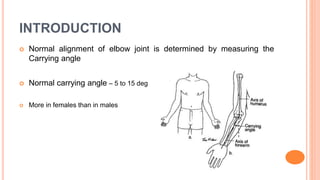
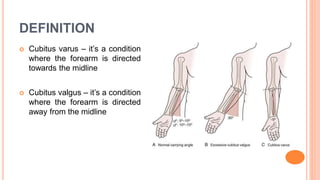
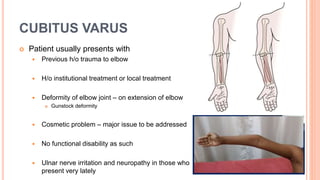
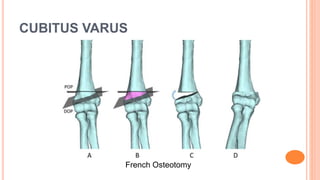
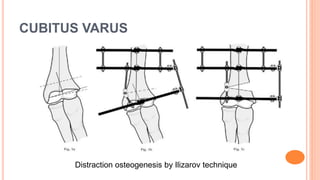
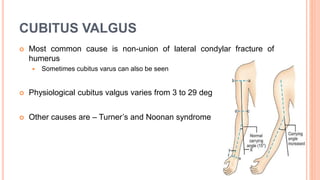
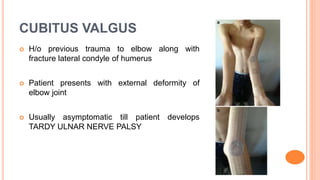
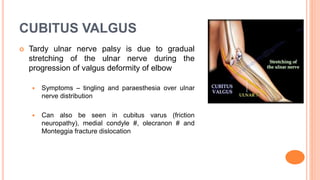
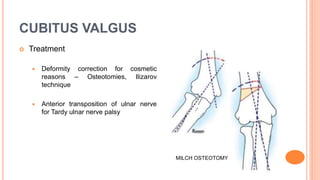
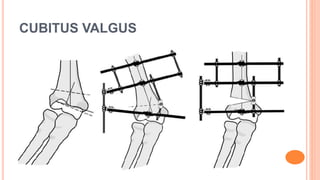
This document discusses cubitus varus and cubitus valgus deformities of the elbow. Cubitus varus is when the forearm is directed towards the midline, while cubitus valgus is when it is directed away from the midline. Cubitus varus is most commonly caused by malunion of a supracondylar fracture of the humerus. Treatment options include corrective osteotomies such as lateral closing wedge or medial open wedge osteotomies. Cubitus valgus is most often due to non-union of a lateral condylar fracture of the humerus and can cause tardy ulnar nerve palsy if not corrected surgically using procedures like osteotom