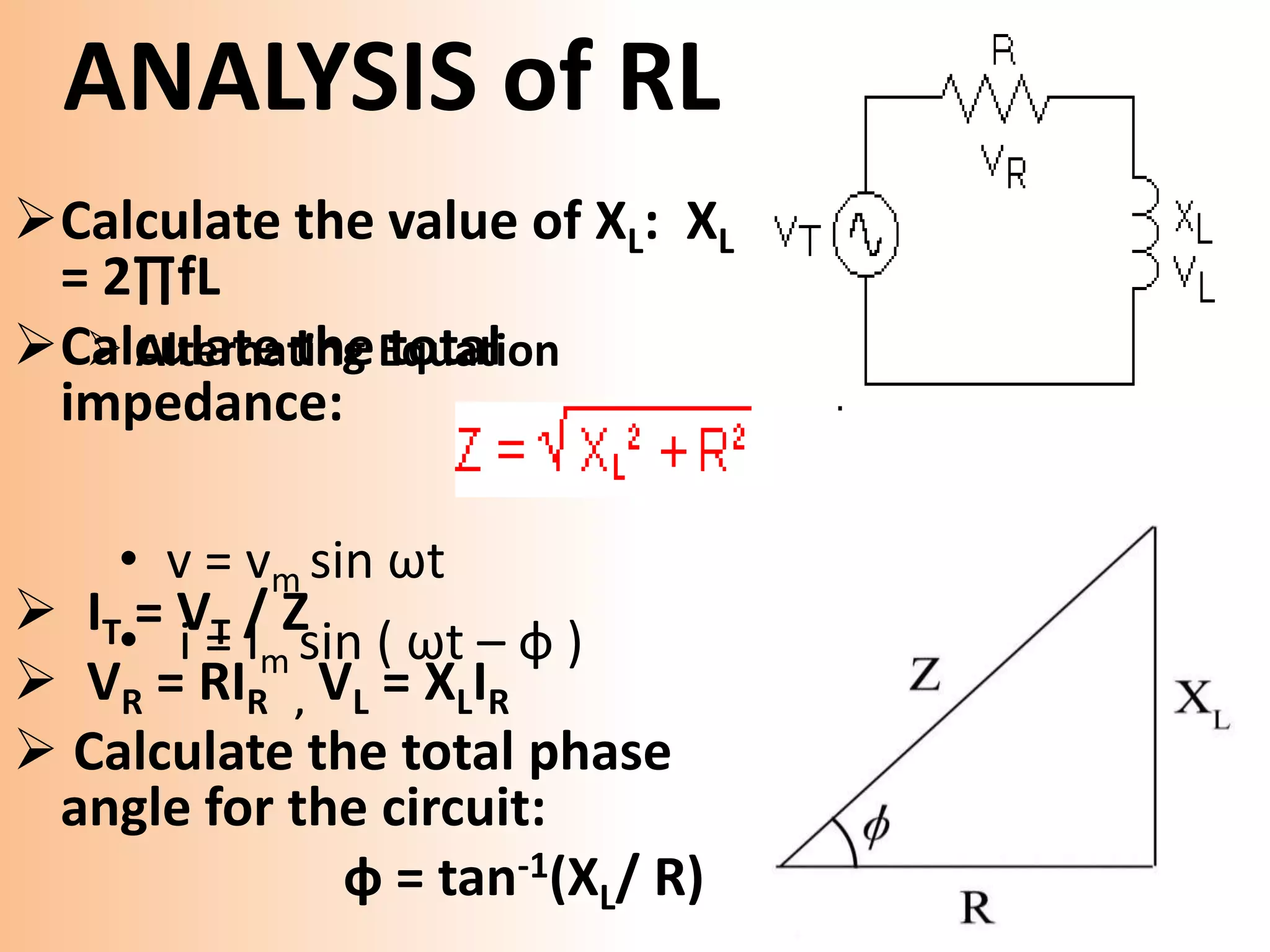
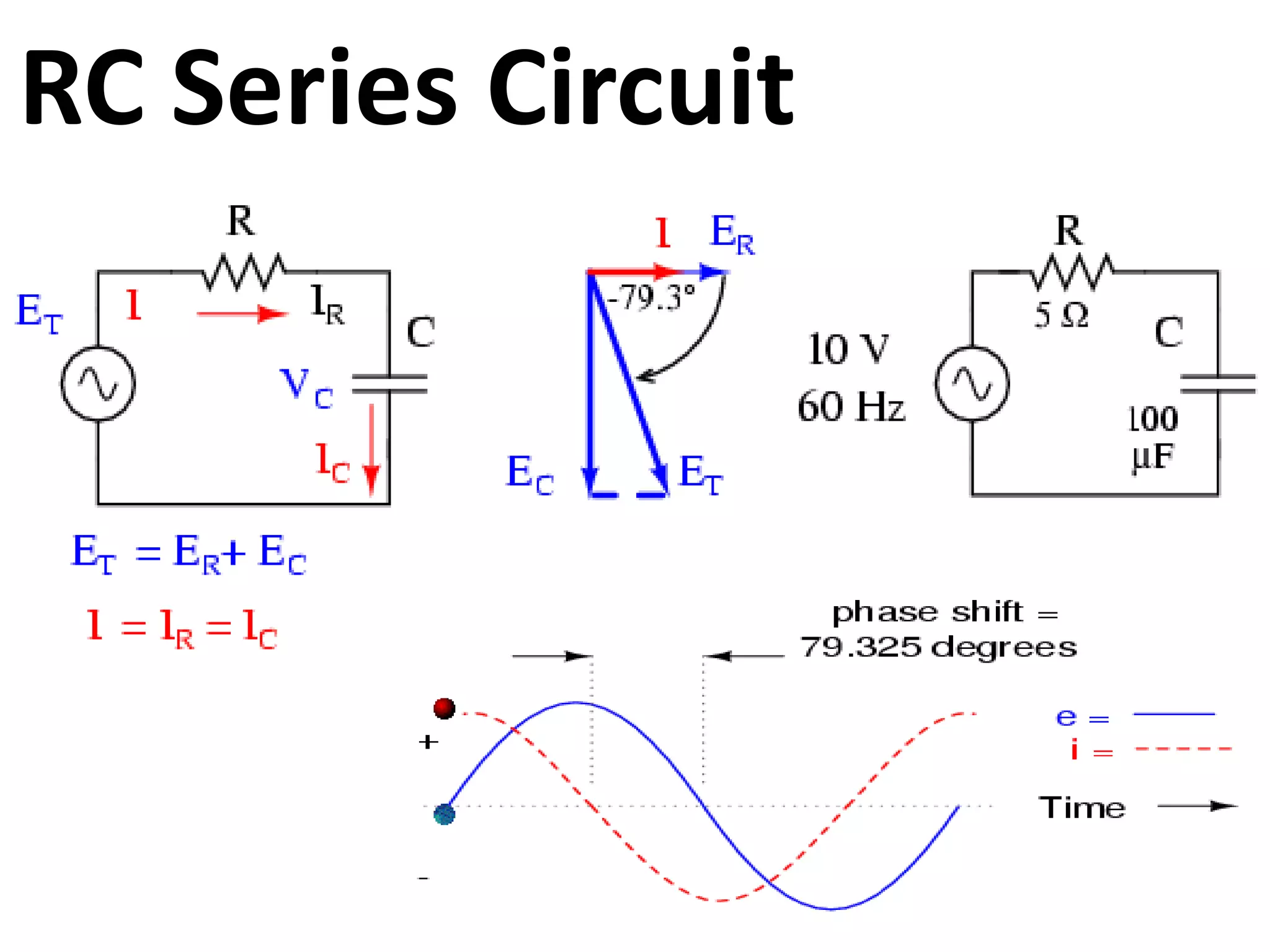
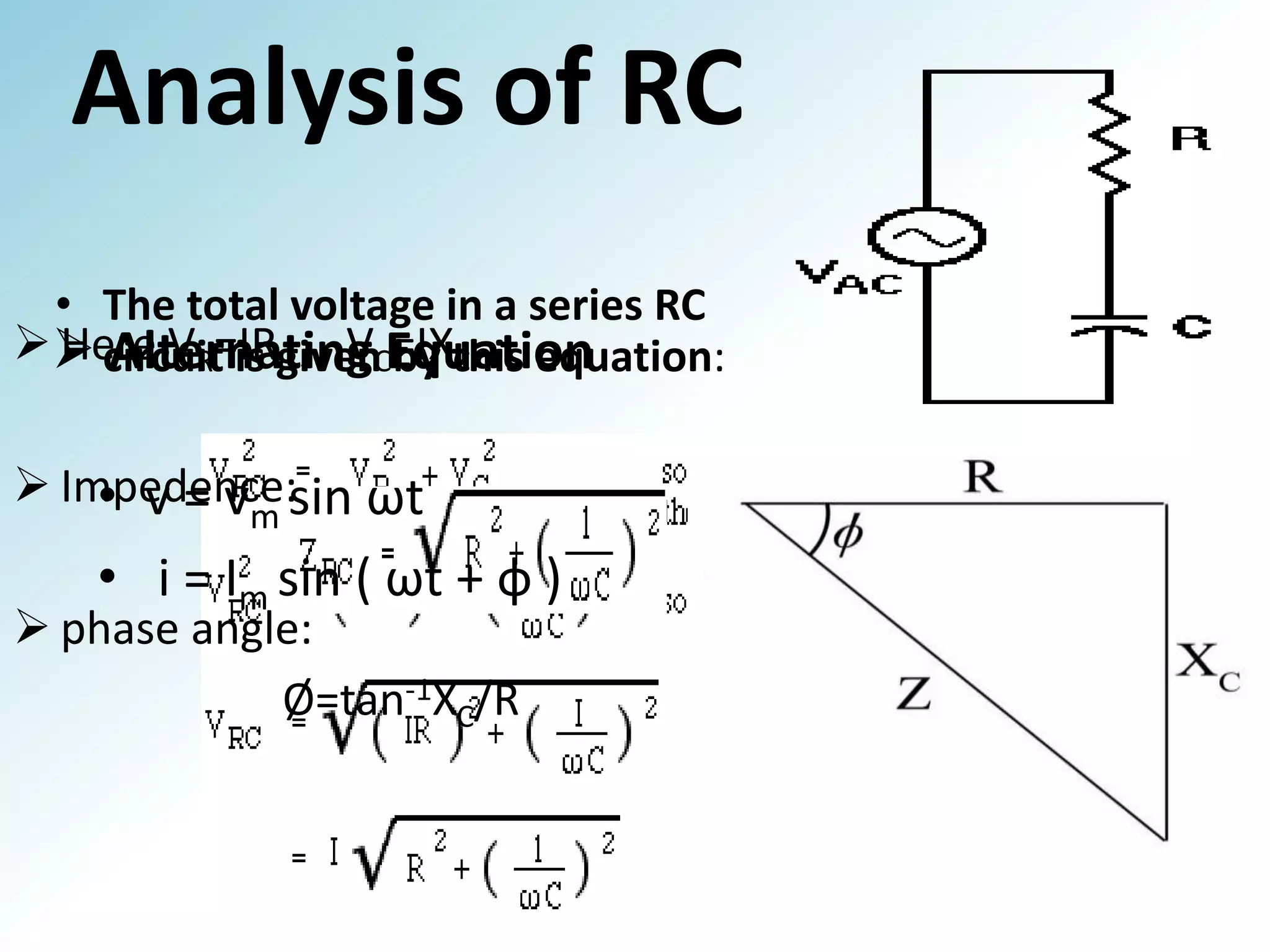

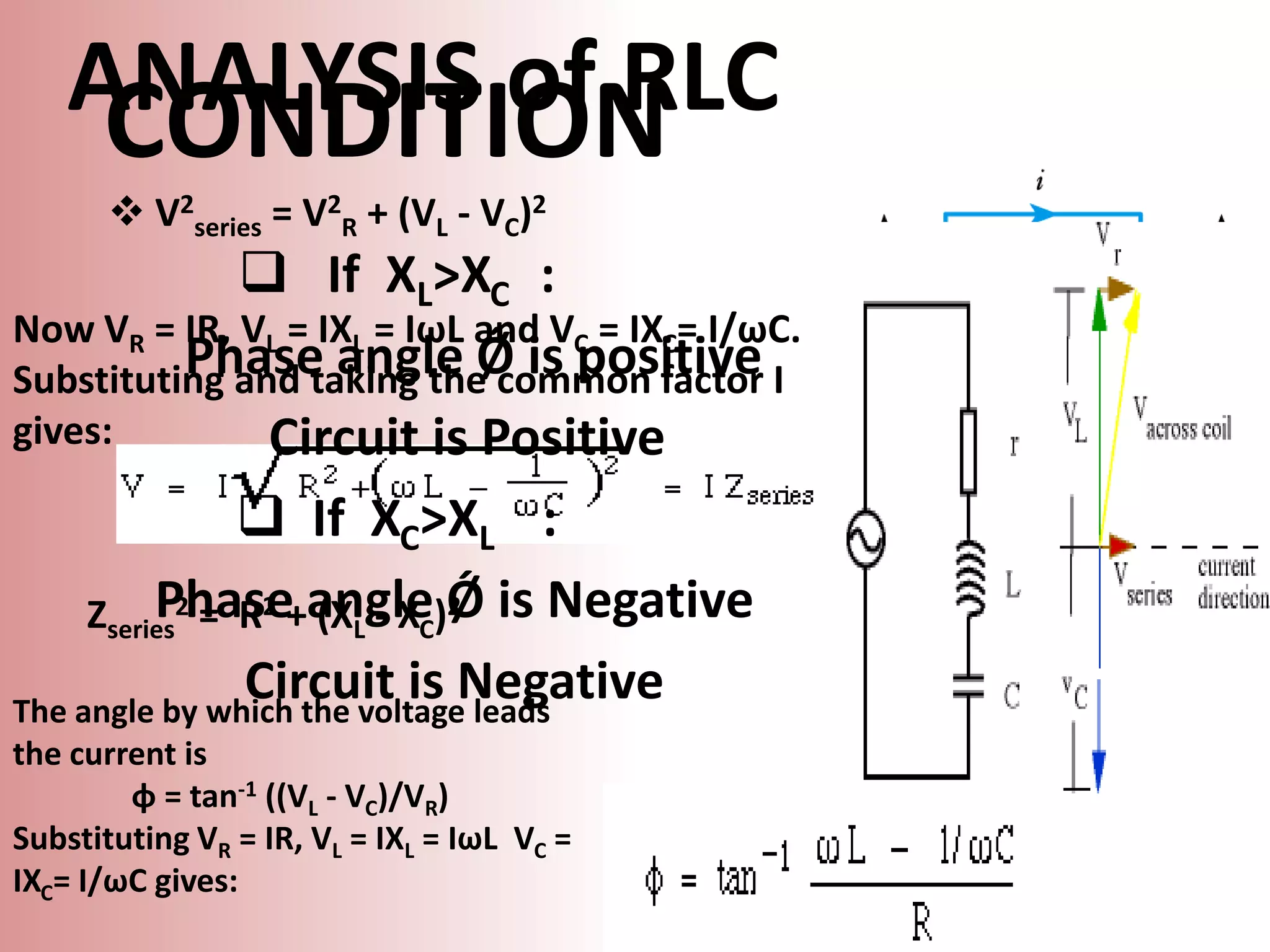





This document provides a summary of a group presentation on series AC circuits. Group 11, consisting of Robiul Awal Robi, Abdul Wahid, and Abu Jauad Khan Aliv, will be presenting on R-L series circuits, R-C series circuits, and R-L-C series circuits. The document outlines the analysis of each circuit type, including equations for total voltage and phase angle. It also notes a special case where the inductor and capacitor impedances are equal, resulting in a purely resistive circuit with zero phase angle. Sources for the material are listed at the end.













