This presentation discusses binomial probability distributions through the following key points:
- It defines basic terminology related to random experiments, events, and variables. The binomial distribution specifically describes discrete data from Bernoulli processes.
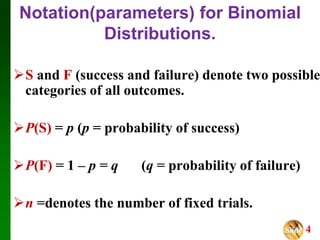
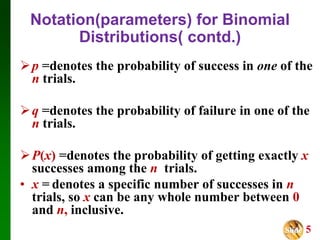
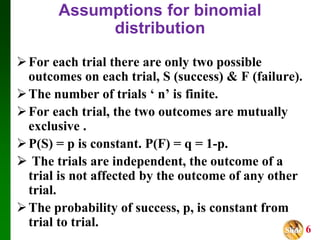
- It outlines the notation and assumptions for binomial distributions, including that there are two possible outcomes for each trial (success/failure), a fixed number of trials, and constant probabilities of success/failure.
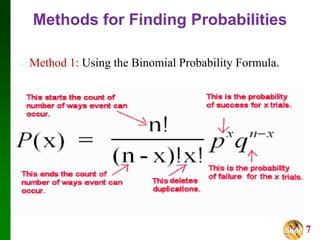
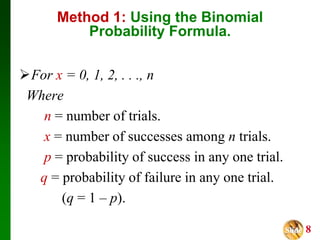
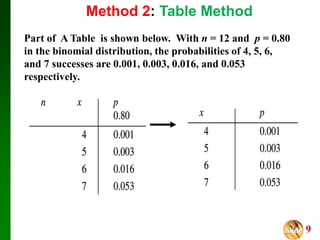
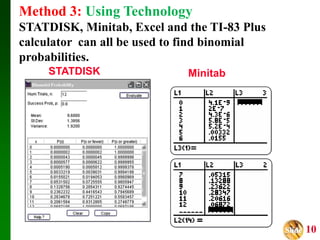
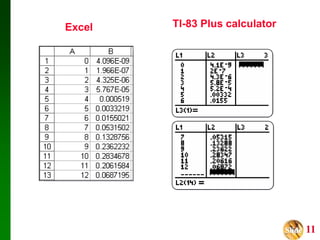
- It presents three methods for calculating binomial probabilities: the binomial probability formula, table method, and using technology like Excel.
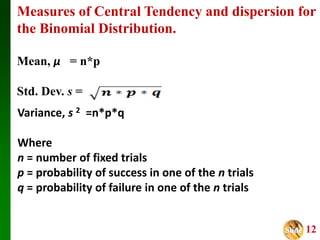
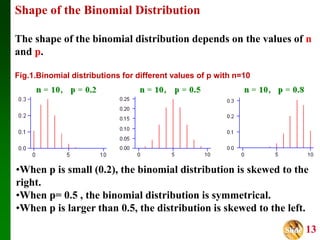
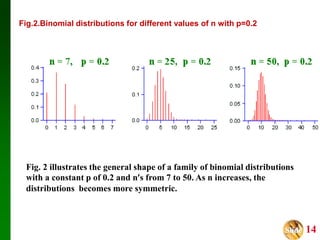
- It discusses measures of central tendency and dispersion for binomial distributions and how the shape of the distribution depends on the number of trials and probability of success.
- Real-world