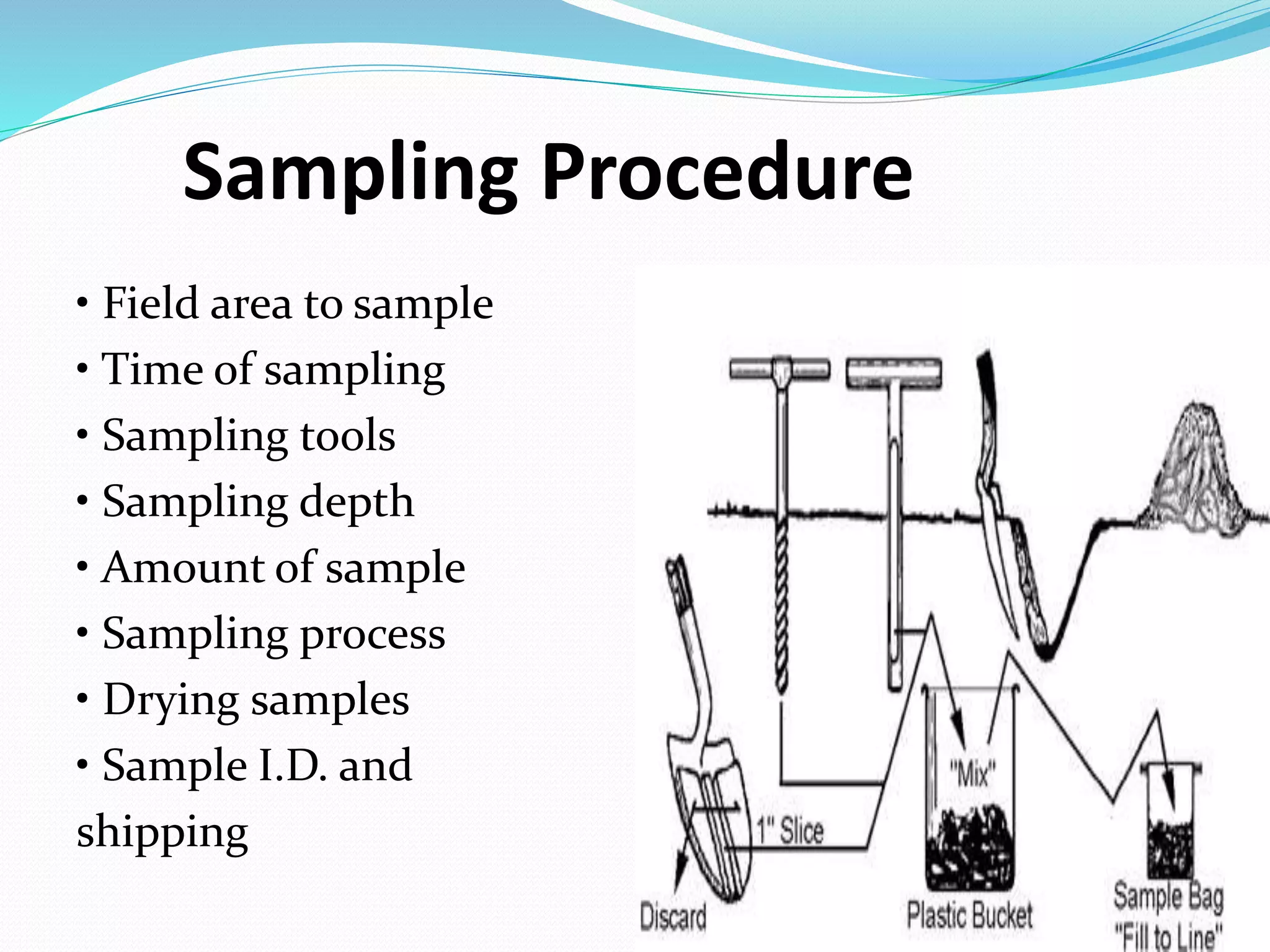
The document discusses soil sampling procedures and methods. It describes different types of soil sampling including disturbed sampling, undisturbed sampling, random sampling, grid sampling, zone sampling, and topographic/geographic unit sampling. It provides details on sampling depths and tools for different field types such as vegetables, field crops, and orchards. Finally, it lists common soil sampling tools including shovels, augers, split-spoon samplers, and shelby tube samplers.