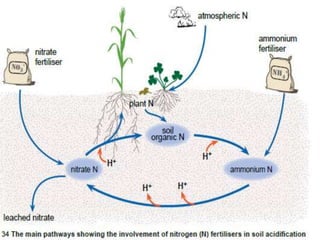
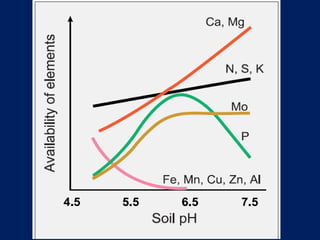
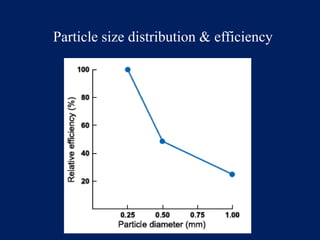
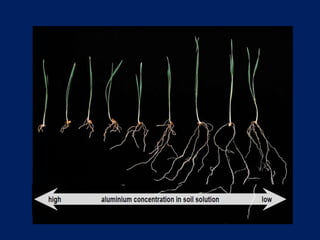
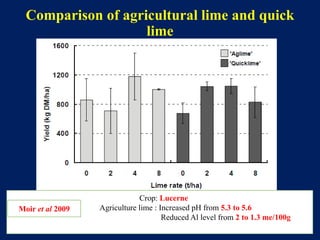
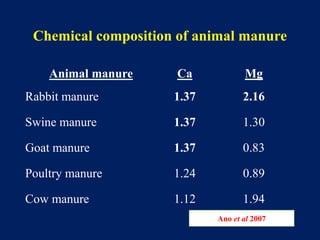
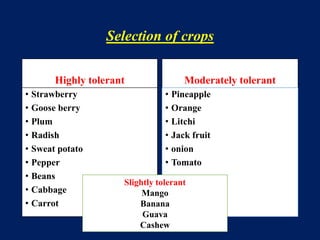
This document discusses acid soils, including their classification, formation processes, characteristics, impacts, and management. It defines acid soils as having a pH below 5.5 and lists various natural and human-induced causes of acidification like rainfall, parent material, and fertilizer use. Characteristics include low nutrient availability, aluminum toxicity, and reduced biological activity. Management involves applying lime to raise pH and supply calcium, with different lime sources and particle sizes impacting effectiveness. Crop residues and manures can also reduce acidity through mineralization reactions.