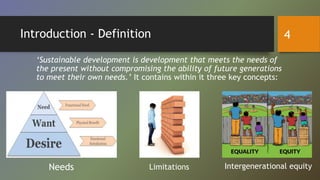
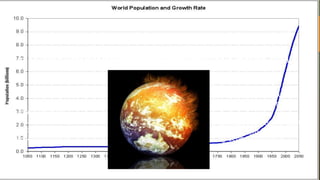
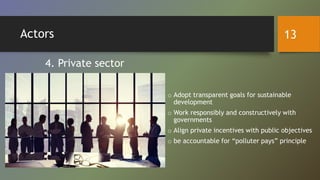
This document discusses sustainable development. It begins with a brief history of sustainable development, noting key publications and agreements from 1987 to the present. It then defines sustainable development as meeting present needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet their own needs. The document outlines the main goals of sustainable development, including economic development, social inclusion, environmental sustainability, and good governance. It also discusses some of the main challenges to sustainable development, such as population growth, resource overuse, and environmental problems, as well as potential pathways and solutions. Finally, it examines the roles of various actors - including governments, private sector, technology, civil society - in working towards sustainable development.