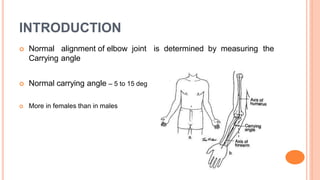
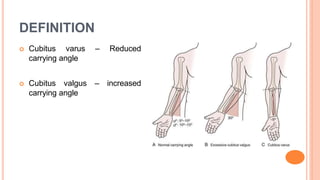
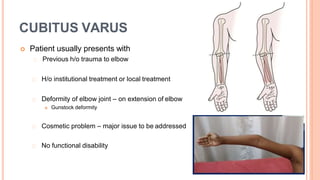
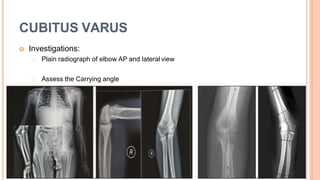
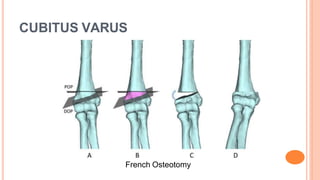
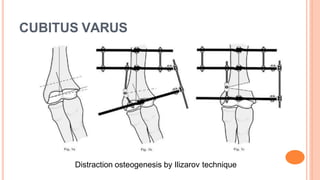
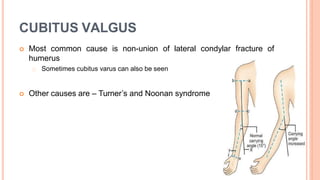
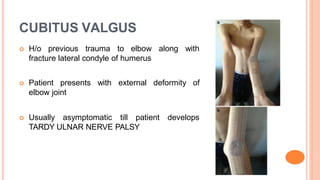
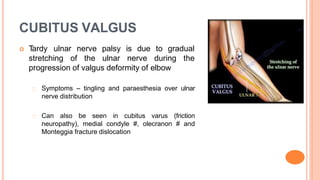
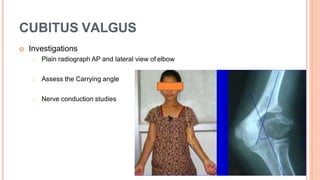
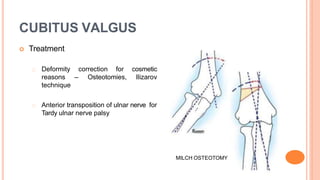
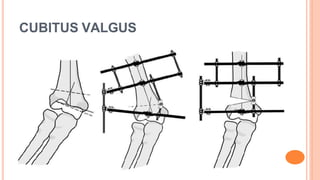
This document discusses cubitus varus and cubitus valgus deformities of the elbow. Cubitus varus is a reduced carrying angle, most commonly caused by malunion of a supracondylar humerus fracture. Cubitus valgus is an increased carrying angle, most often due to non-union of a lateral condylar humerus fracture. Both conditions are typically corrected surgically through osteotomies if causing cosmetic issues, with cubitus valgus at risk of tardy ulnar nerve palsy requiring nerve transposition.