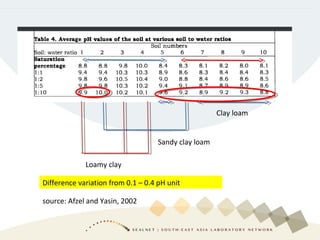
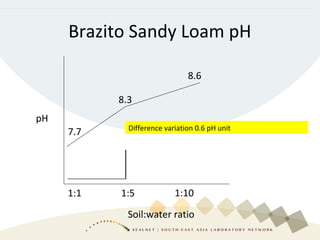
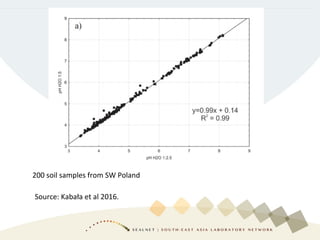
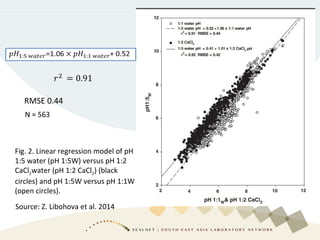
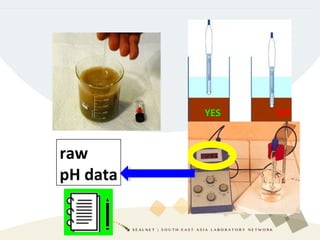
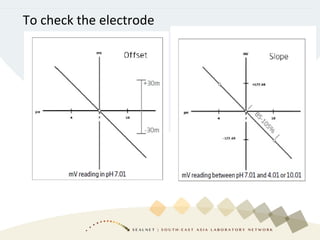
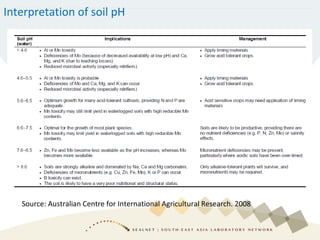
Soil pH is a crucial chemical property that influences plant growth and nutrient availability, being a measure of the soil solution's acidity and alkalinity. Various testing methods exist, such as different soil-to-water ratios and standardized procedures, highlighting the importance of consistency in testing for accurate data. Factors affecting pH readings, including suspension measurement protocols and electrode position, must be standardized to ensure valid comparisons over time.

![Basic theoretical principles
• Soil pH is considered the single most important
chemical property of soil because it affects plant
growth and nutrient availability in many different
and complex ways.
• Soil pH is a measure of the soil solution’s (soil
water) acidity and alkalinity.
• pH is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion
concentration [H+]
pH = -log [H+]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/item13soilphfinalv2-171207164039/85/Soil-pH-2-320.jpg)