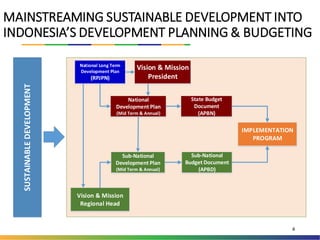
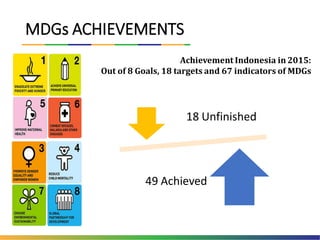
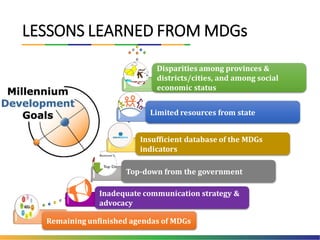
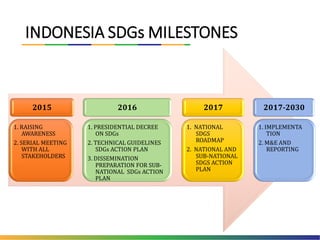
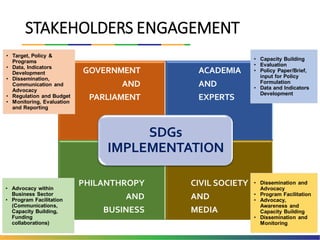
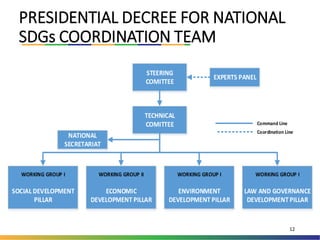
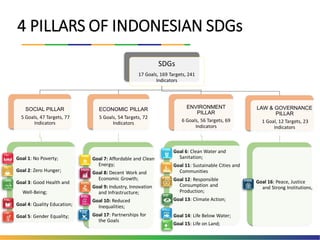
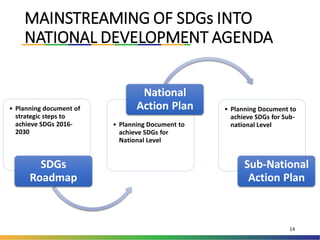
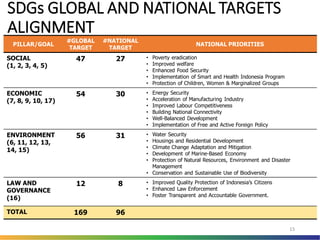
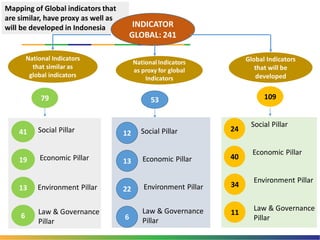
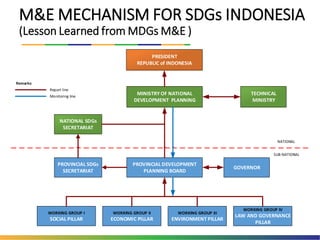
The document outlines Indonesia's approach to integrating the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) into its national development planning and budget processes, highlighting significant progress and challenges since the MDGs. Key milestones include raising awareness, establishing coordination teams, and planning both national and sub-national SDGs action plans. It identifies priorities across social, economic, environmental, and governance pillars, with appropriate targets and indicators to guide implementation from 2016 to 2030.