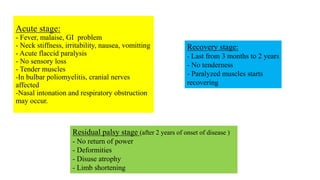
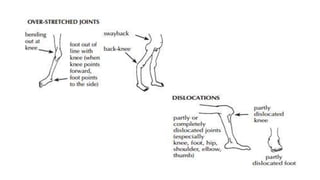
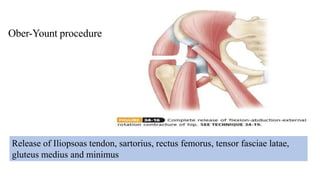
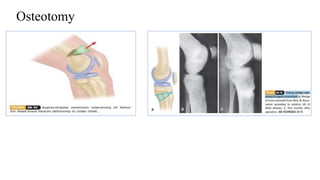
This document summarizes information about post-polio residual palsy. It discusses that polio is caused by enterovirus infection that affects motor neurons in the spinal cord. While most polio infections are asymptomatic, it can cause acute flaccid paralysis. After the initial infection, patients enter the residual palsy stage where muscles remain paralyzed and deformities develop over time due to muscle imbalance, spasm, growth issues, and lack of movement. The management of residual palsy involves physical therapy, orthotics, and sometimes surgery to address deformities and improve function and mobility.