Embed presentation
Downloaded 44 times


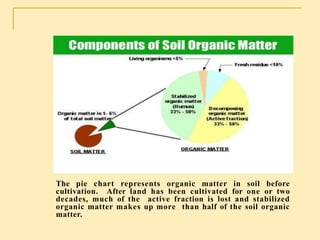
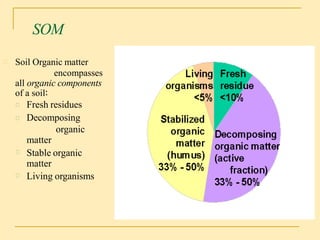





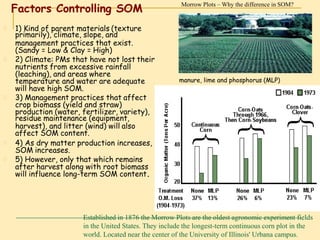

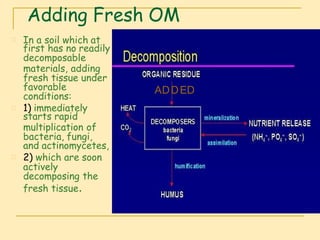
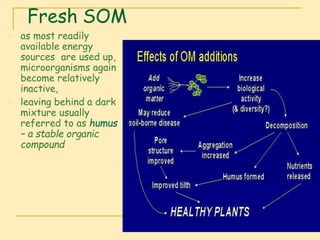
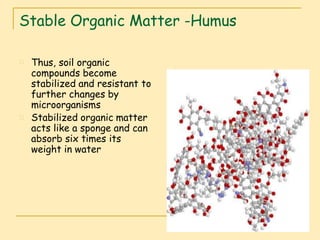




Soil organic matter (SOM) is composed of decomposing plants and animal residues and soil organism cells and tissues. SOM improves soil physical and chemical properties as well as ecosystem services. It is critical for soil function and quality. SOM includes fresh residues, decomposing organic matter, and stable organic matter such as humus. Maintaining adequate SOM levels through practices like fertilization, crop rotation, and returning crop residues is important for soil health.

















