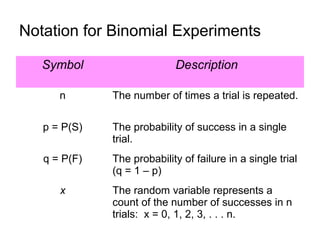
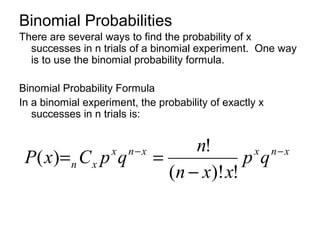
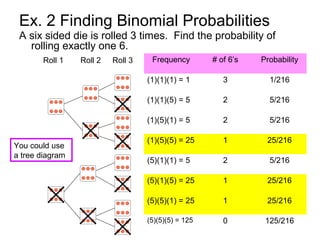
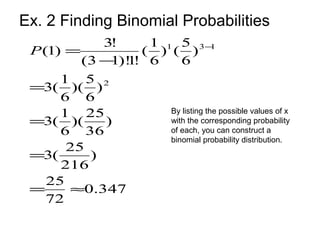
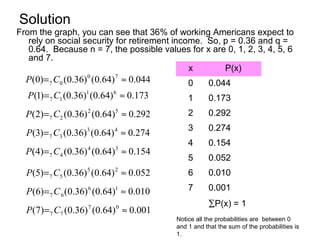
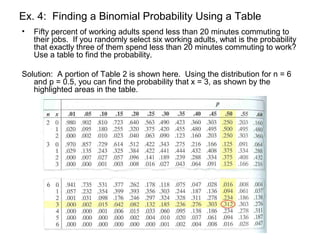
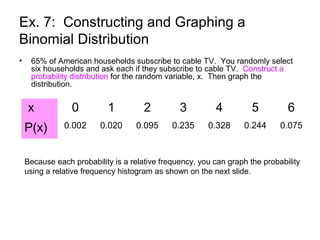
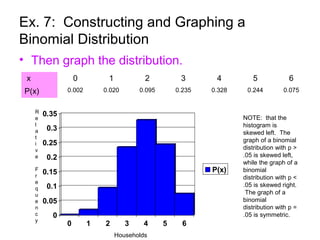
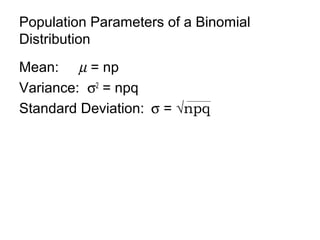
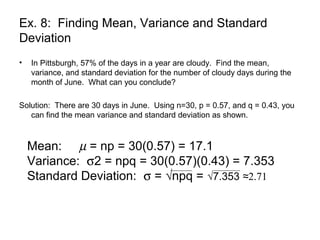
This document discusses binomial distributions and provides examples of determining if experiments are binomial, calculating binomial probabilities, constructing binomial distributions, and graphing binomial distributions. It defines a binomial experiment as having a fixed number of independent trials with two possible outcomes, where the probability of success is the same for each trial. Examples demonstrate how to identify n, p, q, and the possible values of x for binomial experiments. The document also shows how to use the binomial probability formula, tables, and technology to calculate probabilities.