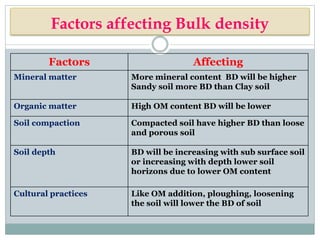
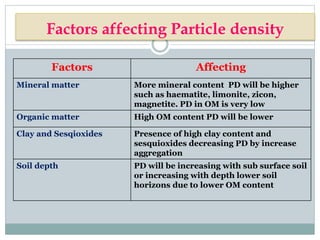
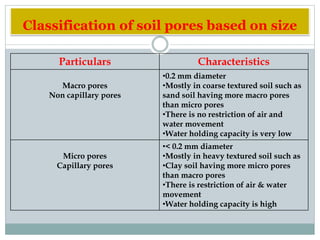
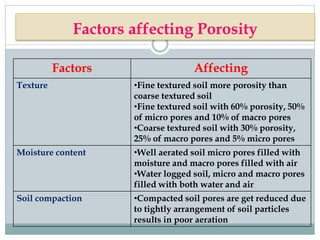
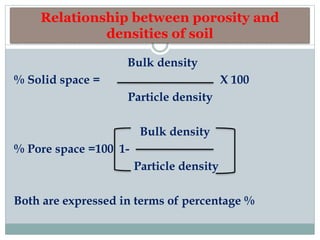
This document discusses soil bulk density, particle density, and porosity and factors that influence them. It defines each term and provides typical values. Bulk density is the weight of soil per unit volume and is affected by mineral content, organic matter, compaction, and depth. Particle density is the weight of soil solids per unit volume and is influenced by mineral and organic matter content. Porosity refers to pore space and is classified by pore size. Factors like texture, moisture, and compaction impact porosity. The relationship between bulk density, particle density, and porosity is expressed through equations calculating percent solid and pore space. An example calculation is provided.